Examine the end-user experience with Safe Links
When a user selects a link in an email and Safe Links later identifies the target web site as malicious, the Safe Links process automatically warns the user. Here's a summary of how Safe Links works in email:
- Someone sends a user an email message that contains a URL to a web site.
- The message flows through the anti-malware pipeline. Assuming the message passes through all the initial checks, it eventually arrives in the recipient’s inbox.
- The user opens the message and selects the link.
- When the user selects the link, Safe Links redirects the URL to a secure server that checks the URL against a blocklist of known malicious web sites.
- If the link is safe, the user’s browser navigates to the target web site.
- If the link is malicious, the user’s browser displays a warning page.
Now consider the scenario when a user receives a message from an external sender that contains two URLs, one to the malicious www.spamlink.contoso.com site and another to the legitimate www.bing.com site.
The user selects the
www.spamlink.contoso.comlink. The user doesn't know that this URL is a phishing link the service previously identified as malicious.The organization’s Safe Links policy detects the link and redirects it to the secure server in Microsoft 365. The secure server determines the URL is malicious.
Because the link is malicious, Safe Links redirects the user to a protective shell. The shell alerts the user about the classification of the URL (see the following graphic).
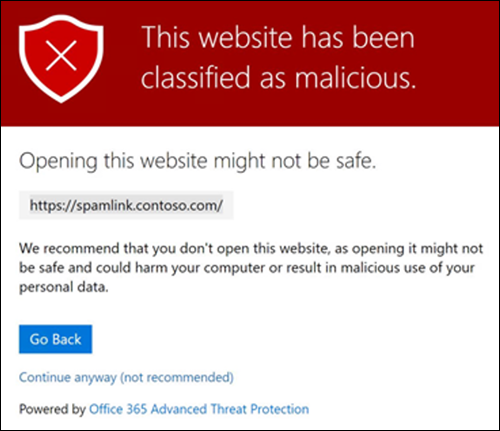
The policy is selective enough to remove only the malicious link. When the user selects the link to www.bing.com, the user is successfully able to navigate to Bing.com as expected.
Note
The sample web page, as shown in the prior image, includes the option to continue to the site (although not recommended). This text indicates the administrator who created the policy selected this option to let users select through to the original URL. Had the administrator not selected this option, this text wouldn't have appeared on the page.
URL detonation end-user experience
URL detonation combines elements of Safe Links and Safe Attachments into a single feature. This feature is designed to protect users in the event a URL points to a malicious file on a web site.
When you select the link, the system downloads the file into the Safe Attachments sandbox environment and detonates it just like an attachment. During this process, the system redirects the recipient to a warning page like the one in the following screenshot. It also informs the user the system is scanning the file for malicious content.
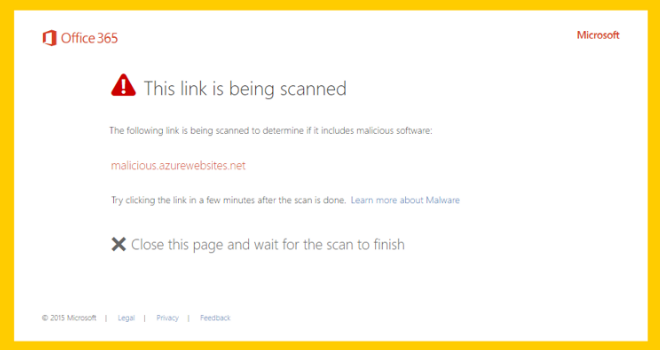
If the system ultimately determines the file is malicious, it redirects the user to the warning page like the one in the previous screenshot. The warning page advises the user the site is malicious.
Knowledge check
Choose the best response for the following question. Then select “Check your answers.”