Implement ESAE forests
As IT environments expand beyond the boundaries of internal networks, the role of identity as a security perimeter becomes increasingly important. One way to enhance its security capabilities is to implement the ESAE forest model, which is what Contoso is planning to do in the upcoming months.
What is ESAE forest?
ESAE forests represent an architectural approach in which a dedicated administrative Active Directory forest hosts privileged accounts, privileged groups, and privileged access workstations. This ESAE forest is configured with a one-way trust relationship with a production forest. A one-way trust relationship means that accounts from the ESAE forest can be used in the production forest, however, accounts in the production forest can't be used in the ESAE forest. A production forest is a forest in which administrators perform an organization’s day-to-day activities. The production forest is then configured so that administrative tasks in the production forest can be performed only by using accounts that the ESAE forest hosts.
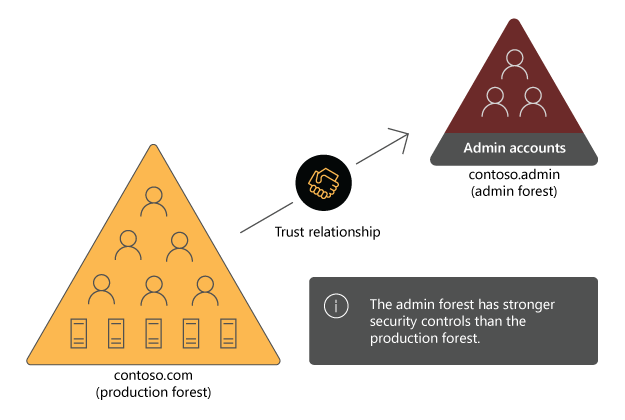
ESAE forests have the following benefits:
- Locked-down accounts. Standard nonprivileged user accounts in the ESAE forest can be configured as highly privileged in the production forest. For example, a standard user account in the ESAE forest is a member of the Domain Admins group in a domain in the production forest. It is possible to lock down the standard user account hosted in the ESAE forest so that it can't sign in to hosts in the ESAE forest and can only be used to sign in to hosts in the production forest. This design is more secure if an account is compromised while it is used in the production forest, because the malicious hacker can't use that account to perform administrative tasks in the ESAE forest.
- Selective authentication. ESAE forest design allows organizations to leverage the trust relationship’s selective authentication feature. For example, sign-ins from the ESAE forest will be restricted to specific hosts in the production forest. This is another method that helps limit credential exposure. For example, you can limit credential exposure when you configure selective authentication so that privileged accounts in the production forest can only be used on privileged access workstations or jump servers.
- Simple way to improve security. ESAE forest design provides substantive improvement in the security of existing production forests without requiring complete rebuilding of the production environment. The ESAE forest approach has a small hardware/software footprint and affects only IT Operations team users. In this design, standard user accounts remain hosted in the production forest. Only privileged administrative accounts are hosted in the ESAE forest. Because they are hosted in a separate forest, privileged administrative accounts can be subject to more stringent security requirements than standard user accounts in the production forest.
What is the clean-source principle?
The clean-source principle specifies that all security dependencies are as trustworthy as the item being secured. In the context of ESAE forests, the clean-source principle involves ensuring that all of the security accounts and workstations that are used are trustworthy.
The clean-source principle is an important aspect of security because, if a malicious hacker can control a security dependency, the hacker also can control the item being secured. One reason for using the ESAE forest design approach is that it helps secure the privileged accounts that manage the production environment.
When securing the ESAE forest, ensure that ESAE domain controllers are running on a secure virtualization fabric and that security technologies such as device guard, credential guard, and BitLocker are in use. The clean-source principle also applies to installation media. If installation media is infected, then all software and operating systems that are deployed from that installation media are untrustworthy and at risk for control by the hacker. Software obtained from vendors through physical media needs to be validated. Software downloaded from the Internet should be checked against vendor-provided file hashes to ensure that it hasn't been tampered with by unauthorized third parties.
Tip
You can use the certutil.exe command, built into the Windows operating system, to compare a downloaded file with the hash file that the vendor provided.
Implementing ESAE forests
You should consider several factors when implementing an ESAE forest. An ESAE forest should have the following properties:
- Limit the function of the ESAE forest to hosting accounts of administrative users for the production forest. To keep the hacker surface minimized, don't deploy applications or additional resources in the ESAE forest.
- The ESAE forest should be a single-domain Active Directory forest. There is no need for multiple domains in an ESAE forest. The ESAE forest hosts only a few accounts to which strict security policies must be applied.
- Only use one-way trusts. You should only configure a one-way trust where the production forest trusts the ESAE forest. This means that accounts from the ESAE forest can be used in the production forest, however, accounts from the production forest can't be used in the ESAE forest. Accounts used for administrative tasks in the production forest should be standard user accounts in the ESAE forest. If an account is compromised in the production forest, it can't be used to elevate privileges in the ESAE forest.
The ESAE forest servers need to be configured in the following ways:
- Installation media should be validated.
- Servers should run the most recent version of the Windows Server operating system.
- Servers should be updated automatically with security updates.
- Security Compliance Manager baselines should be used as the starting point for server configuration.
- Servers should be configured with Secure Boot, BitLocker volume encryption, Credential Guard, and Device Guard.
- Servers should be configured to block USB storage.
- Servers should be on isolated networks. Inbound and outbound Internet connections should be blocked.