Design a solution for secure access to applications
This unit will focus on the use of Azure Web Application Firewall, which can be deployed on Azure App Gateway and Azure Front Door.
What is Azure Web Application Firewall?
Web Application Firewall (WAF) provides centralized protection of your web applications from common exploits and vulnerabilities. Web applications are increasingly targeted by malicious attacks that exploit commonly known vulnerabilities. SQL injection and cross-site scripting are among the most common attacks.
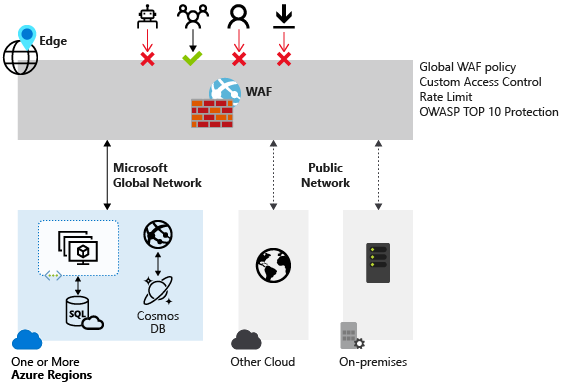
Preventing such attacks in application code is challenging. It can require rigorous maintenance, patching, and monitoring at multiple layers of the application topology. A centralized web application firewall helps make security management much simpler. A WAF also gives application administrators better assurance of protection against threats and intrusions.
A WAF solution can react to a security threat faster by centrally patching a known vulnerability, instead of securing each individual web application.
Supported services
WAF can be deployed with Azure Application Gateway, Azure Front Door, and Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) service from Microsoft. WAF on Azure CDN is currently under public preview. WAF has features that are customized for each specific service. For more information about WAF features for each service, see the overview for each service.
WAF on Azure App Gateway
Azure Web Application Firewall (WAF) on Azure Application Gateway provides centralized protection of your web applications from common exploits and vulnerabilities. Web applications are increasingly targeted by malicious attacks that exploit commonly known vulnerabilities. SQL injection and cross-site scripting are among the most common attacks.
WAF on Application Gateway is based on the Core Rule Set (CRS) from the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP).
All of the WAF features listed below exist inside of a WAF policy. You can create multiple policies, and they can be associated with an Application Gateway, to individual listeners, or to path-based routing rules on an Application Gateway. This way, you can have separate policies for each site behind your Application Gateway if needed. For more information on WAF policies, see Create a WAF Policy.
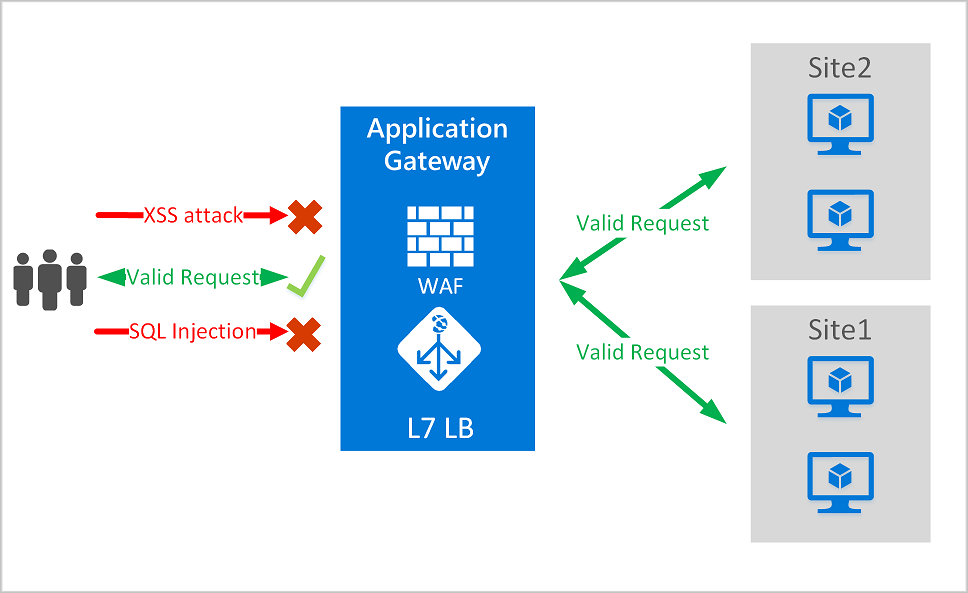
Application Gateway operates as an application delivery controller (ADC). It offers Transport Layer Security (TLS), previously known as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), termination, cookie-based session affinity, round-robin load distribution, content-based routing, ability to host multiple websites, and security enhancements.
Application Gateway security enhancements include TLS policy management and end-to-end TLS support. Application security is strengthened by WAF integration into Application Gateway. The combination protects your web applications against common vulnerabilities. And it provides an easy-to-configure central location to manage.
Benefits
This section describes the core benefits that WAF on Application Gateway provides.
Protection
Protect your web applications from web vulnerabilities and attacks without modification to back-end code.
Protect multiple web applications at the same time. An instance of Application Gateway can host up to 40 websites that are protected by a web application firewall.
