Essential skills for life ready learning
Skills of the future aren’t limited to STEM. Social emotional skills are quickly taking center stage alongside cognitive skills and technical skills in both the classroom and the workforce. For the class of 2030, social emotional skills development is an integral part of learning and is shaped largely by classroom experiences.
"The education systems need to reimagine themselves, need to reframe themselves, and at times, reinvent themselves to best prepare young people to get a job, to create a job, or to keep a job." - Mark Sparvell, Education Leader at Microsoft
What the research says
The shift from a focus on knowing to a focus on doing requires our learners to navigate the volume, velocity, and the variability of knowledge. This highlights the growing global skills gap. Listen in the video (2:54) as Mark Sparvell, Education Leader at Microsoft speaks more to the need for reimagined learning experiences. As you watch, consider what these types of learning experiences can look like both the educators and students in your building.
Social emotional learning
What are the core competencies of social emotional learning?
- Self-awareness
- Self-management
- Social awareness
- Relationship skills
- Responsible decision making
For more information, see CASEL’s SEL Framework.
How does social emotional learning support cognitive and technical skills?
- Social emotional skill development can increase academic performance by 11 percentile points.
- Social and emotional skills are 2x more predictive of a student’s academic achievement than their home environment or demographic.
- Social emotional skills provide students with perspective and flexibility necessary to function at a high level even when faced with uncertainty, change, pressure, stress, and other challenges.
Students care about social emotional learning, and often prioritize these in their top five skills for their own education. The students participating in the research study made clear that they value social emotional skills development over cognitive skills development when they think about their futures and the type of learning and work they will be engaged in. This requires us to alter our perceptions of how we are addressing these skills and which skills are important to students.
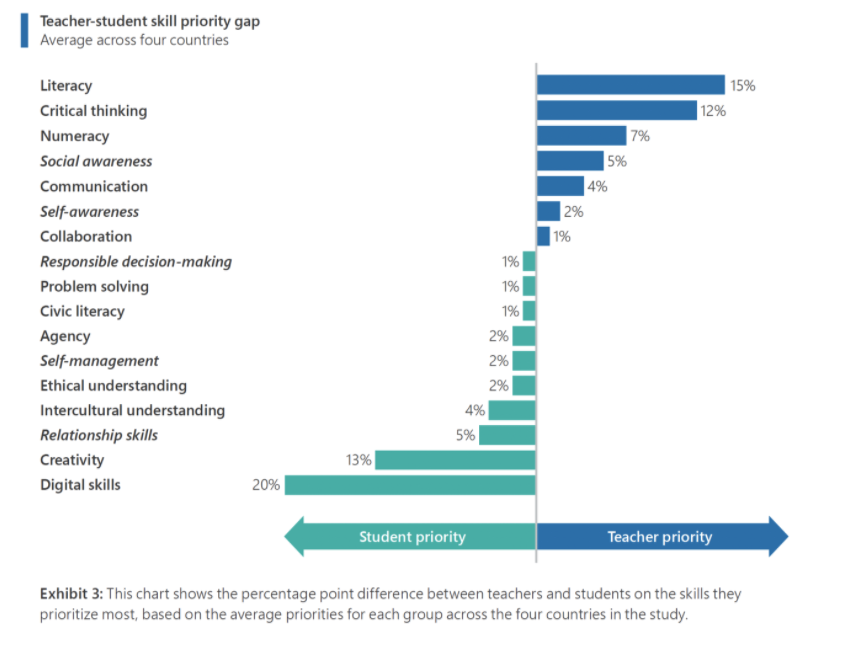
Look at the skills included in the image (original image found on p.12). How would you rank these skills from most to least important for your learners? What is happening in your building to support your ranking?
"Emotions drive attention and learning. How we feel influences our ability to learn and if educators aren’t aware of that, they may not be creating the best environment learning to occur in the classroom." - Marc Brackett, Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence
The types of skills that social emotional learning supports—problem-solving and collaboration, for example—are integral for our learners in developing life ready competencies. Social emotional learning is largely integrated into learning in two ways: “taught” and “caught” curriculum. Students are able to develop some amount of social emotional skills incidentally through influences like environment and interactions with teachers and peers (“caught” curriculum), more needs to be done to proactively develop and apply these skills at scale and depth (“taught” curriculum).
What overt classroom experiences in your school are being used to provide students opportunities to engage in “taught” social emotional learning?
Learn more
- Emotion and Cognition in the Age of AI: A Well-being Agenda for 21st Century Skills (white paper)
- New Vision for Education: Fostering Social and Emotional Learning Through Technology (white paper)
What it can look like
In this video (3:32), learn more about how educators in Cherokee Schools—a suburban school district outside of Atlanta, GA—have designed creative lessons and curriculum to use Minecraft: Education Edition as an instructional tool. The district has seen Minecraft become an avenue for students to learn social emotional skills, including communication, teamwork, and compromise. Students are becoming the leaders, excelling academically and developing life-ready skills. As you watch, notice the types of opportunities educators are creating for both "taught" and "caught" curriculum.
Dive further into the ways educators are supporting students’ SEL growth by incorporating gaming into their lessons via Minecraft: Education Edition, as well as insights for supporting a SEL program within your school.
Actions you can take
As a leader, there are many things you can do to foster an environment where social emotional learning and skills development thrive.
- Share existing research with educators to elevate buy-in to teaching SEL
- Gather data to identify students’ mental and emotional health
- Track supportive measures that are working
- Involve students in determining and addressing school climate
- Involve educators in planning and implementing social emotional learning efforts
- Employ curricula that promotes social emotional skills
- Provide educators with training to deliver social emotional learning content
- Provide educators with flexibility in implementing curricula
- Provide educators with more time for direct interactions with students
You can also consider how to leverage technology to provide educators opportunities to create learning experiences that support social emotional learning and give students opportunities to engage in skills development. One way to do this is through a collaborative platform, such as Microsoft Teams.
Microsoft Teams
- Allow people in different communities or locations to work together
- These environments give students opportunities to collaborate across time zones and multilingual contexts
- Students can quickly crowdsource topics and content, iterate, and co-create
- Educators can leverage these environments to give students safe rehearsal space to make responsible decisions and explore identity as they co-create
Learn more
- Transform Learning with Microsoft Teams
- Crafting a collaborative learning environment with Class Teams
- Immersive Experiences in Education (white paper)
Reflection questions
The shift from a focus on knowing to a focus on doing has led to students' prioritization of social emotional learning and skills development. Consider how this is represented in your building. Share your thoughts, wonderings, and ideas with other participants on the module Flipgrid or with your team or colleagues.
- What curricula, support services, strategies, are currently employed in your school to support SEL skills development?
- How can your effort to support SEL better align with your students’ and educators’ needs?