Explore data governance and compliance in Microsoft Purview
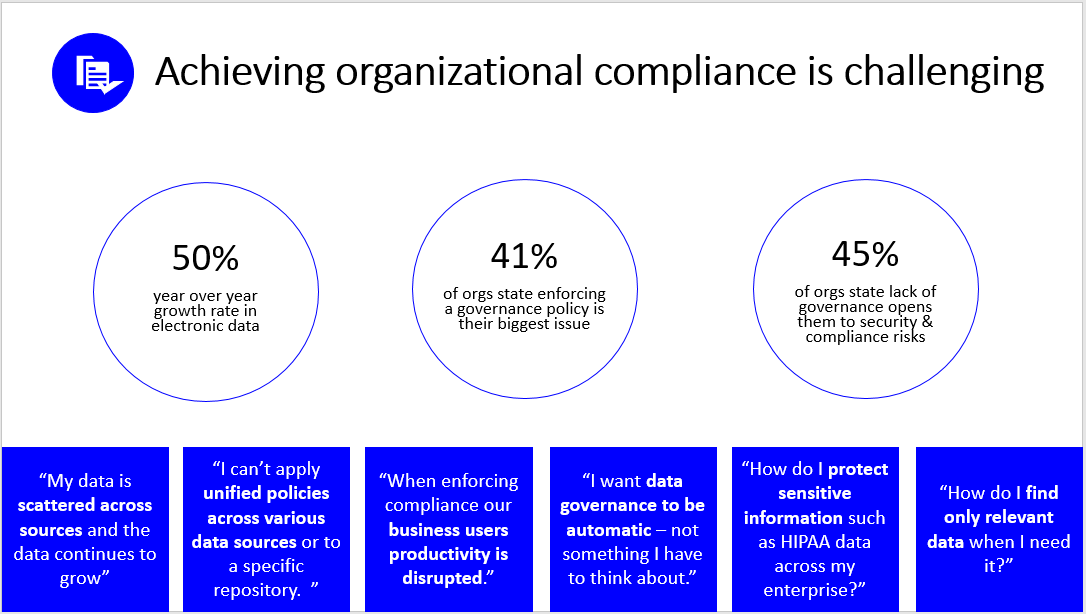
The amount of data that organizations around the world must manage and care for is staggering. On average, companies are experiencing a 50% year-over-year growth of electronic data. When you factor in the entire body of information they're already expanding upon, the total amount of information they're managing doubles every 18 months.
Managing such a large volume of data can be challenging, especially in today’s information age when the data isn't just email; it's documents, video files, instant messaging, and so on. It's no surprise that companies struggle to manage the liability and risk associated with data governance and compliance. The fact that many companies don't even know what data they have, the location of their data, or what their data is doing just compounds the problem.
Common questions asked by organizations when faced with challenges of data governance and compliance include:
- How should we manage all the data scattered across the enterprise or organization? And how do we manage it while it continues to exponentially grow?
- How can we apply business policies universally across the organization and across multiple business solutions?
- Is there a way of implementing business policies so that we don't interrupt user productivity?
- Can we make data governance something that’s automatic so that we don’t have to dedicate someone to manage it each day?
- How do we protect sensitive information, such as health care records and financial information?
- How do we find relevant data when we really need it?
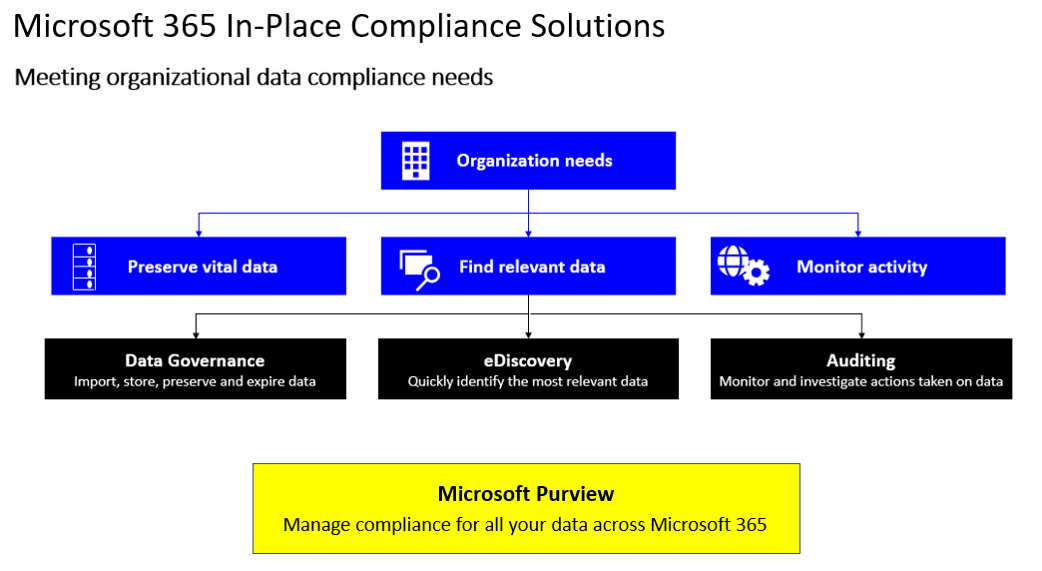
To address these concerns, Microsoft 365 provides a state-of-the-art compliance solution - Microsoft Purview. It targets the three core aspects that every organization generally requires:
- Preserving vital data.
