Exercise - Run an NVIDIA DeepStream Graph Composer reference application
Let's take a closer look at the IVA application workflow that's enabled by the DeepStream Graph Composer. We mentioned previously that NVIDIA's Cloud Repository or another external registry can provide drag-and-drop components for use within the DeepStream Composer application.
By using these extensions, you can add features and functionality to the Composer application. Ultimately, you can use this tool to package and distribute IVA workloads by using the bundled container-builder. The following diagram shows this process.
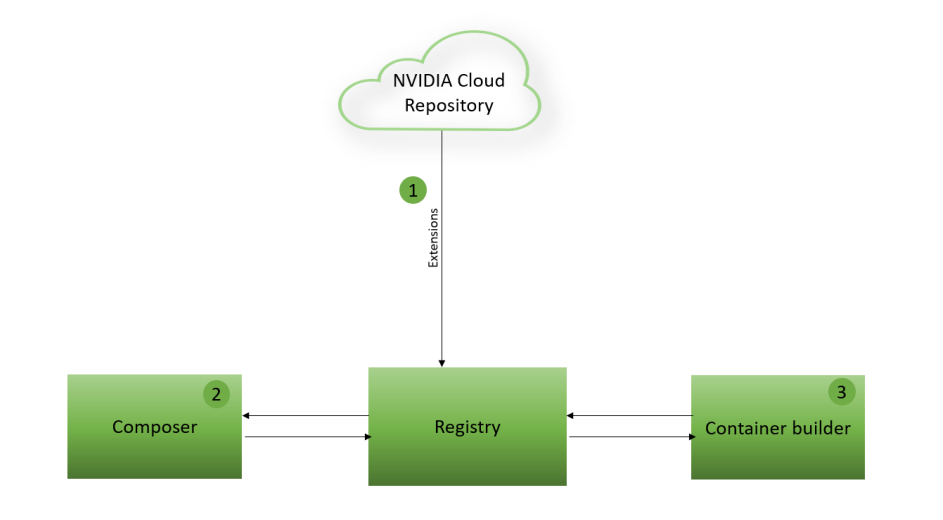
To begin, sync to NVIDIA's public Cloud Repository to bring in the latest available extensions. To accomplish this process, run the following command in a terminal on the host machine:
registry repo sync -n ngc-publicThis command produces output similar to the following output:
2021-09-13 21:32:39,127 - Registry - INFO - Syncing repo ngc-public ... 2021-09-13 21:32:41,022 - Registry - INFO - Syncing extension NvDsBaseExt version 0.0.1 2021-09-13 21:32:45,833 - Registry - INFO - Syncing extension NvDsAnalyticsExt version 0.0.1 2021-09-13 21:32:50,676 - Registry - INFO - Syncing extension NvDsCloudMsgExt version 0.0.1 2021-09-13 21:32:55,743 - Registry - INFO - Syncing extension NvDsConverterExt version 0.0.1 2021-09-13 21:33:00,579 - Registry - INFO - Syncing extension NvDsDewarperExt version 0.0.2 2021-09-13 21:33:05,283 - Registry - INFO - Syncing extension NvDsDewarperExt version 0.0.1 2021-09-13 21:33:10,300 - Registry - INFO - Syncing extension NvDsInferenceExt version 0.0.1 2021-09-13 21:33:15,899 - Registry - INFO - Syncing extension NvDsInferenceUtilsExt version 0.0.2 2021-09-13 21:33:20,574 - Registry - INFO - Syncing extension NvDsInferenceUtilsExt version 0.0.1 2021-09-13 21:33:25,722 - Registry - INFO - Syncing extension NvDsInterfaceExt version 0.0.1 2021-09-13 21:33:30,814 - Registry - INFO - Syncing extension NvDsMuxDemuxExt version 0.0.1 Repository syncedVerify that the extensions are installed and available by using this command:
registry extn listYou might notice that many of these extensions begin with prefixes that map to the NVIDIA optimized GStreamer plug-ins included in the DeepStream SDK. For example, the NvDsMuxDemuxExt extension provides a visual component for interacting with Gst-nvstreamdemux.
