Manage hybrid resources at scale
You've seen how Relecloud can secure customer resources at scale with Azure Lighthouse. Lamna Healthcare is about to refocus their efforts on growing the business. The company is impressed with the way that Relecloud manages their existing Azure resources and assets. To free up resources, Lamna Healthcare wants Relecloud to take over the managing their on-premises operation. This would be in addition to managing their existing Azure resources. You're aware of a service called Azure Arc. You'll need to explore the capabilities of Azure Arc to see how you might use it to meet Lamna Healthcare's new requirements. Finally, you'll see how to use Azure Arc within your existing Azure Lighthouse service offering.
Understand Azure Arc
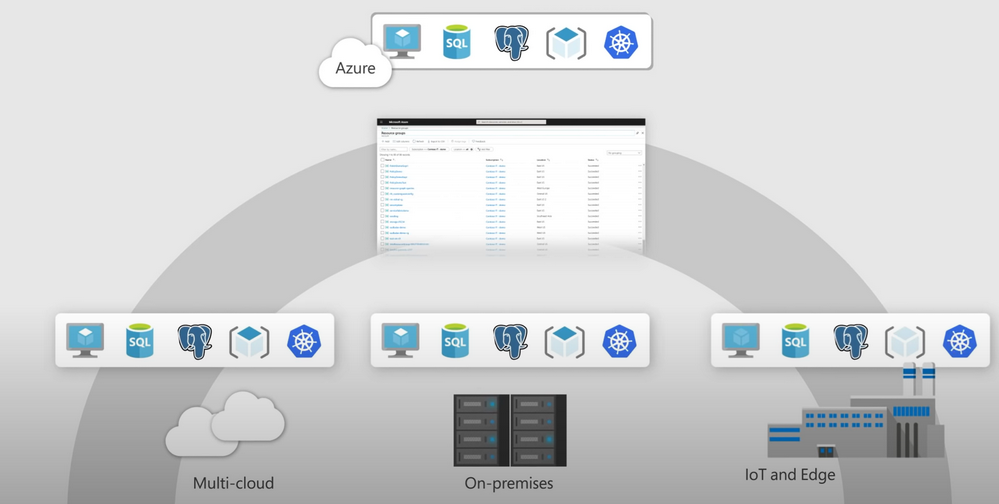
Relecloud currently uses Azure Resource Manager to manage Lamna Healthcare's existing Azure resources. Azure Arc would help extend that capability to manage Lamna Healthcare's on-premises servers. It supports Windows and Linux servers whether they're hosted on-premises at Lamna Healthcare, in Edge, or in the cloud.
Azure Arc for servers will let Lamna Healthcare manage any Windows and Linux machines hosted outside of Azure on their corporate network, in the same way they manage native Azure virtual machines. By linking a hybrid machine to Azure, it becomes connected and is treated as a resource in Azure.
By using Azure Arc, Lamna Healthcare can:
- Organize and govern across environments: Centrally manage, organize and govern Kubernetes clusters, databases, and servers across on-premises, Edge, and multicloud environments.
- Manage Kubernetes apps at scale: Manage and deploy Kubernetes applications across any environment using DevOps techniques.
- Run data services anywhere: Get automated upgrades and patches. Scale on-demand needs across all environments for the entire data estate.
By creating a single control plane, Lamna Healthcare can extend its current Azure native operations and governance to resources that exist outside of Azure.
Use the Azure Connected Machine agent
To make Lamna Healthcare's on-premises servers available to Azure, you'll need to use the Azure Connected Machine agent. This agent has to be installed on each machine that you plan to project into your Azure tenant. The Connected Machine agent works alongside other Azure agents that you might install on the target machine, and provides:
- The ability to manage policy configurations in a similar way to Azure virtual machines.
- The ability to store log data collected from the Log Analytics agent, in the workspace where the machine is registered.
The Connected Machine agent sends an update every five minutes to the Azure tenant where it's registered.
Generate the Connected Machine agent installation script
There are two ways to install the Connected Machine agent on the target machine. The first is to manually download the application and configure it on each machine. The alternative is to take an automated approach, using a template script to download and install the agent. For now, you'll look at how to generate an automated installation script.
Note
To install and configure the agent, you'll need to have administrator permissions on the target machine. For Windows machines, you must be a member of the Local Administrators group. On Linux, you'll need to use the root account.
Azure creates the script required to onboard each server, depending on whether you have Windows or Linux servers, Kubernetes clusters, or other cloud services.
Let's look at how Lamna Healthcare will add a Windows based on-premises server into their Azure tenant.
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- On the Servers - Azure Arc page, select Add at the upper left.
- On the Select a method page, under the Add a single server tile, and then select Generate script.
- Next, you need to provide details regarding the subscription:
- Supply the subscription type that you want to use for these on-premises resources.
- Create or select an existing resource group. You can add these new resources to an existing resource group, but you might want to have them in a dedicated resource group, especially if you later plan to use a service provider to manage them for you.
- Add a region, which should be the closest to your Azure instance.
- Select the operating system for the server you want to onboard. Your choices are: Windows and Linux. In this case, select Windows.
