Describe inventory reservations, picking and packing, replenishment, and shipments
Inventory reservations
You can automatically reserve inventory quantities for a specific sales order. This means that reserved inventory can't be withdrawn from the warehouse for other orders unless the inventory reservation, or part of the inventory reservation, is canceled.
You reserve inventory for several reasons:
First ordered, first delivered, which means that customers get available items in the same order in which they place their orders.
Shortage of items due to a long or unknown delivery time from the vendor. You might want to make sure that certain customers or orders get delivery of the first-available items.
Certain customers and certain types of orders have priority for delivery.
Items with serial or batch numbers. You can mark certain items that have been or will be delivered to specific orders.
Specially ordered items that are reserved for certain orders.
Production orders. For example, you can mark items that are produced for and adjusted to specific orders.
You can reserve inventory automatically when you create a new order line, or reserve inventory manually on individual orders. It's also possible to reserve inventory at different stages of a production process. You can reserve only stocked products. You can't reserve services because there's no on-hand inventory. You can reserve both physical on-hand inventory and ordered but not yet received inventory. If a company reserves a larger quantity than the on-hand inventory, Supply Chain Management displays a message stating that you can't reserve such a large quantity. You can then either reserve the quantity anyway or change the ordered quantity. If a company reserves more items than are available, the shortage is covered the next time items are available for delivery.
Picking and packing
When an outbound order is processed, the item(s) in that order are picked in the warehouse from a picking list then packed for shipping.
With picking and packing:
Warehouse workers can use mobile devices to do cluster picking.
You can use FIFO and LIFO location directive strategies.
The following video explains three important inventory transactions: picking, packing, and registration. These three processes are demonstrated using different user interfaces available in the product.
After the packing slip, the next process is invoicing, which is discussed in the Learn the fundamentals of Dynamics 365 Finance learning path.
Cluster picking
After work orders are released to the warehouse, the worker can use a mobile device to assign the orders to a cluster. The cluster organizes the picking work for the worker. When a work order is assigned to a cluster, the worker must use cluster picking to perform the picking work for the order. The worker can't use other picking methods. If a work order is assigned to a cluster by mistake, the worker must break the cluster, and then recreate it.
If needed, a worker can pass a cluster to another worker. This changes the cluster status to Passed. When the worker uses a mobile device to indicate that the picking and put away work is completed, the shipment or load must be confirmed in the web application.
Output orders
Output orders are used to link sales order lines and transfer order lines with the outbound picking processes that use picking lists.
When picking lists are generated from either sales orders or transfer orders, output orders and shipments are automatically created. Everything on a picklist will be in a single shipment. But multiple picklists can go to the same shipment. The transfer order shipment or the sales order packing slip can be processed from the shipment. The following diagram depicts an overview of the process for outbound orders.
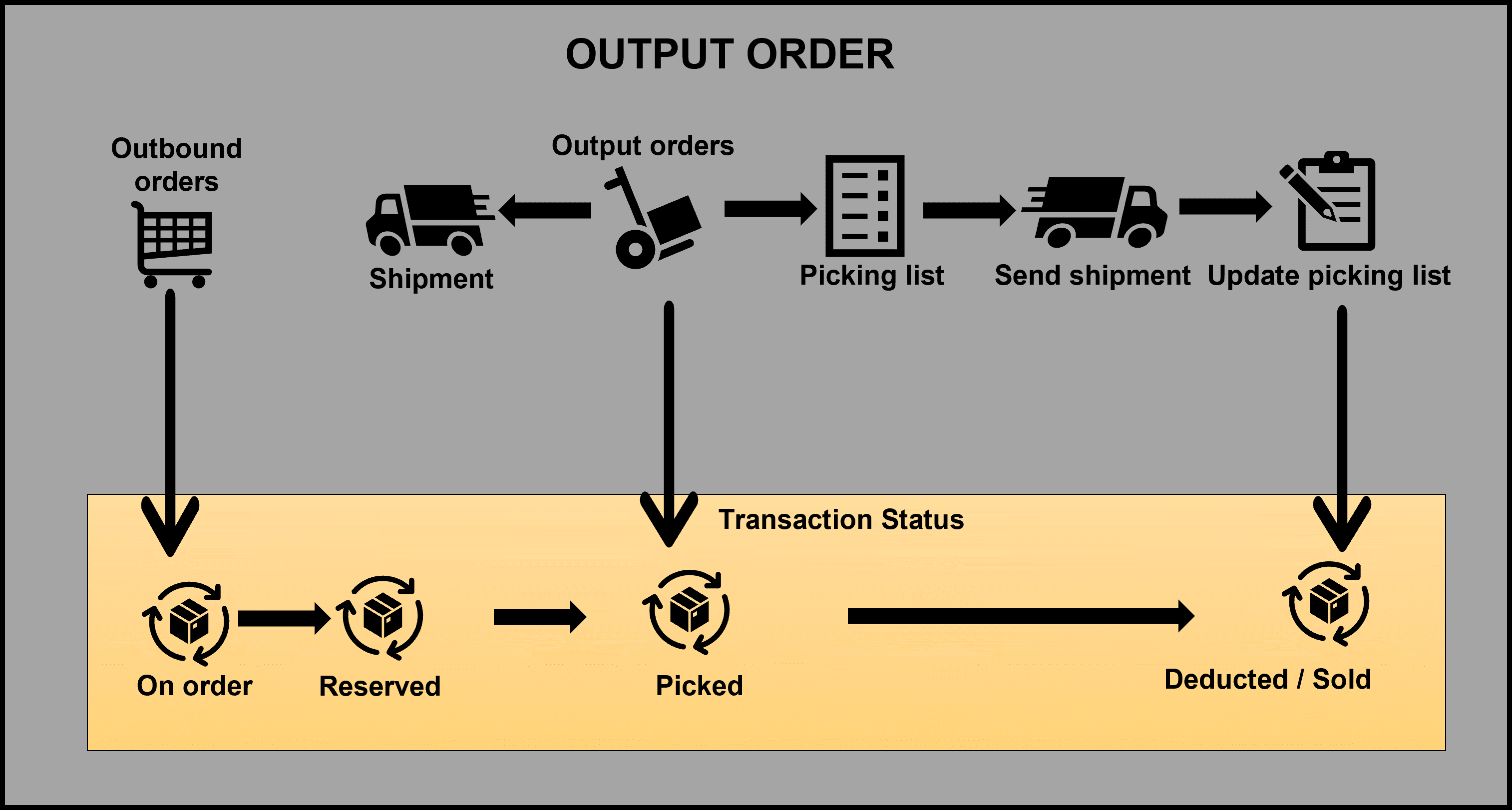
You can set up outbound rules to define how the program should handle the outbound process. You can use these rules to control the shipment process. You can use the rules to control during which stage in the process a shipment can be sent.