Understand external configuration store patterns
External configuration store patterns persist configuration information in dedicated external infrastructure providing efficient interfaces for configuration reading and modification operations.
External store selection depends on application hosting and runtime environment characteristics.
Cloud-hosted deployments typically leverage cloud storage services, though hosted database implementations or alternative backing stores remain viable options.
Configuration backing store architectures require interfaces providing consistent, accessible configuration retrieval exposing correctly typed, structured information.
Implementation requirements include user access authorization protecting configuration data and flexible multi-version configuration storage supporting development, staging, and production environments with corresponding release version differentiation.
Traditional configuration systems load data during application initialization implementing in-memory caching for rapid access minimizing application performance impact.
Backing store latency characteristics may necessitate external configuration store caching mechanisms optimizing configuration retrieval performance.
For more information, see the Caching Guidance. The figure illustrates an overview of the External Configuration Store pattern with optional local cache.
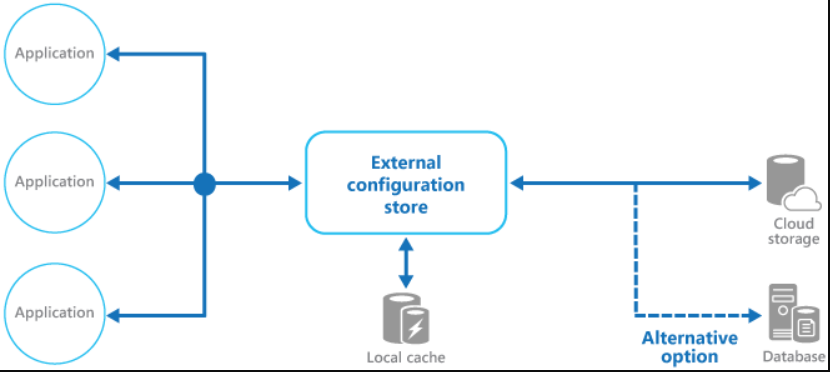
External configuration store pattern applicability:
- Cross-application configuration sharing: Multiple applications and application instances require shared configuration settings or standardized configuration enforcement across distributed application portfolios.
- Extended configuration capabilities: Standard configuration systems lack support for specialized configuration requirements including image storage or complex data type persistence.
- Hybrid configuration strategies: Complementary configuration store implementations enable applications to override centrally stored settings with application-specific configurations.
- Centralized administration and monitoring: Simplified multi-application administration with optional configuration access logging supporting audit and compliance requirements.