Load data using T-SQL
SQL developers or citizen developers, who are often well-versed in the SQL engine and adept at using T-SQL, will find the Warehouse in Microsoft Fabric favorable.
This is because the Warehouse is powered by the same SQL engine they're familiar with, enabling them to perform complex queries and data manipulations. These operations include filtering, sorting, aggregating, and joining data from different tables. The SQL engine’s wide range of functions and operators further allows for sophisticated data analysis and transformations at the database level.
Use COPY statement
The COPY statement serves as the main method for importing data into the Warehouse. It facilitates efficient data ingestion from an external Azure storage account.
It offers flexibility, allowing you to specify the format of the source file, designate a location for storing rows that are rejected during the import process, skip header rows, among other configurable options.
The option to store rejected rows separately is useful for data cleaning and quality control. It allows you to easily identify and investigate any issues with the data that weren't successfully imported.
To connect to an Azure storage account, you need to use either Shared Access Signature (SAS) or Storage Account Key (SAK).
Note
The COPY statement currently supports the PARQUET and CSV file formats.
Handle error
The option to use a different storage account for the ERRORFILE location (REJECTED_ROW_LOCATION) allows for better error handling and debugging. It makes it easier to isolate and investigate any issues that occur during the data loading process. ERRORFILE only applies to CSV.
Load multiple files
