Exercise - Create and run your notebook
A notebook is an interactive environment where you can both write code and document it. Notebooks can also display mathematical computations and charts.
Here, you'll create a local .ipynb file and run it in Visual Studio Code. The suffix .ipynb is used to refer to Jupyter notebooks, which were previously called iPython notebooks: ipynb.
Create a notebook
On your local computer, create a file called ship-manual.ipynb. You can create the file in the Explorer view or via the command palette in Visual Studio Code, by opening the palette and typing Create: New Jupyter Notebook. Open this file in Visual Studio Code. The Jupyter extension should display the file as blank, with the option to add code and Markdown blocks.
Create a document element in Markdown
At the top of the notebook, you see two options to create two different types of content blocks in the notebook: Markdown and runnable code. Your first task is to create a document title. At the top of the notebook interface in Visual Studio Code, select the plus (+) button next to Markdown. A box will appear. Add the following Markdown to the box:
# Ship's Instruction Manual
Run your notebook
Now you need to run your notebook. Choose a kernel from the dropdown list on the top right.
You might have one or several kernels to choose from, so make sure to choose a Python 3 kernel.
Select the tick to complete the Markdown field, and you'll find the text is rendered as an <h1>, or header text. You just named your notebook! To see how this Markdown file is rendered, choose run all from the top of the notebook.
Create runnable code
Now you can add some code to the notebook. Let's add a way to display a widget to start the ship's engine.
First, you need to install a library called ipywidgets. Install the library by adding a new code block under the notebook title block. Use Python's package manager, pip, to install the library.
Add this line to the new code block:
pip install ipywidgets.pip install ipywidgetsRun this block by using the arrow on the left to install the library.
Follow the installation prompts. You should see
ipywidgetsbeing installed. Wait for it to finish before continuing.Then, create a button right in your notebook that, when pressed, displays a message. In a new code block, add the following code:
import ipywidgets as widgets ignition = widgets.ToggleButton( value=False, description='Start Engine', button_style='success', tooltip='Engage your Engine', icon='rocket' ) output = widgets.Output() display(ignition, output) def on_value_change(change): with output: if change['new'] == True: print("engine started!") else: print("engine stopped") ignition.observe(on_value_change, names='value')Run the code by using the arrow on the left.
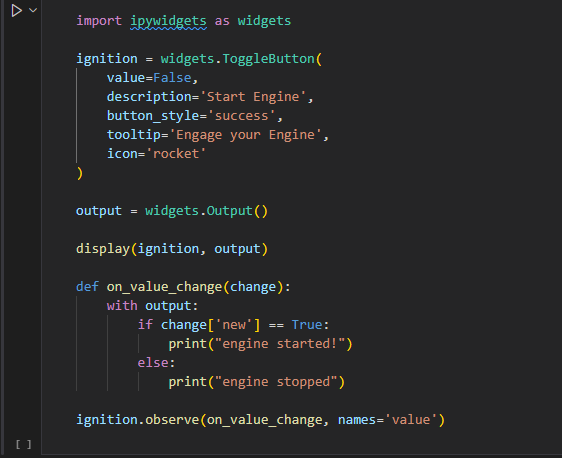
Your code should display a button:

Tip
If the button doesn't render, try changing to a different Python 3 kernel.
Press the button to start the engine.

Press the button again to stop the engine.

What's going on here? You use the ipywidget library to create a button, and listen for its value to change, printing the observed message. Now your manual is starting to look good, and you can start your ship's engine if it stalls!