Explore Endpoint data loss prevention
Organizations can use Microsoft Purview Data Loss Prevention (DLP) to monitor the actions that are being taken on items they've determined to be sensitive. DLP can also be used to prevent the unintentional sharing of those items.
Endpoint data loss prevention (Endpoint DLP) extends the activity monitoring and protection capabilities of DLP to sensitive items that are physically stored on Windows 10, Windows 11, and macOS (Catalina 10.15 and higher) devices. Once devices are onboarded into the Microsoft Purview solutions, the information about what users are doing with sensitive items is made visible in Activity Explorer. Organizations can then enforce protective actions on those items through DLP policies.
Tip
If you're looking for device control for removable storage, see Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Device Control Removable Storage Access Control.
In Microsoft Purview, DLP policy evaluation of sensitive items occurs centrally. As such, there's no time lag for policies and policy updates to be distributed to individual devices. When a policy is updated in the Microsoft Purview compliance portal, it generally takes about an hour for those updates to be synchronized across the service. Once policy updates are synchronized, items on targeted devices are automatically reevaluated the next time they're accessed or modified.
Endpoint activities you can monitor and take action on
Endpoint DLP enables organizations to audit and manage the following types of activities users take on sensitive items that are physically stored Windows 10, Windows 11, or macOS devices.
| Activity | Description | Windows 10 1809 and later/ Windows 11 | macOS Catalina 10.15 | Auditable/restrictable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upload to cloud service, or access by unallowed browsers. | Detects when a user attempts to upload an item to a restricted service domain or access an item through a browser. If they're using a browser that'is listed in Microsoft Purview DLP as an unallowed browser, the upload activity will be blocked and the user's redirected to use Microsoft Edge. Microsoft Edge will then either allow or block the upload or access based on the DLP policy configuration. | Supported | Supported | Auditable and restrictable |
| Copy to another app, process, or item. | Detects when a user attempts to copy information from a protected item and then paste it into another app, process, or item. This activity doesn't detect copying and pasting of information within the same app, process, or item. | Supported | Supported | Auditable and restrictable |
| Copy to USB removable media. | Detects when a user attempts to copy an item or information to removable media or USB device. | Supported | Supported | Auditable and restrictable |
| Copy to a network share. | Detects when a user attempts to copy an item to a network share or mapped network drive. | Supported | Supported | Auditable and restrictable |
| Print a document. | Detects when a user attempts to print a protected item to a local or network printer. | Supported | Supported | Auditable and restrictable |
| Copy to a remote session. | Detects when a user attempts to copy an item to a remote desktop session. | Supported | Not supported | Auditable and restrictable |
| Copy to a Bluetooth device. | Detects when a user attempts to copy an item to an unallowed Bluetooth app (as defined in the list of unallowed Bluetooth apps in the Endpoint DLP settings). | Supported | Not supported | Auditable and restrictable |
| Create an item. | Detects when a user creates an item. | Supported | Auditable | |
| Rename an item. | Detects when a user renames an item. | Supported | Auditable |
Best practice for endpoint DLP policies
Consider the scenario in which an organization wants to block all items that contain credit card numbers from leaving the endpoints of Finance department users. In this example, it's recommended the organization:
- Create a policy and scope it to endpoints and to that group of users.
- Create a rule in the policy that detects the type of information that it wants to protect. In this case, the content contains field is set to Sensitive information type, and Credit Card is selected as the type of sensitive information.
- Set the actions for each activity to Block.
Additional reading. For more information on designing your DLP policies, see Design a data loss prevention policy.
Monitored files
Endpoint DLP supports monitoring of the following file types. Microsoft Purview DLP audits the activities for these file types, even if there isn't a policy match.
- Word files
- PowerPoint files
- Excel files
- PDF files
- .csv files
- .tsv files
- .txt files
- .rtf files
- .c files
- .class files
- .cpp files
- .cs files
- .h files
- .java files
If an organization only wants monitoring data from policy matches, it can turn off the Always audit file activity for devices option in the endpoint DLP global settings.
Note
If the Always audit file activity for devices setting is on, activities on every Word, PowerPoint, Excel, PDF, and .csv file are always audited, even if the device isn't targeted by any policy.
Tip
To ensure activities are audited for all supported file types, create a custom DLP policy.
