Define Azure Arc
Azure Arc is a service that includes a set of technologies you can use to simplify Contoso's complex and distributed compute environment. You can use Azure Arc to provide Contoso with a centralized, unified, and self-service approach to managing their Kubernetes clusters.
Overview of Azure Arc
Azure Arc is a Microsoft Azure service offering that simplifies the management of complex and distributed environments. Azure Arc enables deployment of Azure services and extends Azure management to on-premises infrastructure, multiple clouds (including third-party clouds), and edge environments.
With Azure Arc, you can extend Azure's robust management capabilities into hybrid environments. For example, you can use Azure Arc to manage and configure Windows servers, Linux servers, and Kubernetes clusters that are hosted outside of Azure.
Regardless of where the managed resources are located, you can use Azure Arc to manage your IT resources with tools such as Azure Resource Manager, Azure Cloud Shell, the Azure portal, and Azure Policy.
Specific services available in Azure Arc include:
- Servers
- Kubernetes clusters
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Data controllers
- Azure Stack HCI
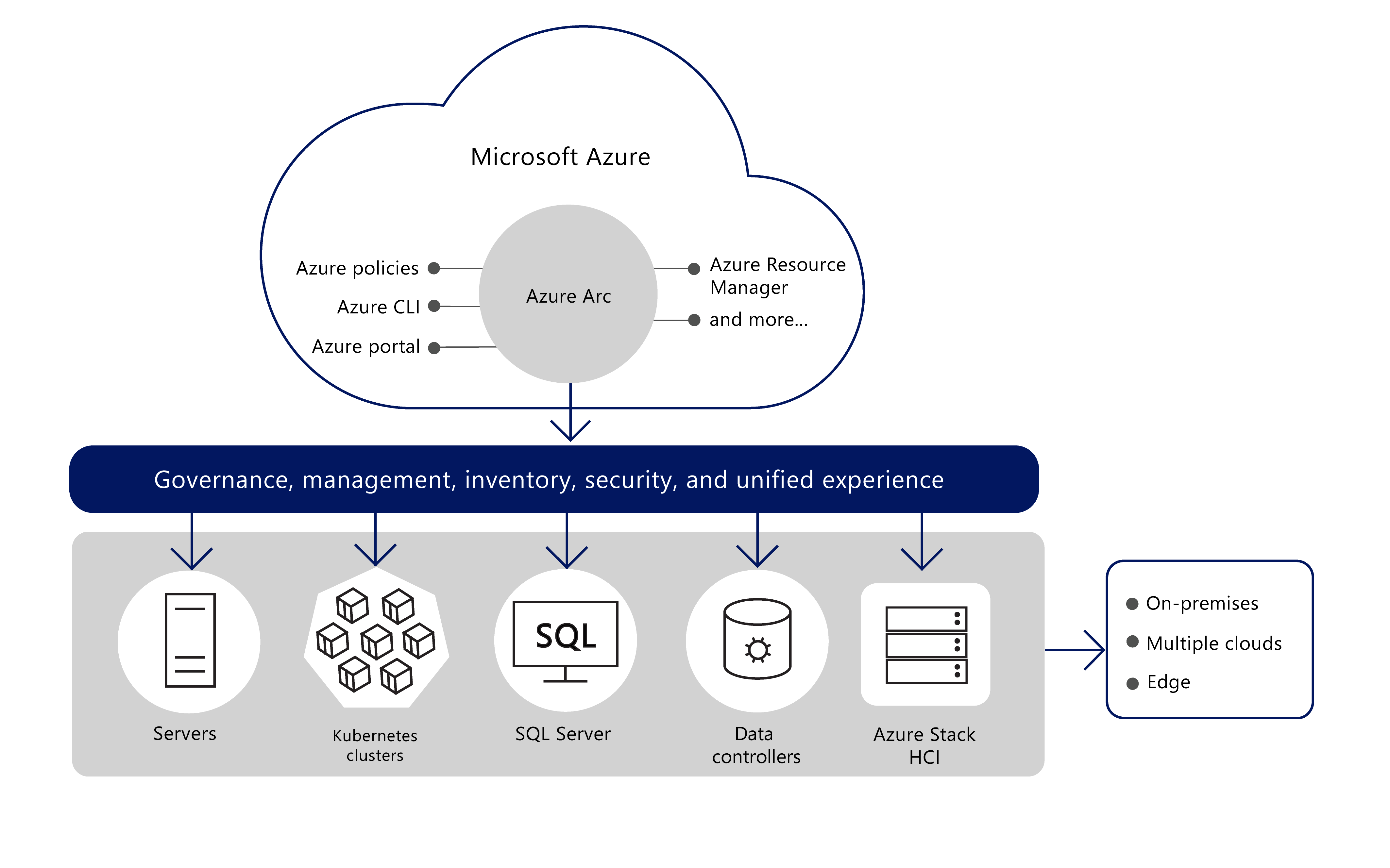
You can also use Azure Arc to extend your organization's DevOps practices, Azure security policies and Azure data services to on-premises, multiple cloud, and edge environments.
Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes
Azure Arc connects your Kubernetes clusters with Azure so you can manage your clusters effectively. With Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes, you can control your cluster configurations and workloads at scale from files that are stored in your Git repositories.
Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes brings an extensive range of Azure features to your Kubernetes clusters to improve how you manage inventory, monitoring, policy compliance, security, and user access.
Note
You can use Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes with any Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) certified Kubernetes cluster.
Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes consists of the following agents (operators) that run in your cluster that is deployed to the azure-arc namespace.
| Kubernetes agents (operators) | Description |
|---|---|
deployment.apps/config-agent |
Watches a connected cluster's source control configuration and updates its compliance state. |
deployment.apps/controller-manager |
Orchestrates interactions between Azure Arc components. |
deployment.apps/metrics-agent |
Collects Azure Arc performance metrics. |
deployment.apps/cluster-metadata-operator |
Gathers cluster metadata such as cluster version, node count, and Azure Arc agent version. |
deployment.apps/resource-sync-agent |
Synchronizes cluster metadata to Azure. |
deployment.apps/clusteridentityoperator |
Maintains the managed service identity (MSI) certificate for communicating with Azure. |
deployment.apps/flux-logs-agent |
Collects source control configuration logs. |
Benefits of Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes
With Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes, your clusters benefit from Azure management services such as:
- Azure portal
- Azure Resource Graph
- Azure Policy
- Azure Monitor
Azure Arc gives you greater control over your clusters. Each Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster benefits from:
- Having an assigned Azure Resource Manager ID.
- Using an Azure managed identity.
- Being located within an Azure resource group and subscription.
- Appearing in the Azure portal.
- Being able to be managed like other Azure resources. For example, it can be tagged for inventory management.
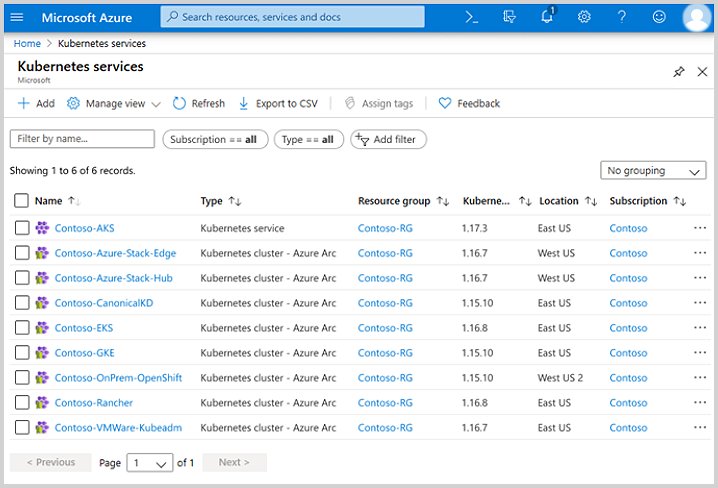
At minimum, you can implement Azure Arc in your Kubernetes clusters to review the inventory of your complete Kubernetes estate, and then group and tag your clusters for finer-grained inventory management. In addition, you can use:
- GitOps-based configuration management to deploy applications and configure the clusters.
- Azure Policy for Kubernetes to enforce run-time policies in your Kubernetes clusters.
- Azure Monitor for containers to consistently monitor all your clusters.