Overview of Azure Arc
In this unit, you learn the basics of Azure Arc and its key capabilities and benefits.
Azure Arc basics
As business technology evolves, it becomes more complex. Multiple applications might run on different hardware across on-premises datacenters, various public and private clouds, and the edge. It's important to manage these disparate environments at scale, enhance security across the entire organization, and enable developer agility.
Azure Arc provides a set of technologies that you can use to simplify administration of complex, distributed, and hybrid environments. It extends the Azure platform to help you build applications and services with the flexibility to run across datacenters, at the edge, and in multicloud environments.
Azure Arc helps enable automation, single-pane-of-glass monitoring, and comprehensive security, enabling a cloud-first strategy regardless of where your resources are located. At the same time, Azure Arc lets you continue using traditional IT tools and practices as you transition to the DevOps model to fully benefit from cloud native architectural and operational patterns.
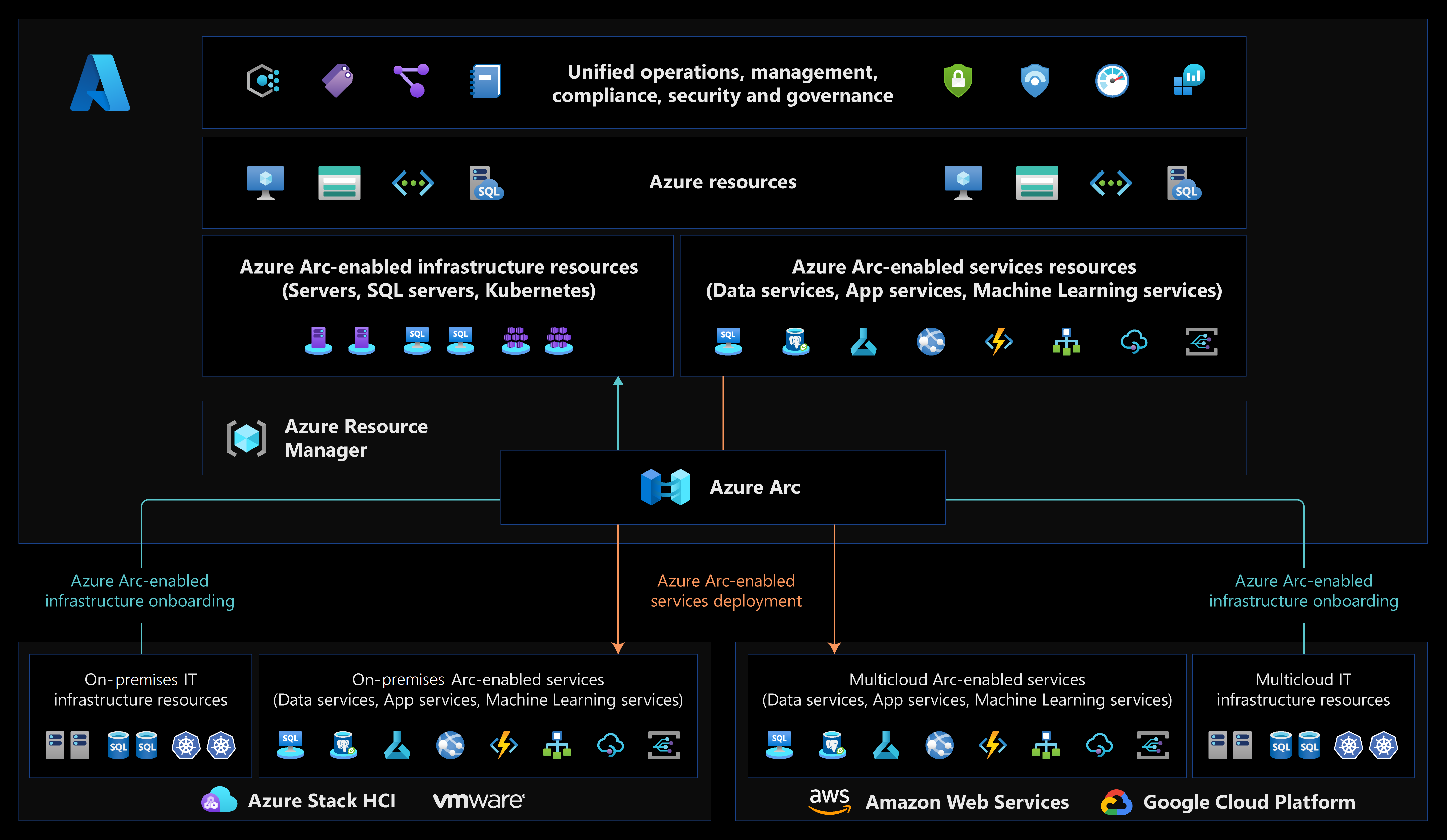
Azure Arc architecture
The following diagram shows how Azure Arc operates across multicloud and on-premises Kubernetes environments.
Azure Arc support for non-Azure resources
Azure Arc supports Azure integration for many types of resources that reside outside of Azure, including:
- Azure Arc-enabled physical servers and virtual machines (VMs) running Windows or Linux operating systems.
- SQL Server instances running on Azure Arc-enabled servers.
- Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes for a wide range of Kubernetes distributions.
- Azure Stack HCI on-premises physical clusters with virtualized workloads and containerized workloads.
- AKS running on Azure Stack HCI clusters (AKS hybrid).
- Azure Arc-enabled data services, such as Azure SQL Managed Instance, running on Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters.
In Azure Arc-enabled scenarios, Azure Arc uses a locally installed agent to establish a logical connection between the local resource and Azure. Through this connection, the non-Azure resource becomes a hybrid Azure resource, with its own identity represented by an Azure resource ID.
After a non-Azure resource is connected through Azure Arc, you can use Azure to manage and monitor its configuration and operations. You can organize Arc-enabled resources alongside native Azure resources by using Azure management groups, subscriptions, resource groups, and tags.