How Azure HDInsight works
Here, you'll learn how Azure HDInsight works. You'll find out about the following components and how they fit together to provide data control and management:
- Apache Hadoop
- HDInsight storage
- HDInsight processing
What is Apache Hadoop?
Apache Hadoop is a cloud-distributed data-processing system at the core of HDInsight. It has three components, which the following table describes:
| Apache Hadoop component | Description |
|---|---|
| HDFS | The Apache Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) provides storage for the Hadoop system. |
| YARN | The Apache Hadoop Yet Another Resource Negotiator (YARN) component provides processing for the system. |
| MapReduce | MapReduce is a programming model that enables you to process and analyze data. |
How do the components interact?
The following diagram depicts storage and processing components interacting in a typical HDInsight Hadoop cluster. It illustrates the following components:
- The head node and worker nodes, which do the processing.
- Multiple Windows Azure Storage Blob (WASB) storage centers, within the nodes. HDFS interacts with these containers.
- Multiple default, linked, and unlinked storage containers. These are available to the two nodes.
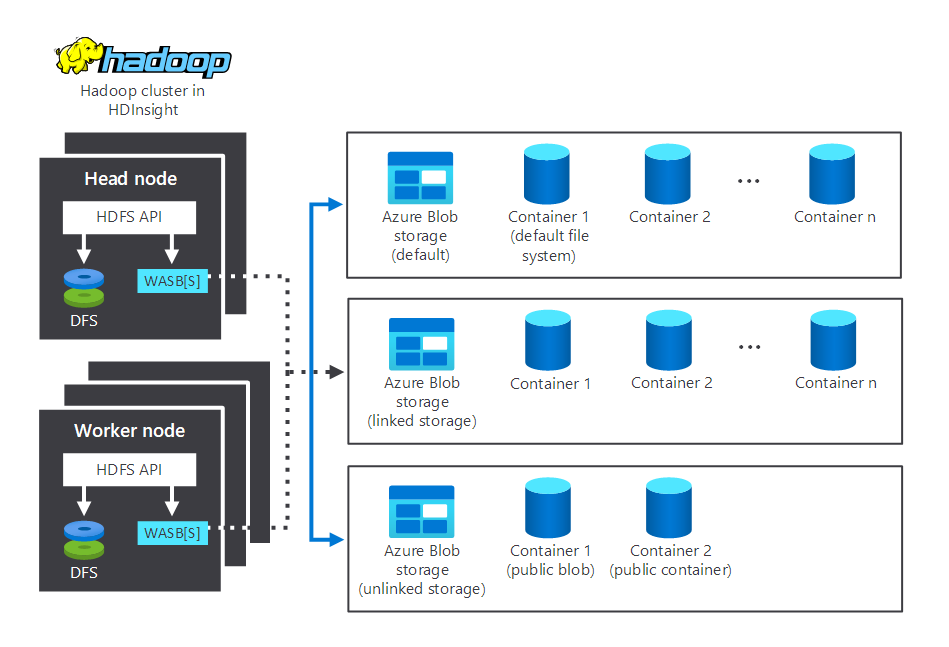
Let's now examine how storage and processing work.
How does storage work?
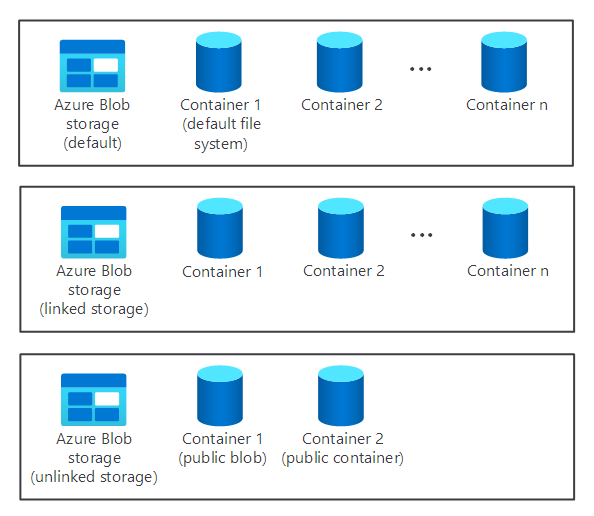
A cluster's storage component isn't created automatically when you provision an HDInsight cluster. Instead, it's provided by an HDFS-compliant system such as Azure Storage or Azure Data Lake.
There are benefits in separating a cluster's storage component from the processing component. For example, you can safely delete any HDInsight clusters used only for computation without worrying about losing data. When you're adding an HDInsight cluster, you must define a default file system.
Important
For Azure Storage, you must specify a blob container as the default file system.
Providing a default file system ensures that HDInsight can resolve relative file references when searching for files.
Tip
When you want to increase available storage, you can link and unlink additional file systems as required.
How does processing work?
When processing data, a Hadoop cluster's compute component on HDInsight breaks into two logical areas. The following table describes these two areas:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Head node | The head node accepts and manages client requests and passes the requests to the worker nodes. |
| Worker node | The worker nodes process data. |
Note
The head node is sometimes referred to as a master node.
Most clusters contain two head nodes, including:
- An active head node, which manages client connections.
- A passive head node, which provides resilience should the active node go offline.
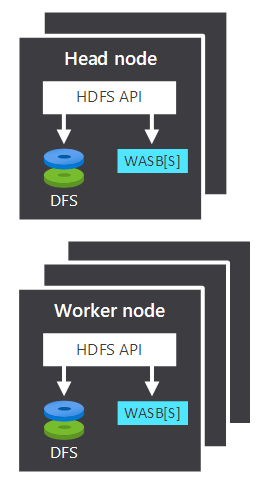
Both the head and worker nodes can connect directly to a locally attached HDFS or access data that is stored in Azure Blob or Azure Data Lake. What data gets managed depends on two factors:
- How the MapReduce programming model has defined how to work with the data
- How the head node allocates the work
What does YARN do?
The YARN performs resource management within an HDInsight cluster. When you're processing data, this service manages resources and job scheduling.
YARN sits between the HDFS and the computation system of the HDInsight cluster. It works with the head node to help distribute a job across the cluster's worker nodes. This helps to ensure that the data processing jobs occur in parallel.