Monitor system health by using Syslog Server
This unit shows you how to use syslog to integrate Azure Stack Hub infrastructure with external security solution(s) already deployed in your datacenter. For example, a security information event management (SIEM) system. The syslog channel exposes audits, alerts, and security logs from all the components of the Azure Stack Hub infrastructure. Use syslog forwarding to integrate with security monitoring solutions and to retrieve all audits, alerts, and security logs to store them for retention.
Azure Stack Hub has an integrated syslog client that, once configured, emits syslog messages with the payload in Common Event Format (CEF).
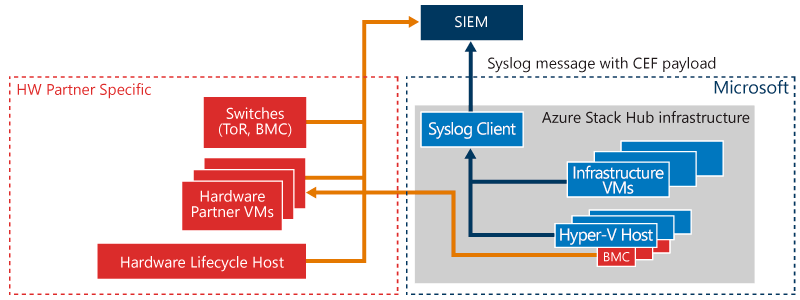
The following diagram describes the integration of Azure Stack Hub with an external SIEM. There are two integration patterns that need to be considered: the first one (the one in blue) is the Azure Stack Hub infrastructure that encompasses the infrastructure virtual machines and the Hyper-V nodes. All the audits, security logs, and alerts from those components are centrally collected and exposed via syslog with CEF payload. This integration pattern is described in this document page. The second integration pattern is the one depicted in orange and covers the baseboard management controllers (BMCs), the hardware lifecycle host (HLH), the virtual machines, and virtual appliances that run the hardware partner monitoring and management software, and the top of rack (TOR) switches. Since these components are hardware-partner specific, contact your hardware partner for documentation on how to integrate them with an external SIEM.
Configuring syslog forwarding
The syslog client in Azure Stack Hub supports the following configurations:
- Syslog over TCP, with mutual authentication (client and server) and TLS 1.2 encryption: In this configuration, both the syslog server and the syslog client can verify the identity of each other via certificates. The messages are sent over a TLS 1.2 encrypted channel.
- Syslog over TCP with server authentication and TLS 1.2 encryption
- Syslog over TCP, with no encryption
- Syslog over UDP, with no encryption
Important
This unit addresses 1. Syslog over TCP, with mutual authentication (client and server) and TLS 1.2 encryption. Microsoft strongly recommends using TCP using authentication and encryption for production environments to protect against man-in-the-middle attacks and eavesdropping of messages.
Cmdlets to configure syslog forwarding
Configuring syslog forwarding requires access to the privileged endpoint (PEP). Two PowerShell cmdlets have been added to the PEP to configure the syslog forwarding:
### cmdlet to pass the syslog server information to the client and to configure the transport protocol, the encryption, and the authentication between the client and the server.
Set-SyslogServer [-ServerName <String>] [-ServerPort <UInt16>] [-NoEncryption] [-SkipCertificateCheck] [-SkipCNCheck] [-UseUDP] [-Remove]
### cmdlet to configure the certificate for the syslog client to authenticate with the server.
Set-SyslogClient [-pfxBinary <Byte[]>] [-CertPassword <SecureString>] [-RemoveCertificate] [-OutputSeverity]
Cmdlets parameters
Parameters for Set-SyslogServer cmdlet:
| Parameter | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| ServerName | FQDN or IP address of the syslog server. | String | Yes |
| ServerPort | Port number the syslog server is listening on. | UInt16 | Yes |
| NoEncryption | Force the client to send syslog messages in clear text. | flag | No |
| SkipCertificateCheck | Skip validation of the certificate provided by the syslog server during initial TLS handshake. | flag | No |
| SkipCNCheck | Skip validation of the Common Name value of the certificate provided by the syslog server during initial TLS handshake. | flag | No |
| UseUDP | Use syslog with UDP as transport protocol. | flag | No |
| Remove | Remove configuration of the server from the client and stop syslog forwarding. | flag | No |
Parameters for Set-SyslogClient cmdlet:
| Parameter | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| pfxBinary | The contents of the pfx file, piped to a Byte[], containing the certificate to be used by the client as identity to authenticate against the syslog server. | Byte[] |
| CertPassword | Password to import the private key that's associated with the pfx file. | SecureString |
| RemoveCertificate | Remove certificate from the client. | flag |
| OutputSeverity | Level of output logging. Values are Default or Verbose. Default includes severity levels: warning, critical, or error. Verbose includes all severity levels: verbose, informational, warning, critical, or error. | String |
Configuring syslog forwarding with TCP, mutual authentication, and TLS 1.2 encryption
In this configuration, the syslog client in Azure Stack Hub forwards the messages to the syslog server over TCP, with TLS 1.2 encryption. During the initial handshake, the client verifies that the server provides a valid, trusted certificate. The client also provides a certificate to the server as proof of its identity. This configuration is the most secure as it provides a full validation of the identity of both the client and the server and it sends messages over an encrypted channel.
To configure syslog forwarding with TCP, mutual authentication, and TLS 1.2 encryption, run both these cmdlets on a PEP session:
# Configure the server
Set-SyslogServer -ServerName <FQDN or ip address of syslog server> -ServerPort <Port number on which the syslog server is listening on>
# Provide certificate to the client to authenticate against the server
Set-SyslogClient -pfxBinary <Byte[] of pfx file> -CertPassword <SecureString, password for accessing the pfx file>
The client certificate must have the same root as the one provided during the deployment of Azure Stack Hub. It also must contain a private key.
##Example on how to set your syslog client with the certificate for mutual authentication.
##This example script must be run from your hardware lifecycle host or privileged access workstation.
$ErcsNodeName = "<yourPEP>"
$password = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "<your cloudAdmin account password" -AsPlainText -Force
$cloudAdmin = "<your cloudAdmin account name>"
$CloudAdminCred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ($cloudAdmin, $password)
$certPassword = $password
$certContent = Get-Content -Path C:\cert\<yourClientCertificate>.pfx -Encoding Byte
$params = @{
ComputerName = $ErcsNodeName
Credential = $CloudAdminCred
ConfigurationName = "PrivilegedEndpoint"
}
$session = New-PSSession @params
$params = @{
Session = $session
ArgumentList = @($certContent, $certPassword)
}
Write-Verbose "Invoking cmdlet to set syslog client certificate..." -Verbose
Invoke-Command @params -ScriptBlock {
param($CertContent, $CertPassword)
Set-SyslogClient -PfxBinary $CertContent -CertPassword $CertPassword }