The ability to specify wildcards and multiple files in the storage location path allows the COPY statement to handle bulk data loading efficiently. This is useful when dealing with large datasets distributed across multiple files.
Multiple file locations can only be specified from the same storage account and container via a comma-separated list.
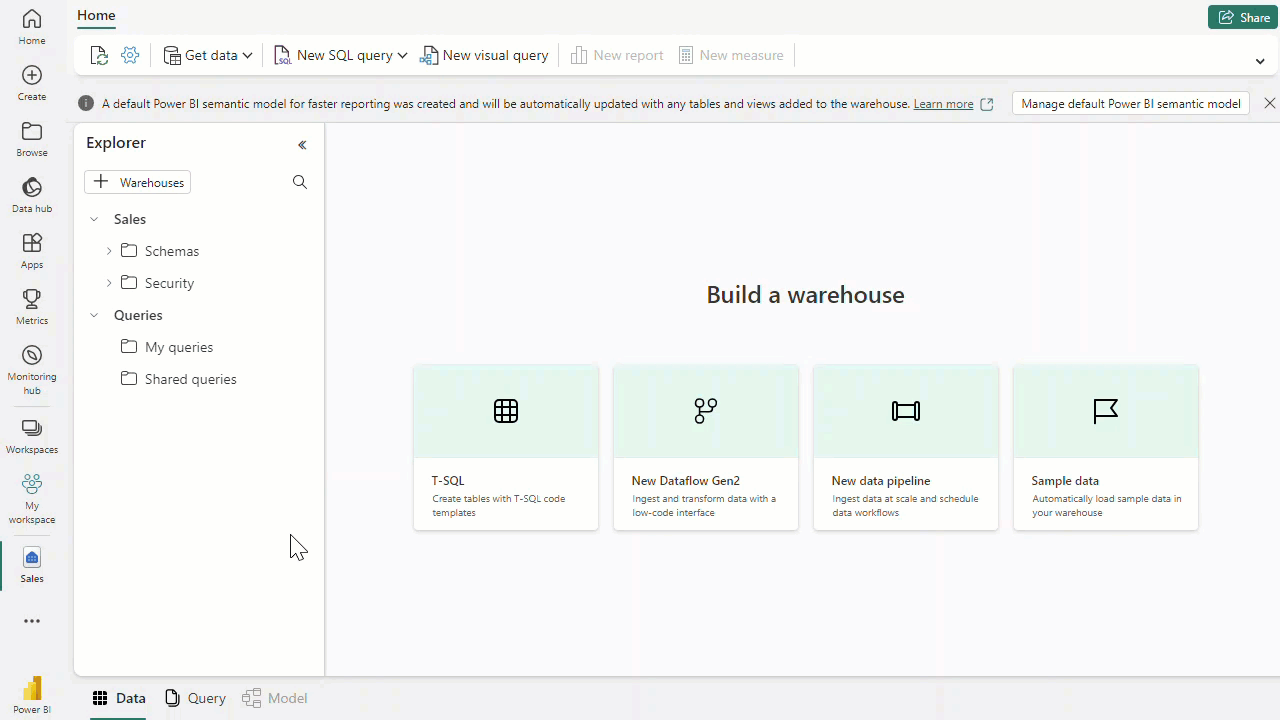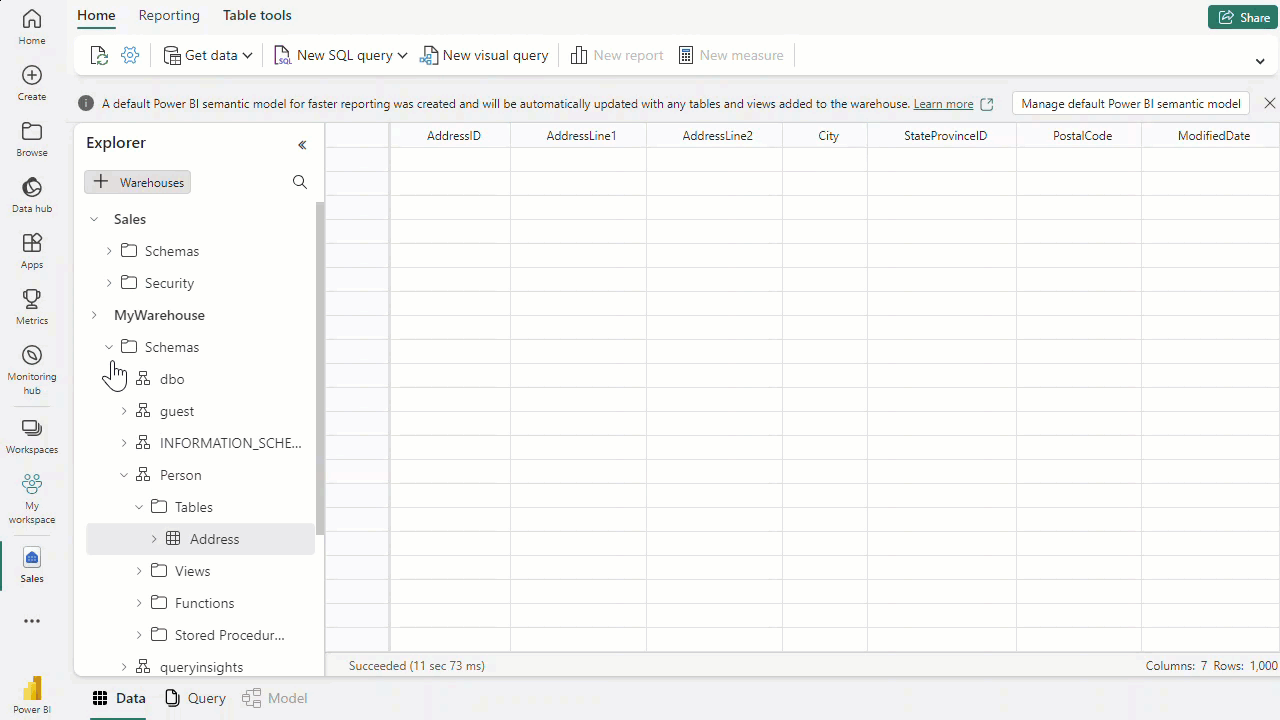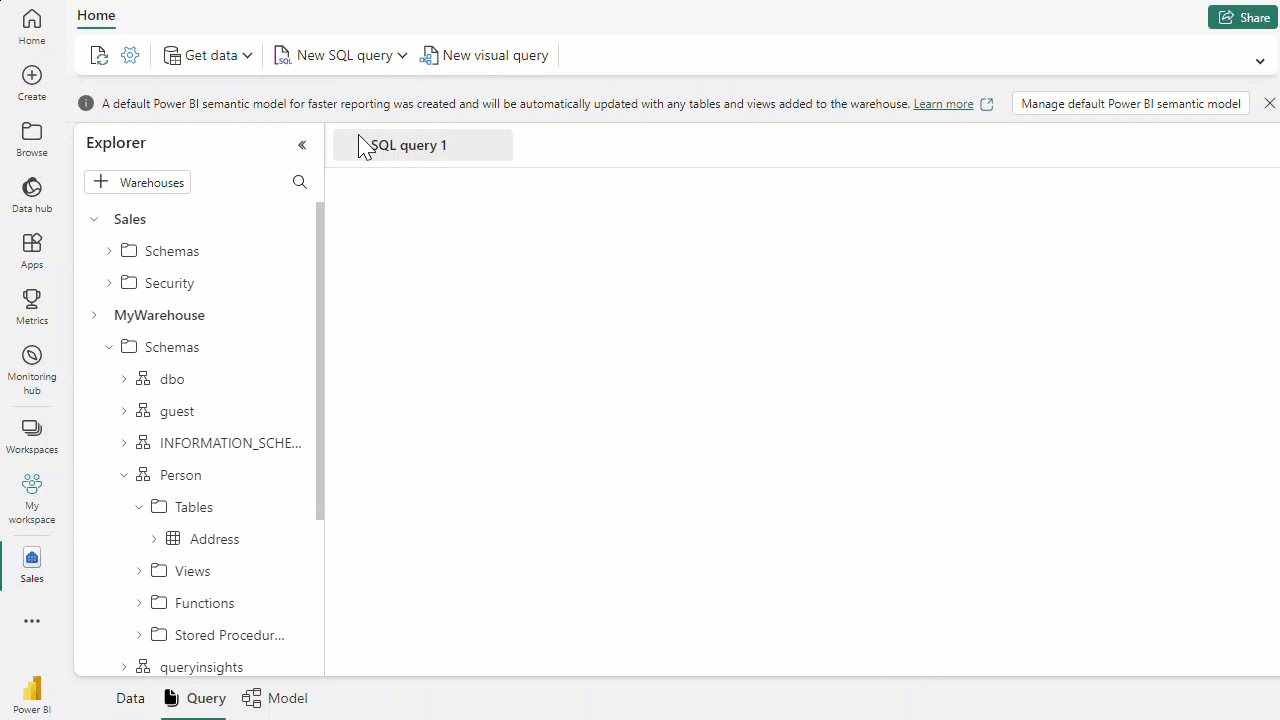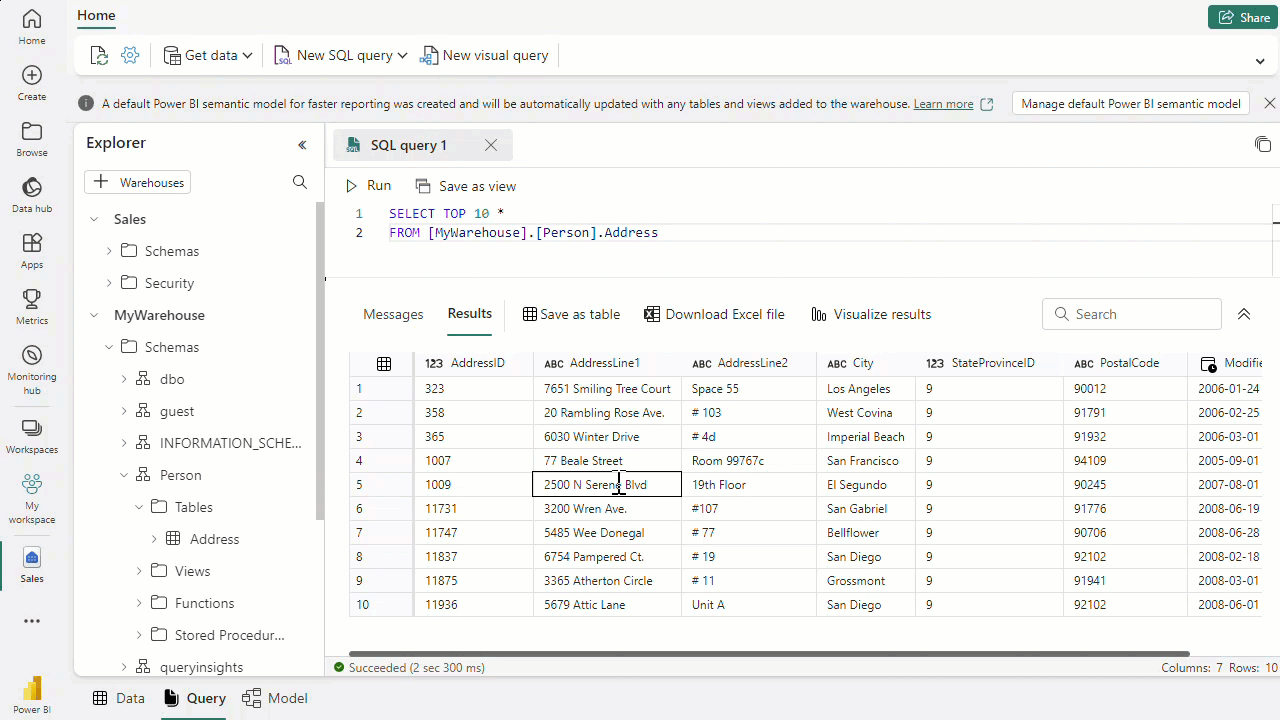
COPY my_table
FROM 'https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/myblobcontainer/folder0/*.csv,
https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/myblobcontainer/folder1/'
WITH (
FILE_TYPE = 'CSV',
CREDENTIAL=(IDENTITY= 'Shared Access Signature', SECRET='<Your_SAS_Token>')
FIELDTERMINATOR = '|'
)
The following example shows how to load a PARQUET file.
