File actions
Working with files is similar to working with folders. File and folder operations are similar, and the file-related actions require the file or folder to be specified by providing its path.
To get a list of all files in a specified folder, you can use the Get files in folder action. This action works similarly to the Get subfolders in folder action. The path of the folder is a required input and you can specify it as a variable.
Optionally, you can filter files by using the File filter action. Add keywords, along with the asterisk (*) wildcard character, and separate multiple terms with a semicolon (;). You can look in subfolders by selecting the Include subfolders action.
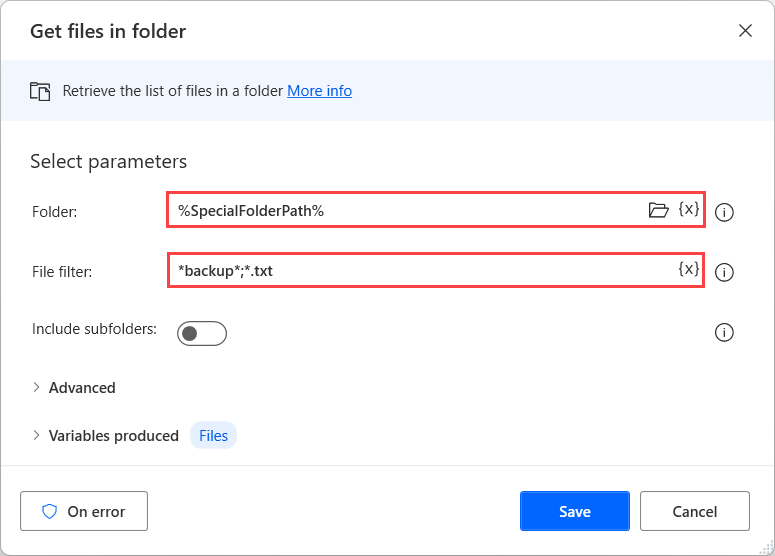
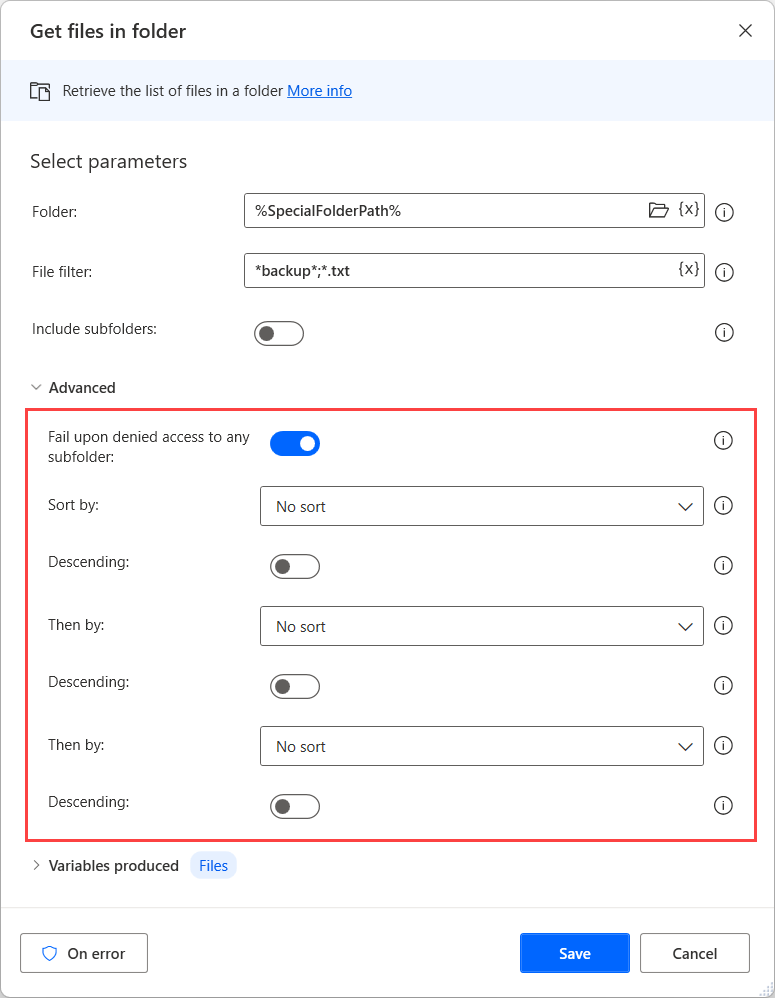
Similar to the Get subfolders in folder action, you can sort the output and set the action to Fail upon denied access to any subfolder in the Advanced section.