- Select the Connectivity method: Public endpoint, Proxy server, or Private endpoint.
- Select Download and run script.
At this stage, the Azure portal will generate the script you'll use to onboard the machine, projecting it into your Azure tenant. Lamna Healthcare can download this script to a local device. When you have a script for a Windows or Linux server, it can be used for all servers of that type.
- For Windows machines, there will be a generated PowerShell script, called OnboardingScript.ps1.
- For Linux machines, the generated script will be a bash script.
For more information on how to manually install the Connected Machine agent on a target machine, see onboarding non-Azure machines using Azure Arc.
Installing the Connected Machine agent on a Windows server
Now that you've created the installation script, Lamna Healthcare will use it to install the Connected Machine agent on the target server. The installation script must be accessible to the target machine.
Note
To install or uninstall the Connected Machine agent, you must have administrator permissions on the target machine.
Log in to the target server.
Copy the generated installation script to a folder on the server.
Open an Elevated PowerShell command prompt.
Go to the folder where the installations script was stored at step 2.
Run this command: ./OnboardingScript.ps1.
The agent will be downloaded and automatically configured on the server.
After installing the agent, you need to configure it to communicate with the Azure Arc service by running the following command:
"%ProgramFiles%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\azcmagent.exe" connect --resource-group "<resourceGroupName>" --tenant-id "<tenantID>" --location "<regionName>" --subscription-id "<subscriptionID>"
Verify the connection with Azure Arc
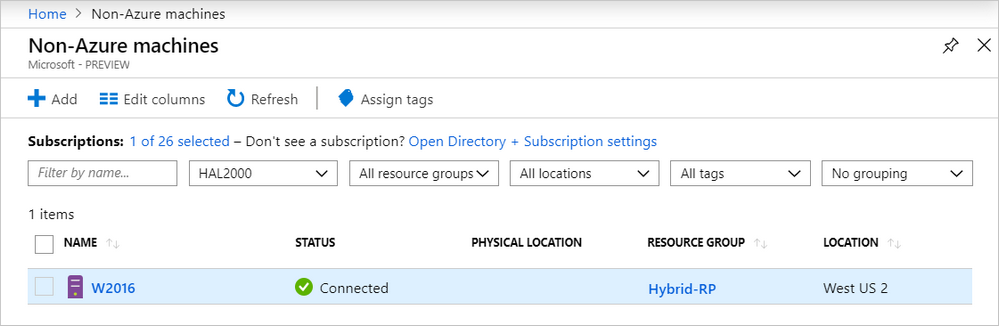
At Lamna Healthcare, after you install the agent and configure it to connect to Azure Arc for servers (preview), go to the Azure portal to verify that the server has been successfully connected. View your machines in the Azure portal.
Use Azure Lighthouse with Azure Arc Connected Machines
Now that Lamna Healthcare has added all their non-Azure machines to Azure Resource Manager in the tenant, Relecloud can manage them. Relecloud will create a service offer to Lamna Healthcare to manage the non-Azure resource groups. As soon as Lamna Healthcare approves the service, Relecloud will manage them in the same way that they manage Azure virtual machines.

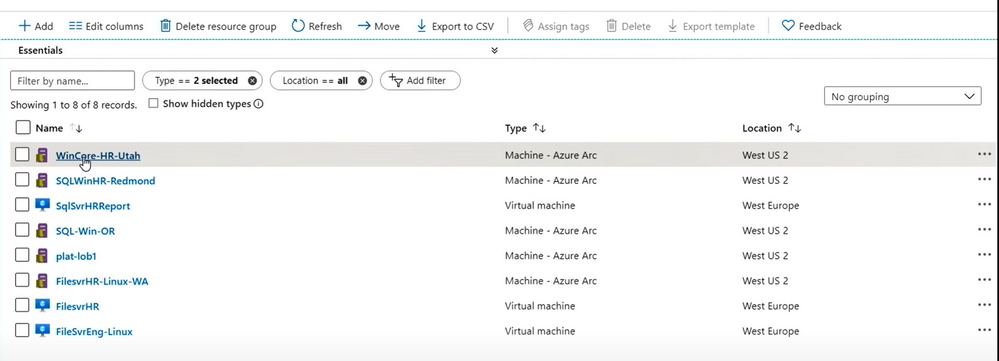
It's easy to identify each non-Azure device from the available resources, as their type is suffixed with Azure Arc; for example, Machine – Azure Arc.
Governance through Azure Policy
Now that Lamna Healthcare's Azure virtual machines and non-Azure servers are projected into the Relecloud Azure tenant, they can use Azure Policy to enforce organizational standards. By using the Azure Policy compliance dashboard, Relecloud staff members can evaluate the overall state of the environment. They can drill down to get per-resource and per-policy granularity. Relecloud can also ensure resource compliance through bulk remediation for existing resources and automatic remediation for the new non-Azure resources.
For more information about Azure Policy see Governance policy overview.
Manage hybrid resources for your customers
In this video, you'll see how to manage a customer's cloud and on-premises resources.