Query relational data in Azure Database for MySQL
As with PostgreSQL, there are many tools available to connect to MySQL that enable you to create and run scripts of SQL commands. You can use the mysql command-line utility, which is also available in the Azure Cloud Shell, or you can use graphical tools from the desktop such as MySQL Workbench.
In this unit, you'll see how to connect to Azure Database for MySQL using MySQL Workbench.
Note
Currently there are no extensions available for connecting to MySQL from Azure Data Studio.
Retrieve connection information for Azure Database for MySQL
Like SQL Database and PostgreSQL, you require the name of the server, and the credentials for an account that has access rights to connect to the server. You can find the server name and the name of the default administrator account on the Overview page for the Azure Database for MySQL instance in the Azure portal. Contact your administrator for the password.
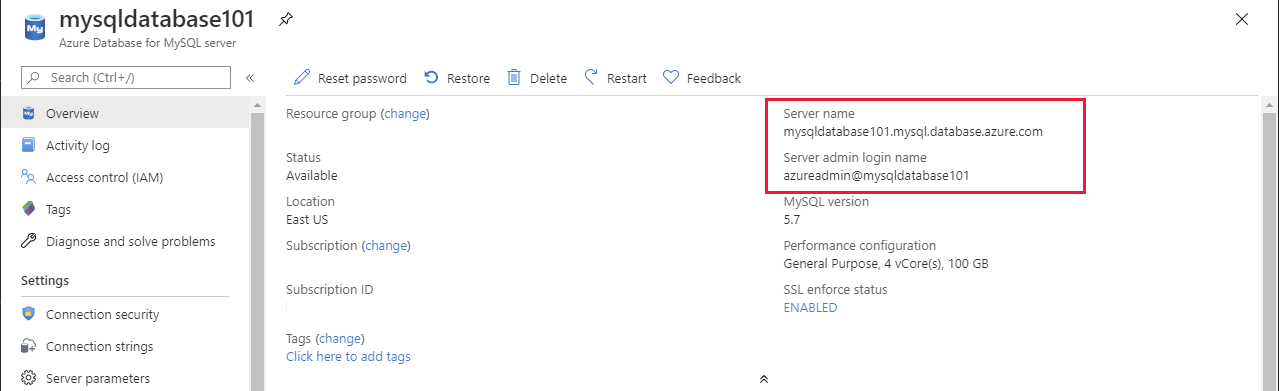
You must also open the MySQL firewall to enable client applications to connect to the service. For detailed information, see Azure Database for MySQL server firewall rules.
Use MySQL Workbench to query a database
You can download and install MySQL Workbench from the MySQL Community Downloads page.
To connect to Azure MySQL Server by using MySQL Workbench, perform the following steps:
Start MySQL Workbench on your computer.
On the Welcome page, select Connect to Database.
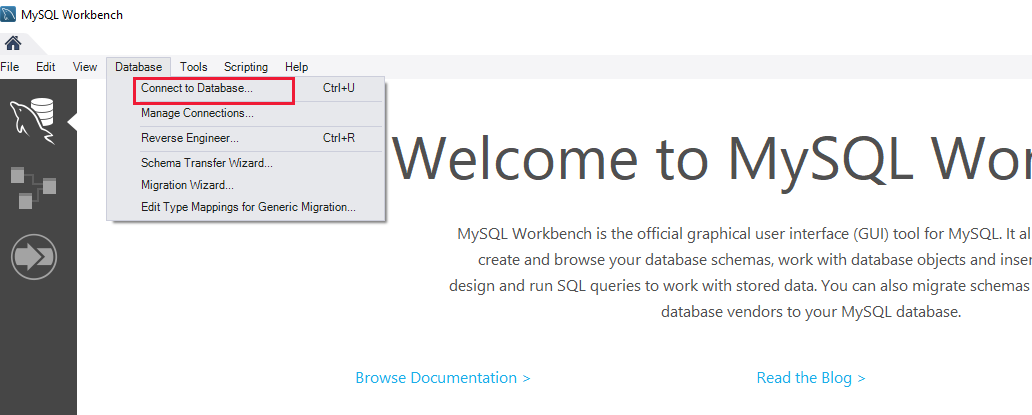
In the Connect to Database dialog box, enter the following information on the Parameters tab:
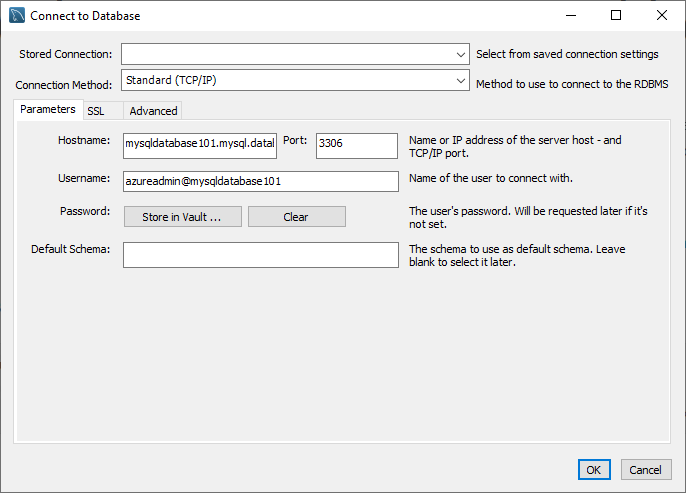
Setting Description Stored connection Leave blank Connection Method Standard (TCP/IP) Hostname Specify the fully qualified server name from the Azure portal Port 3306 Username Enter the server admin login username from the Azure portal, in the format <username><databasename> Password Select Store in Vault, and enter the administrator password specified when the server was created Select OK to create the connection. If the connection is successful, the query editor will open.