Now open the Composer application by using this command:
composerNotice that a list of components populates on the right side of the application user interface. The components are grouped by extension name. If a list doesn't appear, you might need to resync to the ncg-public repo by using the steps done earlier. Select the extension name to view the components it provides, as shown here:
The following guidelines help you understand how to interact with the Composer application to develop custom applications:
- To add a new component instance, select and hold the name of a component. Then drag it into the graph editor space.
- To display the name of a component, look at the header in the graph area. The component also might contain handles for input/output ports.
- To connect components to one another, select a handle and draw a connection between compatible input/output ports.
- To display component details, select the component. Details appear in a Details window on the right side of the application. You can edit the properties in this window to customize the behavior of the component.
Let's examine a reference application to show what you can create by following the preceding guidelines. Earlier when you installed the DeepStream reference graphs package, many examples were installed into the following path:
/opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream/reference_graphs/In the Composer application, select File > Open Graph and go to the /opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream/reference_graphs/deepstream-test1 path. Select the deepstream-test1.yaml file. Then select Okay.
Select the NvDsSingleSrcInput component and the Details pane opens on the right side of the application. Scroll down in the Details pane and notice the uri property where we set the video file that will be used as input in this IVA pipeline.
If you want to modify the uri property to use an RTSP stream, set type equal to 4. Provide the RTSP path rtsp://wowzaec2demo.streamlock.net/vod/mp4:BigBuckBunny_115k.mov. This action has the same effect as the DeepStream [source0] configuration group entry shown here:
