Describe concepts around Azure Automanage best practices
Caution
This content references CentOS, a Linux distribution that is End Of Life (EOL) status. Please consider your use and plan accordingly. For more information, see the CentOS End Of Life guidance.
Azure Automanage machine best practices eliminates the need to discover and know how to onboard and configure certain Azure services to benefit your virtual machines. These Azure services help enhance reliability, security, and management for virtual machines.
Azure Automanage machine best practices provide the following benefits:
- Intelligently onboards virtual machines to select best practices Azure services
- Automatically configures each service per Azure best practices
- Supports customization of best practice services
- Monitors for drift and corrects for it when detected
- Provides a simple experience (point, select, set, forget)
Both Windows Server and Linux virtual machines can use Azure Automanage. Azure Automanage can even be used on Arc-enabled servers to extend these best practices services to machines hosted outside of Azure.
Participating services
After onboarding your machines to Azure Automanage, each best practice service is configured to its recommended settings. The following diagram shows the types of services that can be configured for your virtual machines using Azure Automanage best practices.
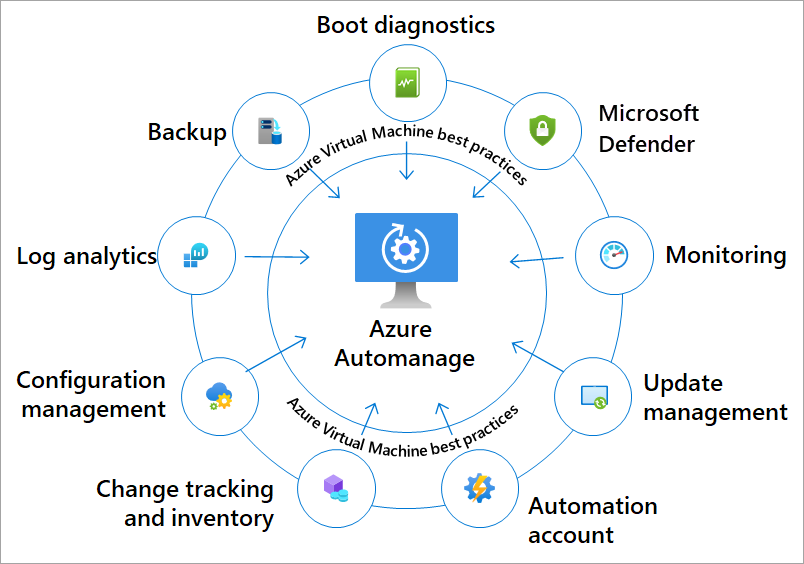
Your VMs are automatically onboarded to these participating services when you use the best practices configuration profiles. Following is a list of participating services:
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| VM Insights Monitoring | Azure Monitor for VMs monitors the performance and health of your virtual machines, including their running processes and dependencies on other resources. |
| Backup | Azure Backup provides independent and isolated backups to guard against unintended destruction of the data on your VMs. |
| Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a unified infrastructure security management system. It strengthens the security posture of your data centers, and provides advanced threat protection across your hybrid workloads in the cloud. |
| Microsoft Anti-malware | Microsoft Anti-malware for Azure is a free real-time protection that helps identify and remove viruses, spyware, and other malicious software. It generates alerts when known malicious or unwanted software tries to install itself or run on your Azure systems. |
| Update Management | You can use Update Management in Azure Automation to manage operating system updates for your virtual machines. You can quickly assess the status of available updates on all agent machines and manage the process of installing required updates for servers. |
| Change Tracking & Inventory | Combines change tracking and inventory functions to allow you to track virtual machine and server infrastructure changes. |
| Azure Automanage Machine Configuration | Azure Automanage Machine Configuration is used to monitor the configuration and report on the compliance of the machine. |
| Azure Automation Account | Azure Automation supports management throughout the lifecycle of your infrastructure and applications. |
| Log Analytics Workspace | Azure Monitor stores log data in a Log Analytics workspace, which is an Azure resource and a container where data is collected and aggregated. |
Configuration profiles
Configuration profiles are the foundation of Azure Automanage best practices. They define which services are onboarded for your machines and, to some extent, what the configuration of those services are.
