Explore auto-failover groups for Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance
An auto-failover group is an availability feature that can be used with both Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance. Autofailover groups let you manage how databases on an Azure SQL Database server or databases in SQL Managed Instance are replicated to another region, and let you manage how failover could happen. The name assigned to the autofailover group must be unique within the *.database.windows.net domain. SQL Managed Instance only supports one autofailover group.
Auto-failover groups provide AG-like functionality called a listener, which allows both read-write and read-only activity. This functionality can be seen in the image below which is slightly different than the one for active geo-replication. There are two different kinds of listeners: one for read-write and one for read-only traffic. Behind the scenes in a failover, DNS is updated so clients will be able to point to the abstracted listener name and not need to know anything else. The database server containing the read-write copies is the primary, and the server that is receiving the transactions from the primary is a secondary.
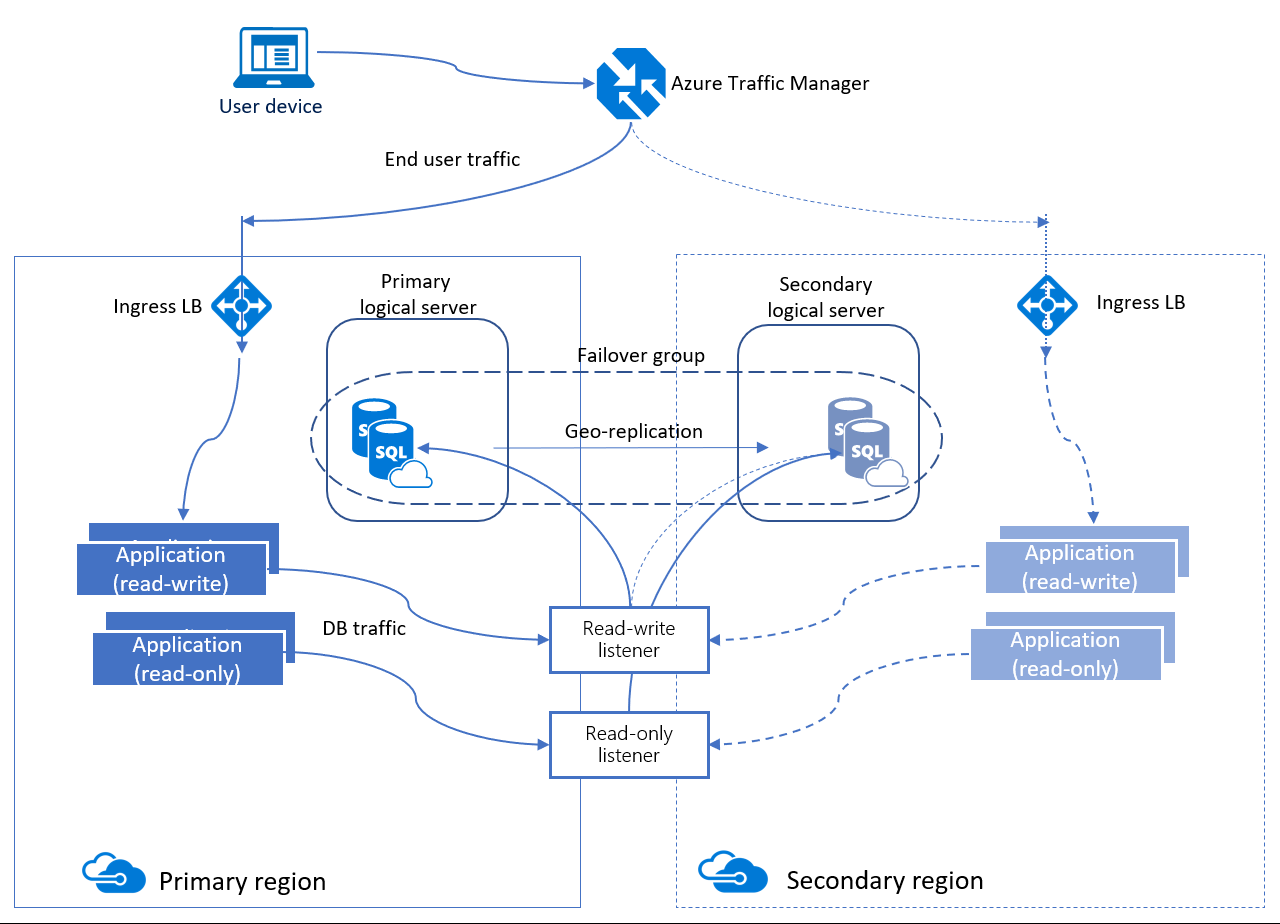
Auto-failover groups have two different policies that can be configured.
- Automatic – By default, when a failure occurs and it's determined that a failover must happen, the auto-failover group will switch regions. The ability to fail over automatically can be disabled.
- Read-Only – By default, if a failover occurs, the read-only listener is disabled to ensure performance of the new primary when the secondary is down. This behavior can be changed so that both types of traffic are enabled after a failover.
Failover can be performed manually even if automatic failover is allowed. Depending on the type of failover, there could be data loss. Unplanned failover could result in data loss if forced and the secondary isn't fully synchronized with the primary. Configuring GracePeriodWithDataLossHours controls how long Azure waits before failing over. The default is one hour. If you have a tight RPO and can't afford much data loss, set the value higher. Although Azure will wait longer before failing over, this approach may result in less data loss as the secondary has more time to fully synchronize with the primary.
One auto-failover group can contain one or more databases. The database size and edition will be the same on both the primary and secondary. The database is created automatically on the secondary through a process called seeding. Depending on the size of the database, this may take some time. Ensure that you plan accordingly and that you take into account things like the speed of the network.