Learners as users of AI
AI is defined as “a computer system designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.” (American Heritage Dictionary: artificial intelligence (ahdictionary.com)) This intelligence has been living in the background of everyday lives for years and works by analyzing data or following a simple rule-based algorithm. The youngest consumers of technology have already engaged with the many benefits of AI like:
- Facial recognition on smartphones
- Suggestions on streaming services
- Recommendations in online shopping
- GPS navigation
- Grammar and spell check
- Accessibility tools like dictation
- Predictive text on mobile phones and emails
Generative AI is a special type of AI that can generate new content like images, words, music, or videos by learning from multiple examples. Generative AI can use the patterns it finds in the data to create something new. This is different from other kinds of AI that we use every day, like search engines, voice assistance, or facial recognition.
Learner use of AI
Modeling the use of generative AI tools in a class setting can be a powerful skill that supports all learners. Businesses are considering the value of generative AI in helping employees become more efficient and productive. Jobs in prompt engineering with competitive salaries are increasing in number. Preparing learners to use a large language model (LLM) generative AI tool can empower them in their future careers. (Work Trends Index: Will AI Fix Work?)
Copilot in Edge is a generative AI tool that uses an LLM. Type in any prompt and the AI responds to the given prompt using natural language.
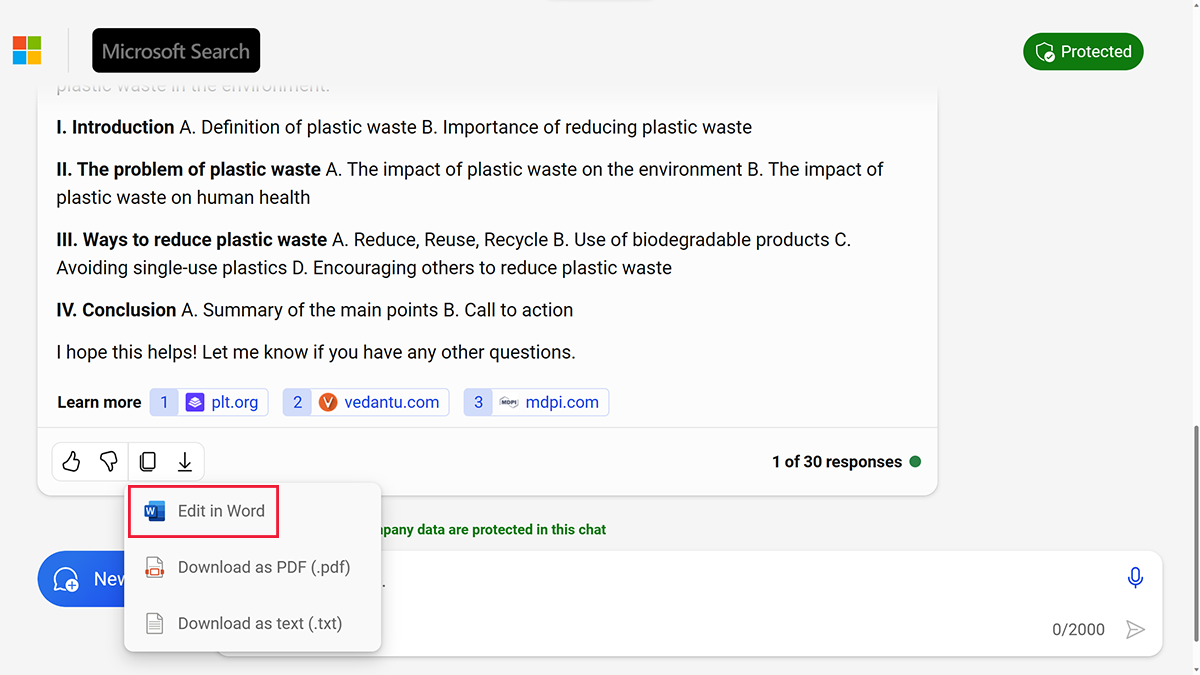
A learner in a secondary class has a project with a spoken presentation about reducing plastic waste in the environment. The educator allows limited AI use to generate an outline but not to write the script. The educator gives a quick lesson on how to effectively create a prompt in Microsoft Copilot. Then, the educator models how to quickly export the results into a Word document where learners can edit and add content to the outline.
The learner launches Copilot and begins to type in their prompt, asking it to create an outline. Copilot quickly gets to work and provides an outline for the learner to edit and make it more relevant to the research they've already completed. By learning generative AI and working with LLMs, learners can develop their creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills as well as explore the ethical and social implications of using AI to create new content. These skills will prepare them for their future in life and work.
Prompt engineering
Using a generative AI tool like Copilot can be enhanced with a skill called “prompt engineering.” Prompt engineering is the process of finding the best way to ask an AI model to do something. Include the following elements to produce the intended outcome:
- Persona
- Objective
- Audience
- Boundary
Generative AI with guardrails
Not all use cases of generative AI involve learners and educators providing open-ended prompts. For example, Reading Progress will soon allow educators to create personalized reading passages for learners based on words they mispronounced in previous practice assignments. Reading Coach will soon allow learners to create their own stories by choosing the protagonist, setting, and plot from a curated set of options. Microsoft has performed extensive reviews of both apps to ensure they only generate age-appropriate reading passages and keep learner data private and secure.