Create custom WAF policies for different sites behind the same WAF
Protect your web applications from malicious bots with the IP Reputation ruleset
Monitoring
- Monitor attacks against your web applications by using a real-time WAF log. The log is integrated with Azure Monitor to track WAF alerts and easily monitor trends.
- The Application Gateway WAF is integrated with Microsoft Defender for Cloud. Defender for Cloud provides a central view of the security state of all your Azure, hybrid, and multicloud resources.
Customization
- Customize WAF rules and rule groups to suit your application requirements and eliminate false positives.
- Associate a WAF Policy for each site behind your WAF to allow for site-specific configuration
- Create custom rules to suit the needs of your application
Features
- SQL injection protection.
- Cross-site scripting protection.
- Protection against other common web attacks, such as command injection, HTTP request smuggling, HTTP response splitting, and remote file inclusion.
- Protection against HTTP protocol violations.
- Protection against HTTP protocol anomalies, such as missing host user-agent and accept headers.
- Protection against crawlers and scanners.
- Detection of common application misconfigurations (for example, Apache and IIS).
- Configurable request size limits with lower and upper bounds.
- Exclusion lists let you omit certain request attributes from a WAF evaluation. A common example is Active Directory-inserted tokens that are used for authentication or password fields.
- Create custom rules to suit the specific needs of your applications.
- Geo-filter traffic to allow or block certain countries/regions from gaining access to your applications.
- Protect your applications from bots with the bot mitigation ruleset.
- Inspect JSON and XML in the request body
WAF on Azure Front Door Service
Azure Web Application Firewall (WAF) on Azure Front Door provides centralized protection for your web applications. WAF defends your web services against common exploits and vulnerabilities. It keeps your service highly available for your users and helps you meet compliance requirements.
WAF on Front Door is a global and centralized solution. It's deployed on Azure network edge locations around the globe. WAF enabled web applications inspect every incoming request delivered by Front Door at the network edge.
WAF prevents malicious attacks close to the attack sources, before they enter your virtual network. You get global protection at scale without sacrificing performance. A WAF policy easily links to any Front Door profile in your subscription. New rules can be deployed within minutes, so you can respond quickly to changing threat patterns.

Azure Front Door has two tiers: Front Door Standard and Front Door Premium. WAF is natively integrated with Front Door Premium with full capabilities. For Front Door Standard, only custom rules are supported.
WAF policy and rules
You can configure a WAF policy and associate that policy to one or more Front Door front-ends for protection. A WAF policy consists of two types of security rules:
- Custom rules that are authored by the customer.
- Managed rule sets that are a collection of Azure-managed pre-configured set of rules.
When both are present, custom rules are processed before processing the rules in a managed rule set. A rule is made of a match condition, a priority, and an action. Action types supported are: ALLOW, BLOCK, LOG, and REDIRECT. You can create a fully customized policy that meets your specific application protection requirements by combining managed and custom rules.
Rules within a policy are processed in a priority order. Priority is a unique integer that defines the order of rules to process. Smaller integer value denotes a higher priority and those rules are evaluated before rules with a higher integer value. Once a rule is matched, the corresponding action that was defined in the rule is applied to the request. Once such a match is processed, rules with lower priorities aren't processed further.
A web application delivered by Front Door can have only one WAF policy associated with it at a time. However, you can have a Front Door configuration without any WAF policies associated with it. If a WAF policy is present, it's replicated to all of our edge locations to ensure consistent security policies across the world.
WAF modes
WAF policy can be configured to run in the following two modes:
Detection mode: When run in detection mode, WAF doesn't take any other actions other than monitors and logs the request and its matched WAF rule to WAF logs. You can turn on logging diagnostics for Front Door. When you use the portal, go to the Diagnostics section.
Prevention mode: In prevention mode, WAF takes the specified action if a request matches a rule. If a match is found, no further rules with lower priority are evaluated. Any matched requests are also logged in the WAF logs.
WAF actions
WAF customers can choose to run from one of the actions when a request matches a rule’s conditions:
- Allow: Request passes through the WAF and is forwarded to back-end. No further lower priority rules can block this request.
- Block: The request is blocked and WAF sends a response to the client without forwarding the request to the back-end.
- Log: Request is logged in the WAF logs and WAF continues evaluating lower priority rules.
- Redirect: WAF redirects the request to the specified URI. The URI specified is a policy level setting. Once configured, all requests that match the Redirect action will be sent to that URI.
- Anomaly score: This is the default action for Default Rule Set (DRS) 2.0 or later and is not applicable for the Bot Manager ruleset. The total anomaly score is increased incrementally when a rule with this action is matched.
Azure-managed rule sets
Azure-managed rule sets provide an easy way to deploy protection against a common set of security threats. Since such rulesets are managed by Azure, the rules are updated as needed to protect against new attack signatures. The Azure-managed Default Rule Set includes rules against the following threat categories:
- Cross-site scripting
- Java attacks
- Local file inclusion
- PHP injection attacks
- Remote command execution
- Remote file inclusion
- Session fixation
- SQL injection protection
- Protocol attackers
Custom rules are always applied before rules in the Default Rule Set are evaluated. If a request matches a custom rule, the corresponding rule action is applied. The request is either blocked or passed through to the back-end. No other custom rules or the rules in the Default Rule Set are processed. You can also remove the Default Rule Set from your WAF policies.