Tip
For example, if the file filter is set to *backup*; *.txt, all text files (with the extension .txt) and the files whose names contain the string backup will be stored in the list of files.
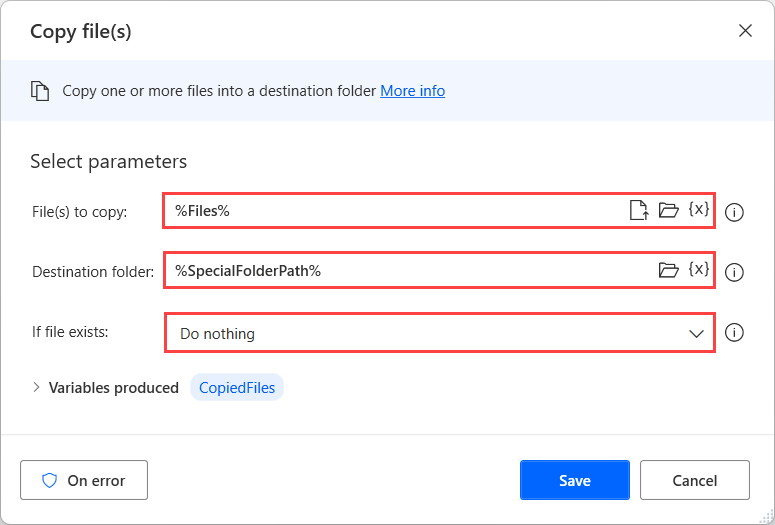
To copy or move files, use the Copy file(s) and Move file(s) actions, respectively. These actions take as input a file, or a list of files, and a destination folder. Set If file exists to Overwrite or Do nothing.
To delete files, use the Delete file(s) action, which requires the file or list of files as input.
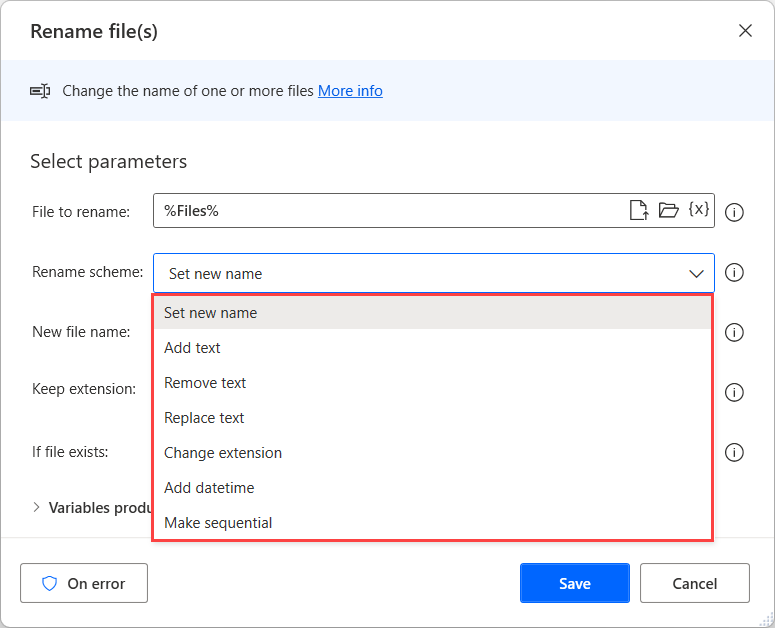
Rename files in a batch for grouping or organization purposes to ensure that they correctly adhere to a certain naming convention by using the Rename files action. This action contains a variety of ways to dynamically alter a file name. As with the previous actions, the required input is a file or list of files. Additional requirements depend on the option that is selected in the Rename scheme drop-down menu.
For example, the Set new name option requires a new name with the option to remove the extension. The Replace text option requires the text that you want to replace and the text to replace it with.
Changing the extension requires that you specify the new extension. If a file with the new name that you have specified exists, you can choose to overwrite it or to perform no action at all.