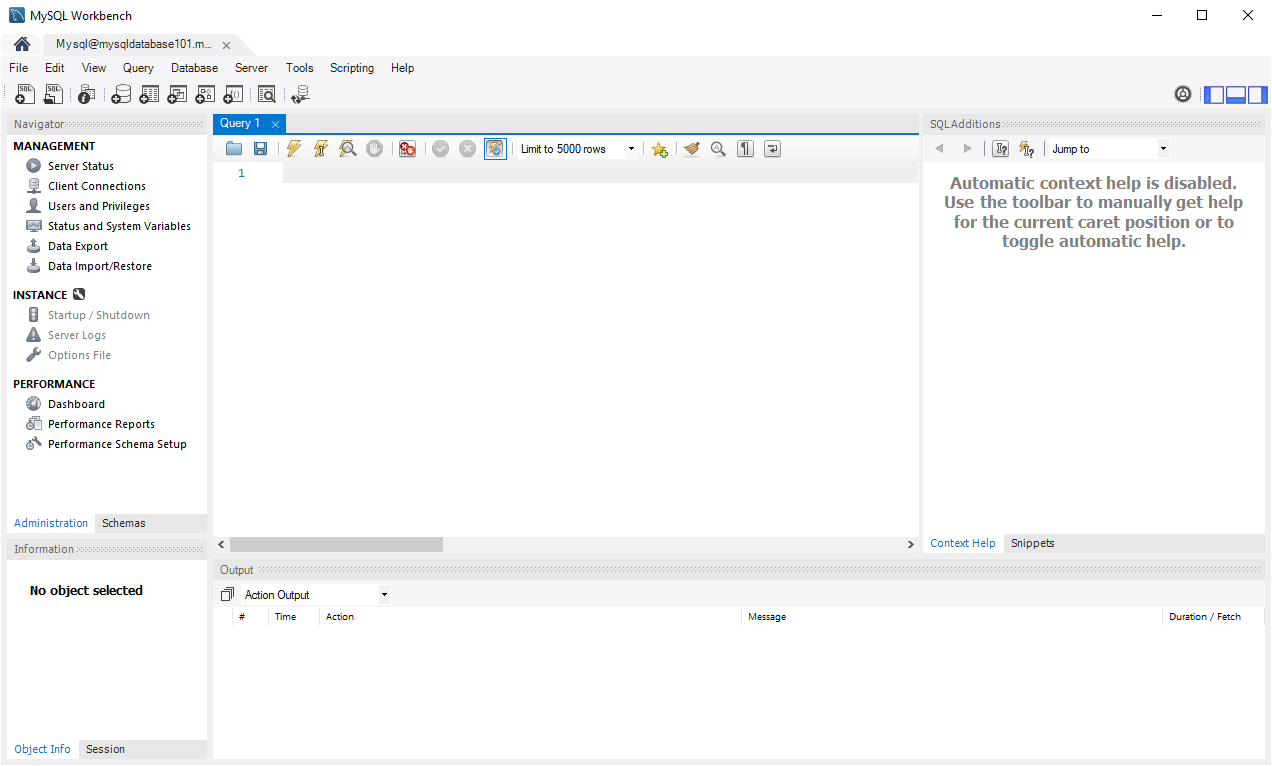
You can use this editor to create and run scripts of SQL commands. The following example creates a database named quickstartdb, and then adds a table named inventory. It inserts some rows, then reads the rows. It changes the data with an update statement, and reads the rows again. Finally it deletes a row, and then reads the rows again.
