Describe Azure Machine Learning AutoML
Automated machine learning, also referred to as automated ML or AutoML, is the process of automating the time-consuming, iterative tasks of machine learning model development. It allows data scientists, analysts, and developers to build ML models with large scale, high efficiency, and productivity while sustaining model quality. Automated ML in Azure Machine Learning is based on a breakthrough from our Microsoft Research division.
Traditional machine learning model development is resource-intensive, requiring significant domain knowledge and time to produce and compare dozens of models. With automated machine learning, you'll accelerate the time it takes to get production-ready ML models with great ease and efficiency.
When to use AutoML: classify, regression, & forecast
Apply automated ML when you want Azure Machine Learning to train and tune a model for you using the target metric you specify. Automated ML democratizes the machine learning model development process and empowers its users, no matter their data science expertise, to identify an end-to-end machine learning pipeline for any problem.
Data scientists, analysts, and developers across industries can use automated ML to:
- Implement ML solutions without extensive programming knowledge
- Save time and resources
- Leverage data science best practices
- Provide agile problem-solving
Classification
Classification is a common machine learning task. Classification is a type of supervised learning in which models learn using training data and apply those learnings to new data. Azure Machine Learning offers featurizations specifically for these tasks, such as deep neural network text featurizers for classification.
The main goal of classification models is to predict which categories new data will fall into based on learnings from its training data. Common classification examples include fraud detection, handwriting recognition, and object detection. Learn more and see an example at Create a classification model with automated ML.
Regression
Similar to classification, regression tasks are also a common supervised learning task. Azure Machine Learning offers featurizations specifically for these tasks.
Different from classification, where predicted output values are categorical, regression models predict numerical output values based on independent predictors. In regression, the objective is to help establish the relationship among those independent predictor variables by estimating how one variable impacts the others. For example, automobile prices are based on features like gas mileage, safety rating, etc.
Time-series forecasting
Building forecasts is an integral part of any business, whether it's revenue, inventory, sales, or customer demand. You can use automated ML to combine techniques and approaches and get a recommended, high-quality time-series forecast. Learn more with this how-to: automated machine learning for time series forecasting.
An automated time-series experiment is treated as a multivariate regression problem. Past time-series values are "pivoted" to become additional dimensions for the regressor together with other predictors. Unlike classical time series methods, this approach has the advantage of naturally incorporating multiple contextual variables and their relationship to one another during training. Automated ML learns a single but often internally branched model for all items in the dataset and prediction horizons. More data is thus available to estimate model parameters and generalization to unseen series becomes possible.
Advanced forecasting configuration includes:
- holiday detection and featurization
- time-series and DNN learners (Auto-ARIMA, Prophet, ForecastTCN)
- many models support through grouping
- rolling-origin cross-validation
- configurable lags
- rolling window aggregate features
How automated ML works
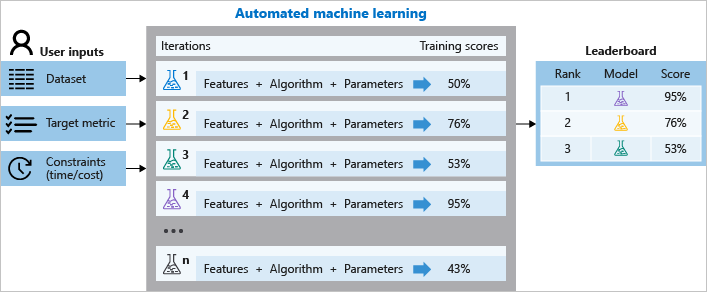
During training, Azure Machine Learning creates several pipelines in parallel that try different algorithms and parameters for you. The service iterates through ML algorithms paired with feature selections, where each iteration produces a model with a training score. The higher the score, the better the model is considered to "fit" your data. It will stop once it hits the exit criteria defined in the experiment.
The following diagram illustrates this process.
Guidance on local vs. remote managed ML compute targets
The web interface for automated ML always uses a remote compute target When combined with Azure Synapse, experiments can be run on the Spark pool inside Synapse Analytics. When you are not running your experiment on Azure Machine Learning's compute resources, the execution environment is considered local compute.
- Local compute: Training occurs on your local laptop, or VM compute.
- Remote compute: Training occurs on Machine Learning compute clusters.