- Finding the data that you preserved and understanding what's there.
- Auditing, reporting, and monitoring business activity to ensure that users are abiding by business policy rules, business processes, and industry regulations.
Microsoft Purview core features
Microsoft Purview is a unified data governance service that helps organizations manage and govern its on-premises, multicloud, and software-as-a-service (SaaS) data. Its foundation includes three core pillars:
- Data governance. Making sure that users have the tools available to import, store, preserve, retire, and expire data as it leaves an organization’s data retention windows.
- eDiscovery. Finding information quickly and ensuring that it's relevant to the user's request.
- Auditing. Enabling organizations to monitor and investigate all the actions taken within the compliance solution and on their data. Doing so ensures that nothing outside the norm is happening.
Microsoft Purview allows an organization to:
- Create a holistic, up-to-date map of its data landscape with:
- Automated data discovery
- Sensitive data classification
- End-to-end data lineage
- Enable data curators to manage and secure its data estate.
- Empower data consumers to find valuable, trustworthy data.
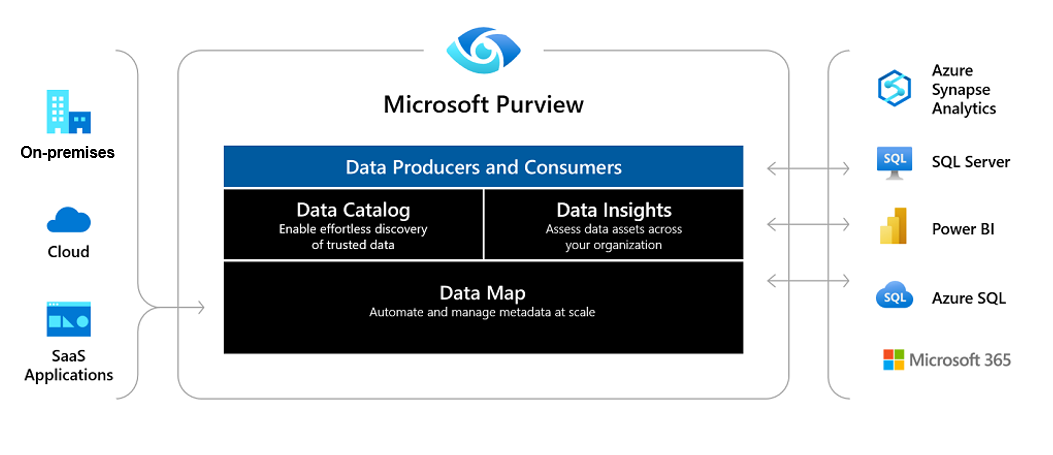
Microsoft Purview automates data discovery. It does so by providing data scanning and classification as a service for assets across an organization's data estate. It integrates metadata and the descriptions of discovered data assets into a holistic map of the data estate. Atop this map, there are purpose-built apps that create environments for data discovery, access management, and insights about your data landscape.
Data Map
Microsoft Purview Data Map provides the foundation for data discovery and effective data governance. Microsoft Purview Data Map is a cloud native PaaS service that captures metadata about enterprise data present in analytics and operation systems on-premises and cloud. A built-in automated scanning and classification system automatically keeps the Microsoft Purview Data Map up to date.
- Business users can configure and use the Microsoft Purview Data Map through an intuitive UI.
- Developers can programmatically interact with the Data Map using open-source Apache Atlas 2.2 APIs.
Microsoft Purview Data Map powers the Microsoft Purview Data Catalog and Microsoft Purview Data Estate Insights as unified experiences within the Microsoft Purview governance portal.
Additional reading. For more information, see Introduction to Data Map.
Data Catalog
With the Microsoft Purview Data Catalog, business and technical users can quickly and easily find relevant data using a search experience with filters based on lenses such as glossary terms, classifications, sensitivity labels and more. For subject matter experts, data managers, and officers, the Microsoft Purview Data Catalog provides various data curation features. For example, business glossary management, and the ability to automate tagging of data assets with glossary terms. Data consumers and producers can also visually trace the lineage of data assets. For example:
- Starting from on-premises operational systems.
- Through movement, transformation, and enrichment with various data storage and processing systems in the cloud.
- To consumption in an analytics system like Power BI.
Additional reading. For more information, see Introduction to search using Data Catalog.
