Introduction
Azure Cosmos DB is Microsoft's fully managed NoSQL database on Azure. As a NoSQL database, Azure Cosmos DB is both horizontally scalable and nonrelational.
Horizontal scalability allows Azure Cosmos DB support data sizes well beyond that of a typical relational database. Horizontal scalability also means that the database provides predictable performance.
To achieve this level of scalability, users need to understand the concepts, techniques unique to NoSQL databases for modeling and partitioning data.
Scenario
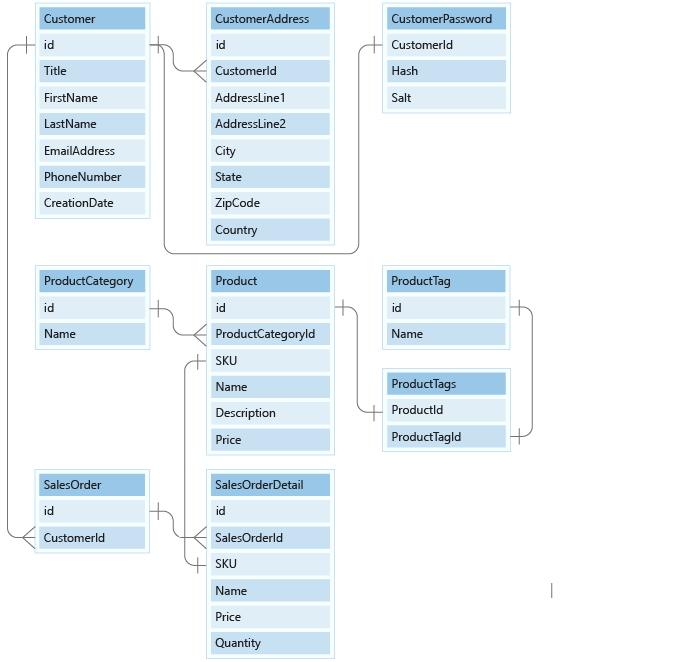
Imagine that you work for a retail startup that's designing a database to manage online orders. You're working on a proposal for an efficient database design using Cosmos DB core (SQL) API. You've been provided an entity-relationship model to start from. You want to provide the maximum scalability, performance, and efficiency possible and to achieve this, the data will need to be modeled correctly.
The following entity-relationship diagram (ER model) provides you with the details of the nine entities you will be working with. The relational model has nine entities in their own tables.
What will we be doing?
In this module, we'll take our existing relational data model and redesign it as a NoSQL database for our e-commerce application. During this process, you'll learn the following concepts:
- Differences between relational versus NoSQL databases: You'll explore some of the differences between NoSQL databases and relational databases and why they are that way.
- Using application data access patterns to model data: You'll learn how understanding the way an application reads and writes data influences how to model it for a NoSQL database.
- Embedding versus referencing: You'll learn when you should embed data within the same document versus when you should store data as a separate document.
- Choosing a partition key: You'll learn key concepts needed for choosing the best partition key to avoid hot partitions and optimize workloads that are either read or write heavy, or both.
- Modeling lookup or reference data: Finally, you'll learn how to model data that's used as a lookup or reference for other data.
What is the main goal?
When you finish this module and the companion module, "Optimize your database by using advanced modeling patterns for Azure Cosmos DB," you'll have the knowledge and skills to properly model and partition data for a NoSQL database deployed on Azure Cosmos DB.
After completing this module, you’ll be able to:
- Determine access patterns for data.
- Apply data model and partitioning strategies to support an efficient and scalable NoSQL database.