[source0] enable=1 #Type - 1=CameraV4L2 2=URI 3=MultiURI 4=RTSP type=4 uri=rtsp://wowzaec2demo.streamlock.net/vod/mp4:BigBuckBunny_115k.mov num-sources=1 #drop-frame-interval=2 gpu-id=0 # (0): memtype_device - Memory type Device # (1): memtype_pinned - Memory type Host Pinned # (2): memtype_unified - Memory type Unified cudadec-memtype=0
Next, look at the overall flow of the IVA pipeline presented in this example. After you understand the overall workflow and expected behavior of the graph, you'll then up this workload as a containerized workload for redistribution and execution.
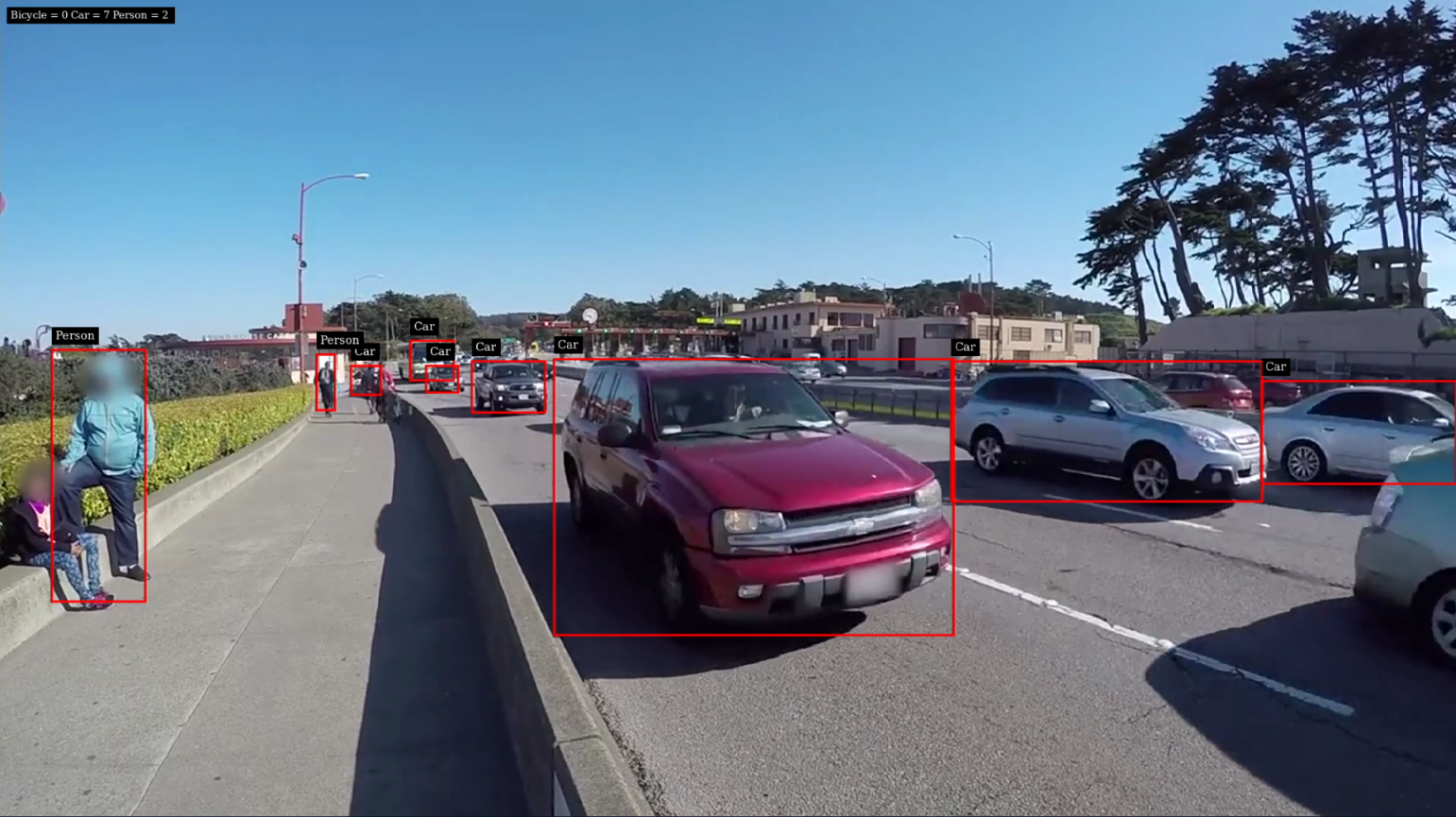
This application takes a video source as input by using
NvDsSingleSrcInput, which is passed intoNvDsStreamMux(which could technically process multiple video inputs). The output ofNvDsStreamMuxprovides a frame from each video input, which is sent for processing inNvDsInferVideo. Inference is applied by using a ResNet 4 class object detector, such as bicycle, car, person, or road sign. The inference results ofNvDsInferVideoare passed to bothNvDsPerClassObjectCounting, to display a count for each detected class, andNvsOSD, which generates the on-screen detections with bounding boxes. The boxes are displayed by the final connection toNvDsVideoRenderer.To verify this behavior and see it in action, invoke the included
execute_graph.shscript and pass in the necessary parameters inparameters.yaml. To execute the graph for deepstream-test1.yaml on the x86-based host, run the following commands in a terminal:cd /opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream/reference_graphs/deepstream-test1 /opt/nvidia/graph-composer/execute_graph.sh deepstream-test1.yaml parameters.yaml -d /opt/nvidia/graph-composer/config/target_x86_64_cuda_11_4.yamlYou should see output similar to that shown here:

Note
If you intend to use a virtual machine to satisfy the host machine requirements, you might encounter issues when you attempt to run a DeepStream application that uses an EGL sink for visualized output. To work around this limitation, change the type of your uri source to 1 for FakeSink. Be aware that FakeSink won't provide any visual output. It allows your workload to execute but without an associated on-screen display of processed results.