Model-driven app data model
It's important that you make sure that the data model is structured properly before you make the app. Model-driven apps automatically generate a user interface (UI) that's responsive across devices. The success of the model-driven app relies heavily on how the data is modeled in Dataverse.
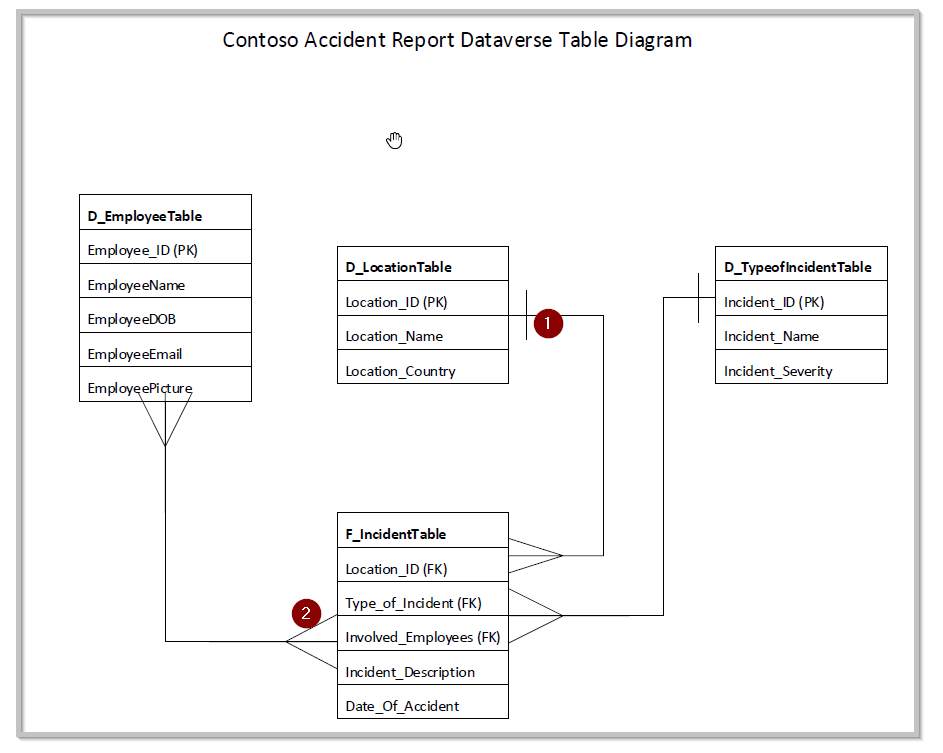
You might find it helpful to visualize the flow of your data in a picture diagram. You can use any tool of your choice such as Visio or Excel, or you can draw it out. The following image is a representation of how the tables in your data model are related to each other. Certain concepts are discussed in this section, such as one-to-many relationships, that will become clearer as you build the app.
In the preceding image, number one represents a one-to-many relationship, and number two represents a many-to-many relationship.
As indicated in the diagram, you'll be creating four different tables in Dataverse to be the base for your model-driven app data model. Additionally, you'll add the following elements to the app:
A many-to-many relationship from the employee table (D_EmployeeTable) to your main accident table (F_IncidentTable). The reason is because an employee can be associated with multiple accidents, and an accident can involve more than one employee.
A one-to-many relationship from the location table (D_LocationTable) to your main accident table (F_IncidentTable). The reason is because, in this scenario, an accident can only happen in one location at a time
A one-to-many relationship from the type of accident table (D_TypeofIncidenttable) to your main accident table (F_IncidentTable). The reason is because, in this scenario, an accident can only be of one defined type.
Note
A many-to-one relationship is the inverse of a one-to-many relationship.
When designing these relationships, you might find the process simpler if you to put it into words by answering the following questions:
Can an accident involve more than one employee?
How many locations can an accident occur in?
Can one accident include more than one type of accident?
Also, you can track as much information as applicable in those tables (metadata). For this module's scenario, you'll keep it simple.