Describe how to create personalized customer experiences by using clienteling
In modern business, retail associates need to establish long-term relationships with customers and understand their preferences, behaviors, and purchases. Clienteling is a technique that guides the associates on providing more personal and informed customer service that helps to influence the customer behavior related to shopping.
Clienteling
Clienteling empowers sales associates to become trusted advisors and establish long-term relationships with their customers by taking advantage of known data about the customer's preferences, behaviors, and purchases. In Commerce, the clienteling capabilities offered allow businesses to:
Keep track of and reference a customer's purchase history across multiple selling channels.
Identify the most loyal customers and their shopping preferences.
Provide a personalized customer experience with targeted product recommendations based on machine learning and artificial intelligence capabilities.
Personalized in-store customer experiences
Many retailers, especially high-end specialty retailers, want their sales associates to form long-term relationships with their key customers. The associates are expected to know about these customers' likes and dislikes, purchase history, product preferences, and important dates, such as anniversaries and birthdays. Associates need a place where they can capture this information and easily find it when it's required. If this information is available in a single view, the associates can easily target customers who meet specific criteria. For example, they can find all customers who prefer to shop for handbags, or customers who have an important event approaching, such as a birthday or anniversary.
Client book
In Commerce, retailers can use the client book functionality and the Store Commerce application to help store associates form long-term relationships with key customers.
The client book includes customer cards that display contact information for each customer, together with three more properties defined by the retailer and configured in Headquarters. Retailers can decide the three most important things that sales associates should know about customers. For example, a jewelry retailer might want to include important dates such as anniversaries or birthdays. These dates are occasions when people might buy more jewelry. Similarly, a fashion retailer might want to include the customer's preferred shopping interests and brands.
The client book also lets sale associates filter the list so that it displays only customers who meet specific criteria. For example, a new collection of shoes has arrived in the store, and an associate wants to inform customers who like to buy shoes. In this case, the associate can filter the client book to find the relevant customers and then take further action.
If any customers are no longer considered key customers for some reason, and therefore shouldn't be closely managed, sales associates can remove them from their client book.
Some retailers don't want to manage customers at the sales associate level. Instead, they want to manage a list of key customers at the store level. These retailers can view customers from store client books. By using this option, retailers can view the customers from the client books of all the sales associates whose address book matches the address book of the current store. In this way, if an associate works in multiple stores of the legal entity, the client book displays the customers from all those stores. This functionality supports more capabilities. For example, customers can be reassigned from one associate to another associate. This capability is useful when associates are transferred or leave the company.
Each sales associate can have one client book per legal entity, and associates can add one or more customers to their client book. In Commerce, each customer can currently be added to only one client book. However, Microsoft plans to add functionality that lets you add a single customer to multiple client books.
Activities and notes
Online channels give retailers ways to learn about customer preferences without requiring that customers explicitly provide this information. By contrast, when customers interact with sales associates in the store, they explicitly share information about their preferences. Unfortunately, this information can be lost after the sale is over. However, if this information is recorded, it can help retailers better understand customers, and therefore help them provide better recommendations and a better overall shopping experience.
To capture the critical information that customers share, sales associates can use not only the client book attributes, but also the activities and notes functionality. Retailers can configure the activity types, such as information about the store visit, email address, phone number, and appointments. Activities that sales associates create can be viewed in a timeline format in the Store Commerce application, and the activities can also be viewed in the back office of Commerce through the Headquarters application.
Sales associates can also use notes to capture generic customer information that can be referenced before every interaction. These notes are saved in Headquarters and can be viewed in the customer profile or on the Customer details page in the call center.
Customer Insights integration
Retailers can optionally use Customer Insights with Commerce. Customer Insights can be used to collect and combine data about customers from different systems, including non-Dynamics 365 applications, where they interact with the retailer's brand. This data is then aggregated into a single view of the customer in real time, so insights can be derived from their behavior.
Customer Insights can:
Employ machine learning templates to predict churn.
Define the next best action.
Provide product recommendations.
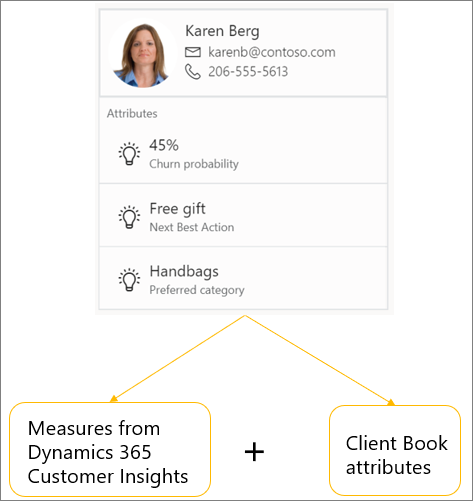
Retailers can aggregate data from the various systems that customers use to interact with the retailer's brand by using the Customer Insights application. They can then use this data to generate a single view of the customer and derive insights. The integration of Customer Insights with Commerce lets retailers select one or more measures that should be displayed on the customer card in the client book in the Store Commerce application.
For example, retailers can use the data in Customer Insights to calculate the "churn probability" for a customer and define the "next best action." If these values are defined as measures, they can be displayed on the customer card and can provide crucial information to sales associates.
To turn on the integration of Customer Insights with Commerce, you must ensure that:
You have an active instance of Customer Insights in the tenant where Commerce is provisioned.
You have a Microsoft Azure Microsoft Entra ID account that has an Azure subscription.
You have an Azure application ID created in the Commerce parameters for authentication purposes.
The following screenshot is an example customer card with attributes from Customer Insights and the Store Commerce Client Book:
Intelligent recommendations
In addition to using known customer activities and preferences to help personalize the shopping experience, Commerce can be used to display product recommendations on the e-Commerce website and Store Commerce devices. Product recommendations are items that a customer might be interested in. The recommendations are based on the purchase trends of other customers in online and brick-and-mortar stores.
Product recommendations allow customers to easily and quickly find products that they want while they have an experience that serves them well. Cross-selling and upselling can even be used to help customers find other products that they didn't originally intend to buy. When recommendations are used to enhance product discovery, the recommendations create more conversion opportunities, help increase sales revenue, and even amplify customer satisfaction and retention.