COPY INTO test_parquet
FROM 'https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/myblobcontainer/folder1/*.parquet'
WITH (
CREDENTIAL=(IDENTITY= 'Shared Access Signature', SECRET='<Your_SAS_Token>')
)
Ensure that all the files have the same structure (that is, same columns in the same order) and that this structure matches the structure of the target table.
Load table from other warehouses and lakehouses
You can load data from various data assets in a workspace, such as other warehouses and lakehouses.
To reference the data asset, ensure that you use three-part naming to combine data from tables on these workspace assets. You can then use CREATE TABLE AS SELECT (CTAS) and INSERT...SELECT to load the data into the warehouse.
| SQL Statement | Description |
|---|---|
CREATE TABLE AS SELECT |
Allows you to create a new table based on the output of a SELECT statement. This operation is often used for creating a copy of a table or for transforming and loading the results of complex queries. |
INSERT...SELECT |
Allows you to insert data from one table into another. It’s useful when you want to copy data from one table to another without creating a new table. |
In a scenario where an analyst needs data from both a warehouse and a lakehouse, they can use this feature to combine the data. They can then load this combined data into the warehouse for analysis. This feature is useful when data is distributed across many assets in a workspace.
The following query creates a new table in the analysis_warehouse that combines data from the sales_warehouse and the social_lakehouse using the product_id as the common key. The new table can then be used for further analysis.
CREATE TABLE [analysis_warehouse].[dbo].[combined_data]
AS
SELECT
FROM [sales_warehouse].[dbo].[sales_data] sales
INNER JOIN [social_lakehouse].[dbo].[social_data] social
ON sales.[product_id] = social.[product_id];
All the Warehouses that share the same workspace are integrated into the same logical SQL server. If you use SQL client tools such as SQL Server Management Studio, you can easily perform a cross-database query like in any SQL Server instance.
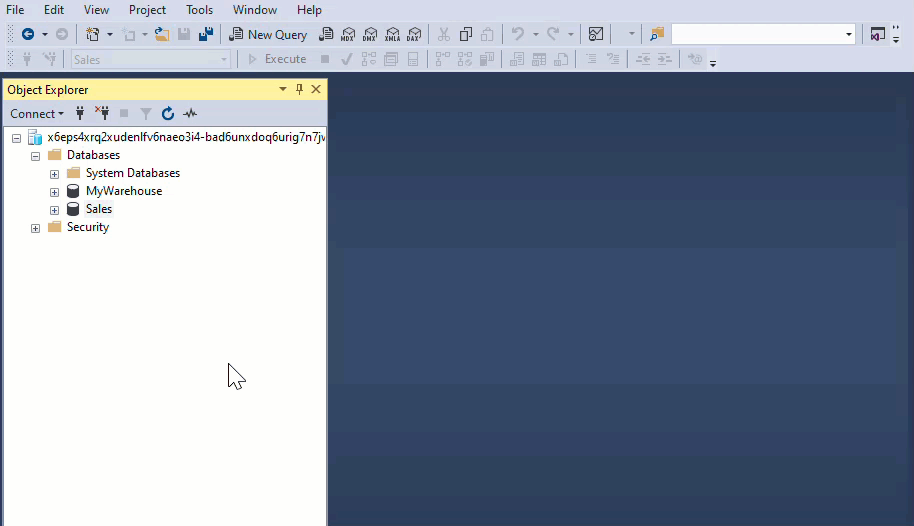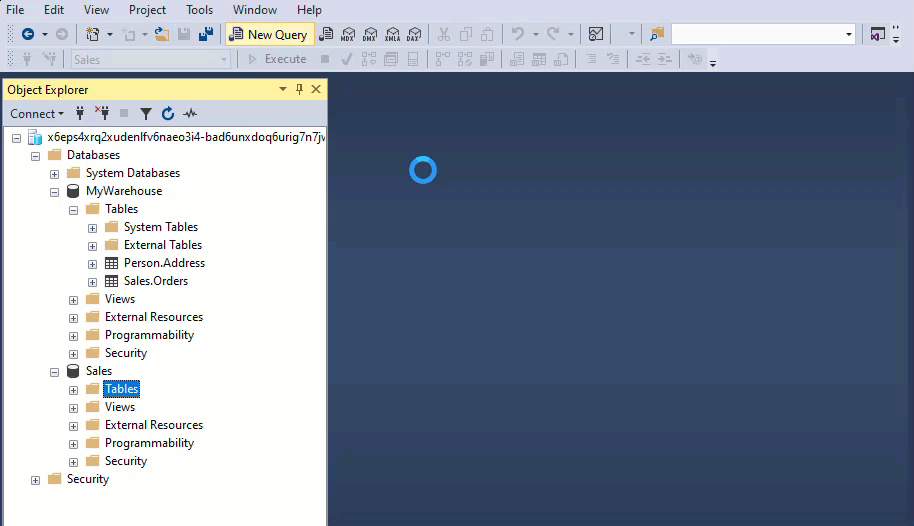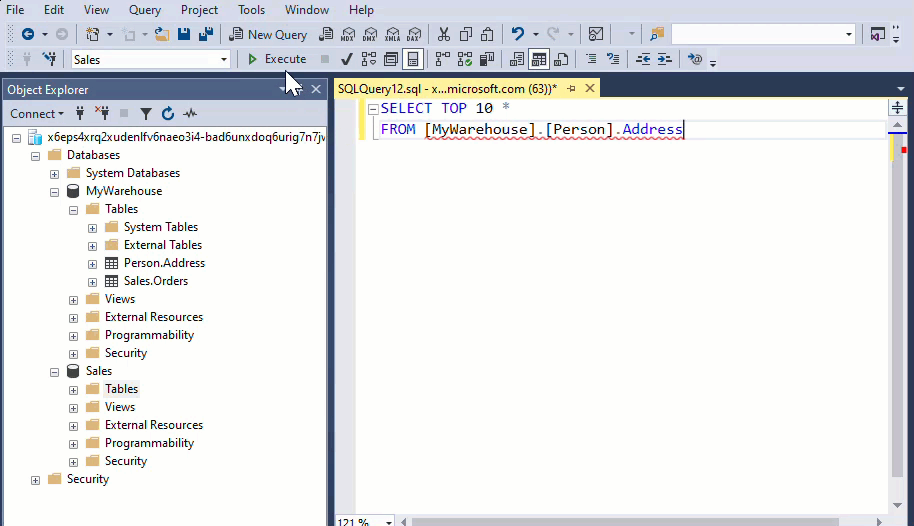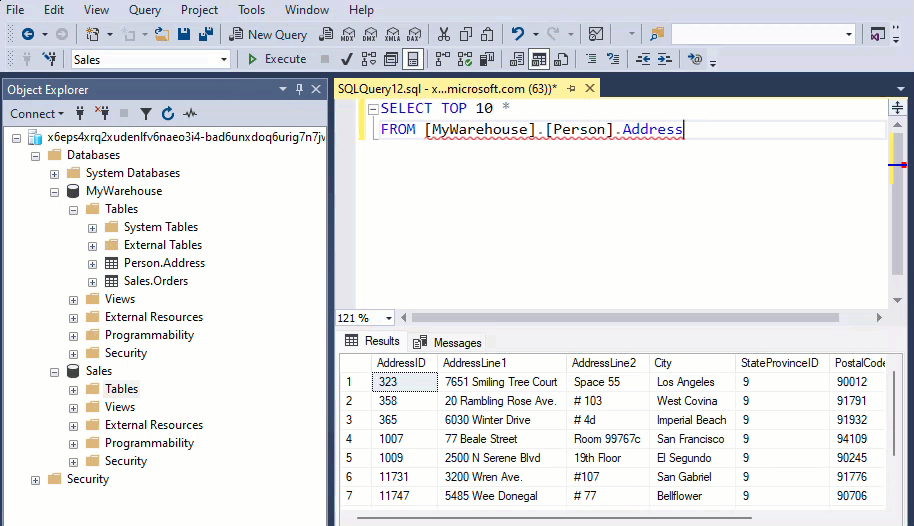
MyWarehouse and Sales are both warehouse assets that share the same workspace.
If you’re using the object Explorer from the workspace to query your Warehouses, you need to add them explicitly. The warehouses added will also be visible from the Visual query editor.
When using T-SQL, data can be efficiently loaded into a warehouse in Microsoft Fabric through the COPY statement, or from other warehouses and lakehouses within the same workspace, allowing for seamless data management and analysis.