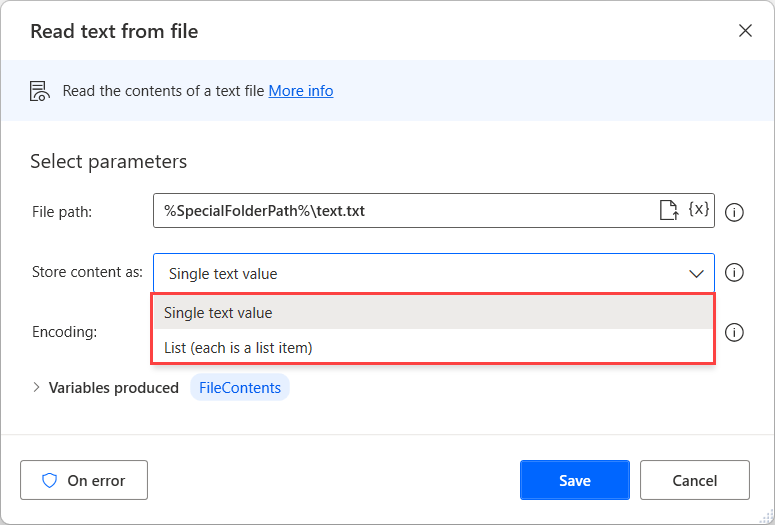
To perform file-related operations based on the contents of a file, use the Read text from file action. This action stores text from a .txt file in a variable. The required input is a .txt file, and the file content is stored as a single text value or as a list. Select a list, and each line of text in the file will be an item in the list. Also, you can select the encoding of the input file from a list of options.
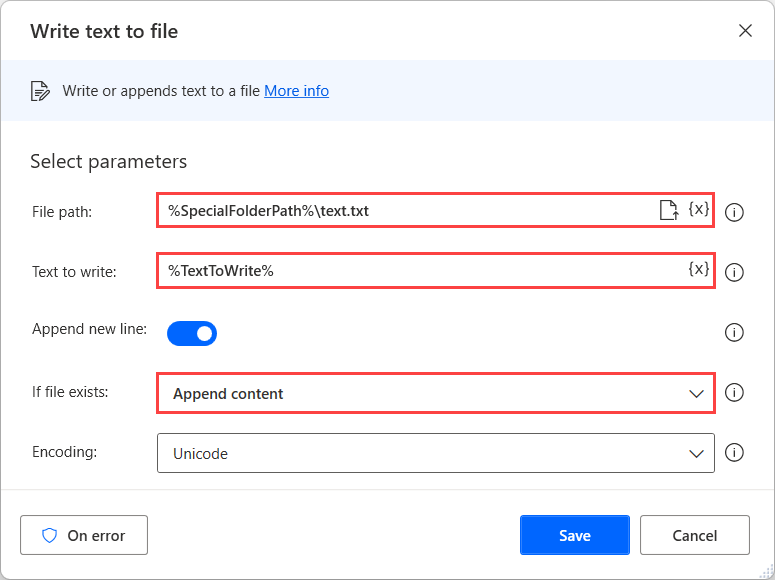
Use the Write text to file action to add text to a file or to create a new file with the specified text. This action requires the path for the text file and the text to append. You can also select to append a new line at the end of the written text. If the file exists, you can select to either overwrite the existing content or append it to the file.
Note
If you provide a path to a non-existent file in the File path field, a file will be created with the contents that are specified in the Text to write field.
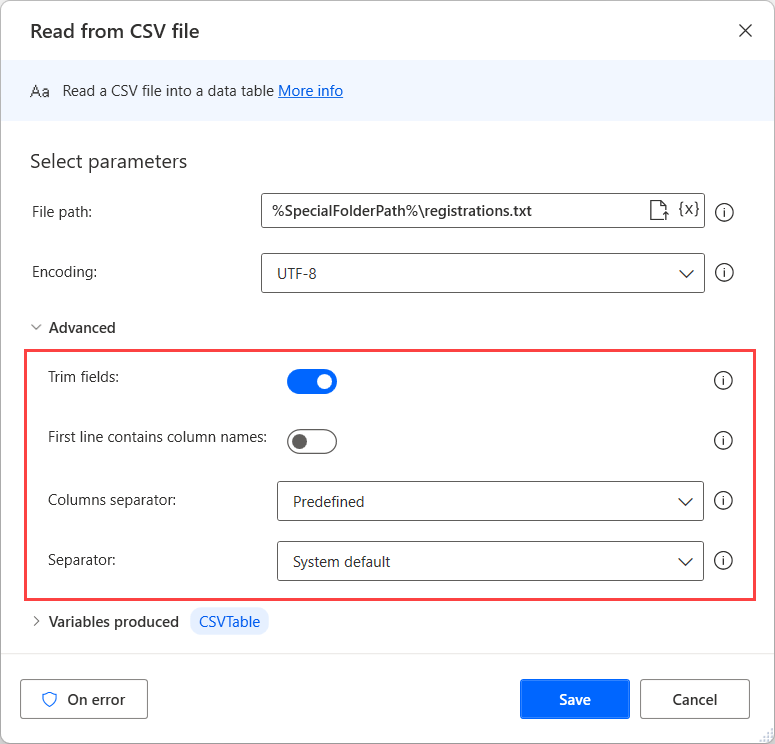
To read data from a comma-separated value (.csv) spreadsheet file, use the Read from CSV file action. The action requires the path to the .csv file and the encoding of the file. The output is a DataTable type variable with the contents of the .csv file.