-- Create a database -- DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS quickstartdb; CREATE DATABASE quickstartdb; USE quickstartdb; -- Create a table and insert rows DROP TABLE IF EXISTS inventory; CREATE TABLE inventory (id serial PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(50), quantity INTEGER); INSERT INTO inventory (name, quantity) VALUES ('banana', 150); INSERT INTO inventory (name, quantity) VALUES ('orange', 154); INSERT INTO inventory (name, quantity) VALUES ('apple', 100); -- Read SELECT * FROM inventory; -- Update UPDATE inventory SET quantity = 200 WHERE id = 1; SELECT * FROM inventory; -- Delete DELETE FROM inventory WHERE id = 2; SELECT * FROM inventory;To run the sample SQL Code, select the lightning bolt icon in the toolbar
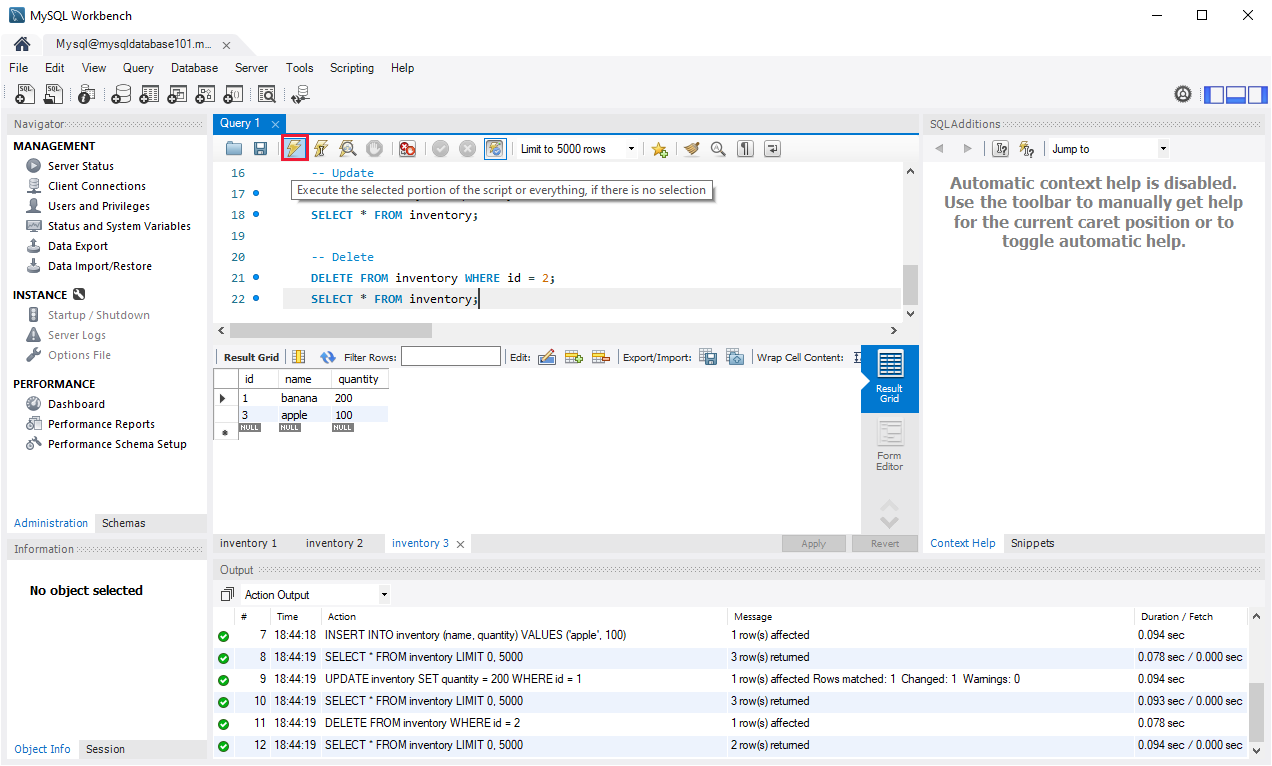
The query results appear in the Result Grid section in the middle of the page. The Output list at the bottom of the page shows the status of each command as it is run.