File types and file extensions
File Types are a grouping of file formats. Each file type is utilized to protect specific workflows or areas of business. Organizations can use one or more File types as conditions in their DLP policies.
| File type | App | Monitored file extensions |
|---|---|---|
| word processing | Word, PDF | .doc, .docx, .docm, .dot, .dotx, .dotm, .docb, .pdf |
| spreadsheet | Excel, CSV, TSV | .xls, .xlsx, .xlt, .xlm, .xlsm, .xltx, .xltm, .xlsb, .xlw, .csv, .tsv |
| presentation | PowerPoint | .ppt, .pptx, .pos, .pps, .pptm, .potx, .potm, .ppam, .ppsx |
| archive | file archive and compression tools | .zip, .zipx, .rar, .7z, .tar, .gz |
| Outlook | .pst, .ost, .msg |
If the File types don't cover the file extensions an organization needs to list as a condition in a policy, it can use file extensions separated by commas instead.
Important
The file extensions and file types options can't be used as conditions in the same rule. If you want to use them as conditions in the same policy, they must be in separate rules.
The following Windows versions support File types and File extension features:
- Windows 10 versions 20H1/20H2/21H1 (KB 5006738)
- Windows 10 versions 19H1/19H2 (KB 5007189)
- Windows 10 RS5 (KB 5006744)
Enabling Device management
Device management is the functionality that enables the collection of customer content from devices. It then brings it into Microsoft Purview solutions like Endpoint DLP and insider risk management. As such, organizations must onboard all devices they want to use as locations in DLP policies.
Onboarding and offboarding are handled through scripts that can be downloaded from the Device Management center. The center has custom scripts for each of the following deployment methods:
- local script (up to 10 machines)
- Group policy
- System Center Configuration Manager (version 1610 or later)
- Mobile Device Management/Microsoft Intune
- VDI onboarding scripts for non-persistent machines
Use the procedures in Getting started with Microsoft 365 Endpoint DLP to onboard devices.
If you have onboarded devices through Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, those devices will automatically show up in the list of devices. You can then turn on device monitoring to use Endpoint DLP.
Viewing Endpoint DLP data
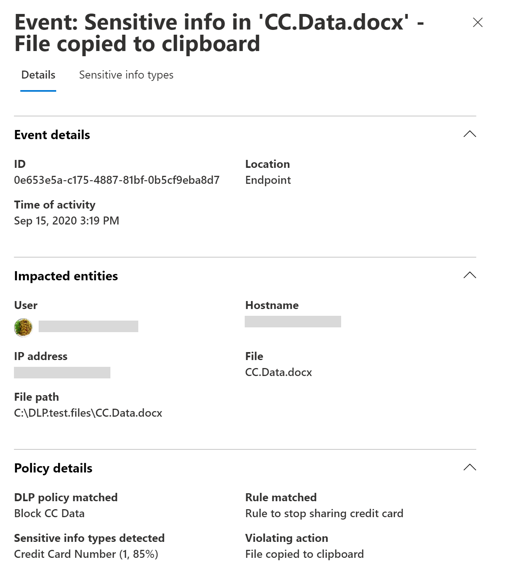
Organizations can view alerts related to DLP policies enforced on endpoint devices by going to the DLP Alerts Management Dashboard. You can also view details of the associated event with rich metadata in the same dashboard.
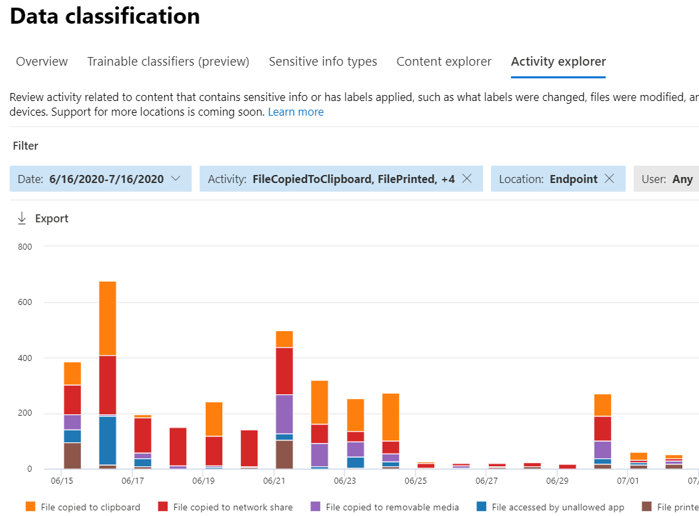
Once a device is onboarded, information about audited activities flows into Activity Explorer. This information is audited even before an organization configures and deploys any DLP policies that have devices as a location.
Endpoint DLP collects extensive information on audited activity. For example, if a file is copied to removable USB media, the following attributes would be displayed in the activity details:
- activity type
- client IP
- target file path
- happened timestamp
- file name
- user
- file extension
- file size
- sensitive information type (if applicable)
- sha1 value
- sha256 value
- previous file name
- location
- parent
- filepath
- source location type
- platform
- device name
- destination location type
- application that performed the copy
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint device ID (if applicable)
- removable media device manufacturer
- removable media device model
- removable media device serial number