If you want to customize the best practice services and settings, you can use the custom profile option. Custom profiles allow you to customize the services and settings you want to apply to your machines. This option is useful when your IT requirements differ from the best practices. For instance, if your IT organization requires you to use an anti-malware solution other than the Microsoft Anti-malware solution, you can toggle off Microsoft Anti-malware when creating a custom profile.
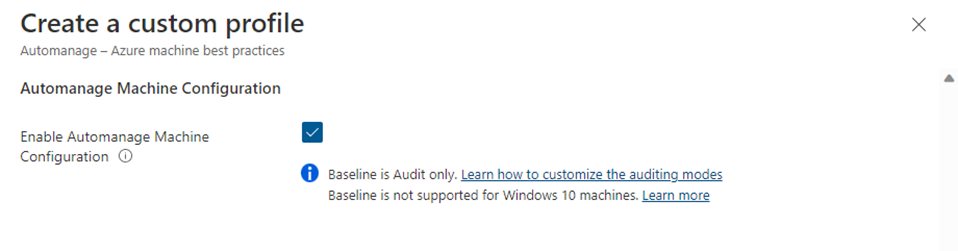
Automanage Machine Configuration
Automanage Machine Configuration provides native capability to audit or configure operating system settings as code, both for machines running in Azure and hybrid Arc-enabled machines. The feature can be used directly per-machine, or at-scale orchestrated by Azure Policy. As Automanage Machine Best Practices lets customers describe desired state for management services, Machine Configuration provides the same functionality within the actual resources.
When creating an Automanage Best Practices configuration profile, enable Machine Configuration either through creating a built-in profile or a custom profile.
Automanage machine statuses
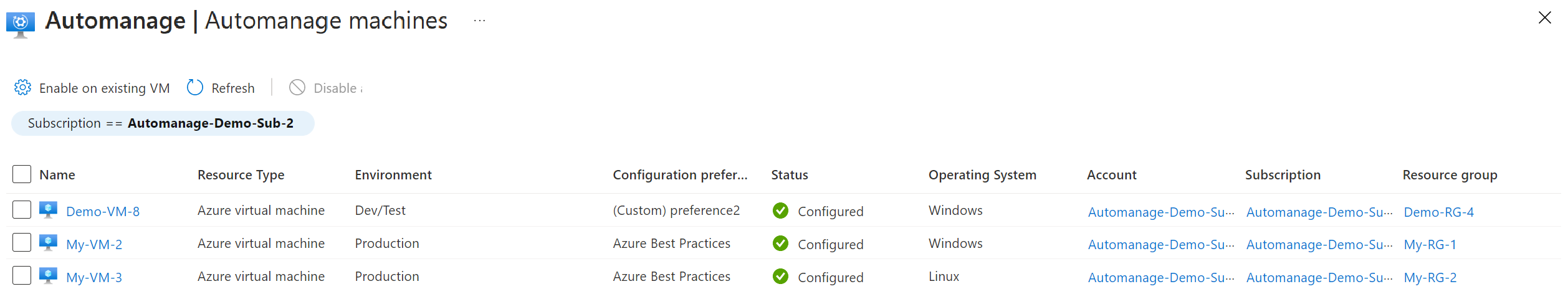
You can view the overall status of all your Azure Automanage machines from the Automanage machine best practices page in the Azure portal:
The page lists each of your Automanage machines, along with the configuration profile assigned to it and other information. The Status column displays the current state of the machine, informing you when a machine is properly configured and running normally or if it needs attention.
For example, when a machine is conformant with its assigned configuration profile, its status reads Conformant. When a machine drifts from the configuration profile, Automanage automatically brings it back into compliance.
Support for Linux VMs
Automanage supports the following Linux distributions and versions:
- CentOS 7.3+, 8
- RHEL 7.4+, 8
- Ubuntu 16.04, 18.04, 20.04
- SLES 12 (SP3-SP5 only), SLES 15
Next unit: Enable Azure Automanage best practices
Having an issue? We can help!
- For issues related to this module, explore existing questions using the #azure training tag or Ask a question on Microsoft Q&A.
- For issues related to Certifications and Exams, post on Certifications Support Forums or visit our Credentials Help.