Handle errors by using try methods
Try methods in AL can help you handle errors that occur in the application during code runs. For example, with try methods, you can provide more user-friendly error messages for your users than the messages that are thrown by the system.
The main purpose of try methods is to catch errors/exceptions that are thrown by Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central or exceptions that are thrown during .NET Framework interoperability operations. Try methods catch errors, such as a conditional Codeunit.Run method call. The exception is that the try method calls don't require that write transactions are committed to the database. Additionally, changes to the database that are made with a try method aren't rolled back.
Because changes that are made to the database by a try method aren't rolled back, you shouldn't include database write transactions within a try method. By default, the Business Central server configuration prevents you from doing this action. If a try method contains a database write transaction, a runtime error will occur.
A method that is designated as a try method has a Boolean return value
(true or false), and has the OK:= MyTrymethod construction.
A try method can't have a user-defined return value.
If a try method call doesn't use the return value, the try method will operate like an ordinary method and errors will be exposed as usual.
If a try method call uses the return value in an OK:= statement or a conditional statement such as if-then, errors will be caught. The try method will return as true if no error occurs and false if an error occurs.
You can use the GetLastErrorText method to obtain errors that are generated by Business Central. To get details of exceptions that are generated by .NET Framework objects, you can use the GetLastErrorObject method to inspect the Exception.InnerException property.
To create a try method, you can add a method in the AL code of an object, such as a codeunit as usual, and then set the TryFunction Attribute.
The following example illustrates how the try method works. First, you'll create a codeunit that has a MyTrymethod local method. Then, you'll add the following code on the OnRun trigger and MyTrymethod method. The following image shows an example of the code that you'd use to accomplish this task.

When you run this codeunit, the implementation of the OnRun trigger will stop. Then, the An error occurred during the operation error message will be thrown in the UI.
Now, set the TryFunction attribute of the MyTrymethod method. Next, you'll add code to the OnRun trigger to handle the return value of the try method, as shown in the following image.
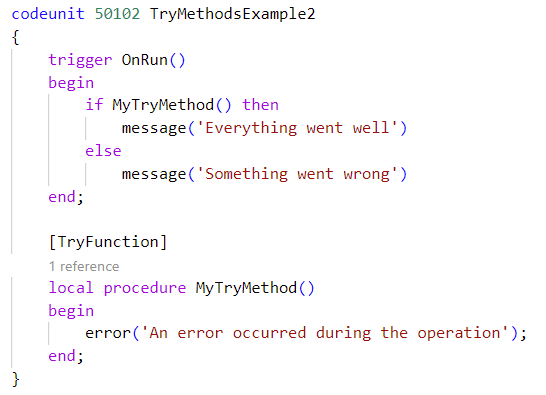
When you run the codeunit, instead of stopping the implementation of the OnRun trigger when the error occurs, the error will be caught and the Something went wrong message will be returned.