Data Estate Insights
Microsoft Purview Data Estate Insights is a cloud-based data management solution. It provides a unified and automated way to discover, understand, and manage data across an organization's hybrid data landscape.
Purview Data Estate Insights helps organizations to gain visibility into their data. It provides a comprehensive inventory of all data assets across different sources such as databases, files, and APIs. It uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to automatically discover and classify sensitive or regulated data, including both personal and financial information. Purview Data Estate Insights allows organizations to manage data assets more effectively and ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
Purview Data Estate Insights also provides advanced data governance capabilities, such as:
- Data lineage
- Data classification
- Data cataloging
These features help organizations understand how data flows through their systems, ensure data quality, and improve collaboration across teams.
With the Microsoft Purview Data Estate Insights service, data officers and security officers can get a quick, high-level view of:
- The data that Data Estate Insights actively scanned.
- The location of sensitive data.
- How data moves.
Additional reading. For more information, see Introduction to Data Estate Insights.
Microsoft Purview - solving data discovery challenges
Microsoft Purview addresses the issues mentioned in the following sections. It also helps enterprises get the most value from their existing information assets. The catalog makes data sources easily discoverable and understandable by the users who manage the data.
Discovery challenges for data consumers
Traditionally, discovering enterprise data sources is an organic process based on communal knowledge. For companies that want the most value from their information assets, this approach presents many challenges:
- Because there's no central location to register data sources, users may be unaware of a data source unless they come into contact with it as part of another process.
- Unless users know the location of a data source, they can't use a client application to connect to the data. Data-consumption experiences require users to know the connection string or path.
- They hide the intended use of the data from users, unless they know the location of a data source's documentation. Data sources and documentation may live in several places. Users may consume it through different kinds of experiences.
- If users have questions about an information asset, they must locate the expert or team responsible for that data and engage them offline. There's no explicit connection between the data and the experts that understand the data's context.
- Unless users understand the process for requesting access to the data source, discovering the data source and its documentation doesn't help them access the data.
Discovery challenges for data producers
Although data consumers face the previously mentioned challenges, users who are responsible for producing and maintaining information assets face challenges of their own:
- Annotating data sources with descriptive metadata is often a lost effort. The data source typically stores descriptions that client applications ignore.
- Creating documentation for data sources can be difficult and it's an ongoing responsibility to keep documentation in sync with data sources. Users may not trust documentation they perceive as outdated.
- Creating and maintaining documentation for data sources is complex and time-consuming. Making that documentation readily available to everyone who uses the data source can be even more so.
- Restricting access to data sources and ensuring that data consumers know how to request access is an ongoing challenge.
When you combine these challenges, they present a significant barrier for companies that want to encourage and promote the use and understanding of enterprise data.
Discovery challenges for security administrators
Users who are responsible for ensuring the security of their organization's data may have many of the same challenges as data consumers and producers. They may also experience the following extra challenges:
- An organization's data is constantly growing. Organizations also store and share their data new directions. The task of discovering, protecting, and governing sensitive data is one that never ends. An organization must ensure that it shares its content with the correct people and applications, and with the correct permissions.
- An organization must understand the risk levels in its data. To do so requires that an organization dive deep into its content, looking for keywords, RegEx patterns, and sensitive data types. For example, sensitive data types may include Credit Card numbers, Social Security numbers, or Bank Account numbers. An organization must constantly monitor all data sources for sensitive content, as even the smallest amount of data loss can be critical.
- An organization must ensure that it continues to comply with corporate security policies. This task can be challenging, especially as an organization's content grows and changes, and as changing digital realities update those requirements and policies. Security administrators must ensure data security in the quickest time possible.
Microsoft Purview advantages
Microsoft Purview provides a cloud-based service into which organizations can register data sources. During registration:
- The data remains in its existing location.
- Authorized personnel within the organization add a copy of its metadata and a reference to the data source location to Microsoft Purview.
- Microsoft Purview indexes the metadata to make each data source easily discoverable through search and understandable to the users who discover it.
After you register a data source, you can then enrich its metadata. Either the user who registered the data source or another user in the enterprise can add other metadata. Any user can annotate a data source by providing descriptions, tags, or other metadata for requesting data source access. This descriptive metadata supplements the structural metadata. For example, column names and data types that you register from the data source.
Discovering and understanding data sources and their use is the primary purpose of registering the sources. Enterprise users may need data for business intelligence, application development, data science, or any other task that requires correct data. They can use the data catalog discovery experience to:
- Quickly find data that matches their needs.
- Understand the data to evaluate its fitness for purpose.
- Consume the data by opening the data source in their tool of choice.
At the same time, users can contribute to the catalog by tagging, documenting, and annotating registered data sources. They can also register new data sources, which the community of catalog users can then discover, understand, and consume.
Knowledge check
Choose the best response for the following question. Then select “Check your answers.”