The Advanced section includes multiple options for handling the data in the .csv file. Trim (remove whitespaces from the beginning and end) the value in each cell to ensure consistency of data and remove redundancy. If the First line contains column names check box is selected, the first line will not be stored in the output variable. Additionally, you can change the columns separator if a different symbol is used in the file.
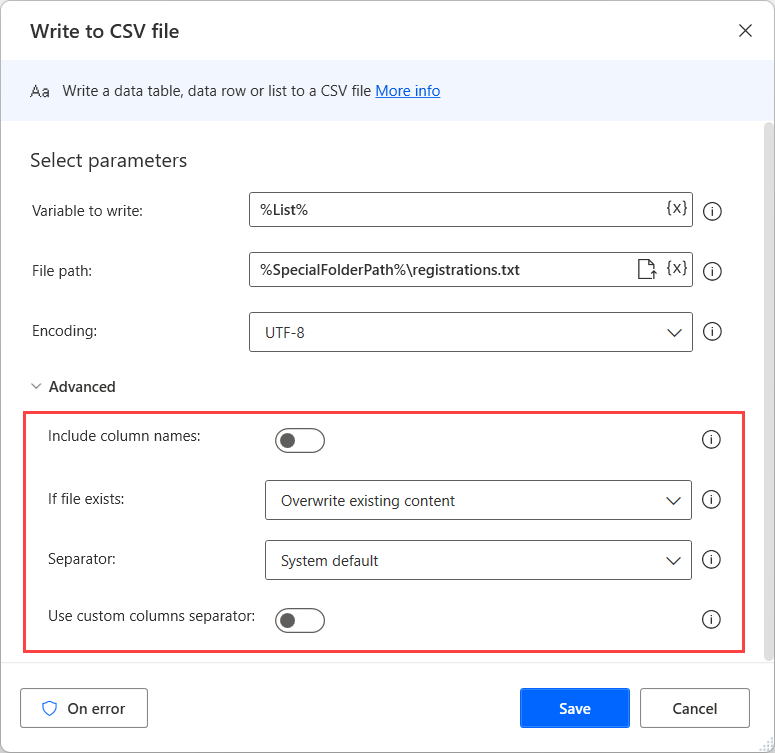
Write any DataRow or DataTable type variable to a .csv file with the Write to CSV file action. Specifying the path of the file and the variable to write are required inputs.
You can specify whether the first row of data includes column names and should not be written to the file. If a file with the same name exists, select to either overwrite or append the data, and then set the columns separator. These settings can be found in the Advanced section.
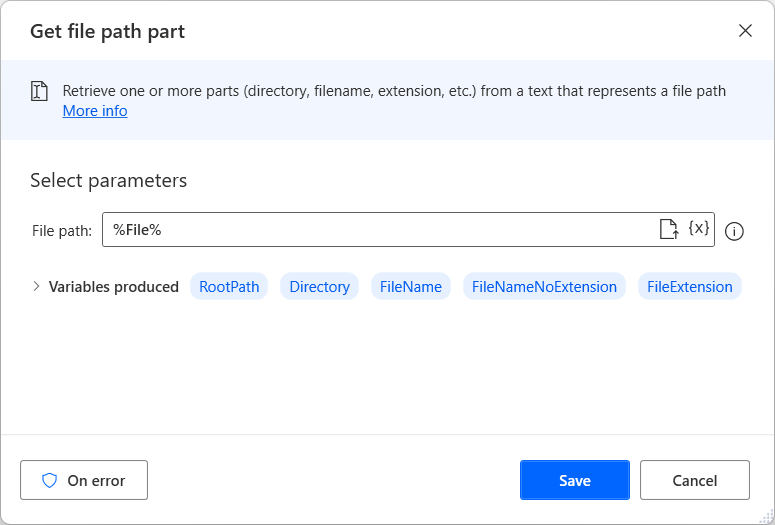
The Get filepath part action requires a file path as input and breaks it down into multiple components, which are all stored as variables.