Define the Host Guardian Service
By implementing a guarded fabric on the Contoso Hyper-V infrastructure, you can use the HGS to ensure the validity of guarded hosts and to protect VMs.
Overview of HGS
HGS provides a Hyper-V guarded fabric with two distinct services:
- HGS Attestation service. The HGS Attestation service ensures that only a safe and authorized guarded host can run a shielded VM. Within the HGS Attestation service, the following two attestation modes are available:
- TPM-trusted attestation. Guarded hosts are approved based on their Trusted Platform Module (TPM) identity, Measured Boot sequence, and code integrity policies to ensure they only run approved code.
- Host Key attestation. Guarded hosts are approved based on possession of a key.
- Key Protection Service (KPS). KPS provides a guarded host with the security keys required to power on a shielded VM, and for migrating a shielded VM to another guarded host.
Note
Windows Server 2016 included another attestation mode called Admin-trusted attestation. However, this attestation mode was deprecated in Windows Server 2019.
Overview of HGS in action
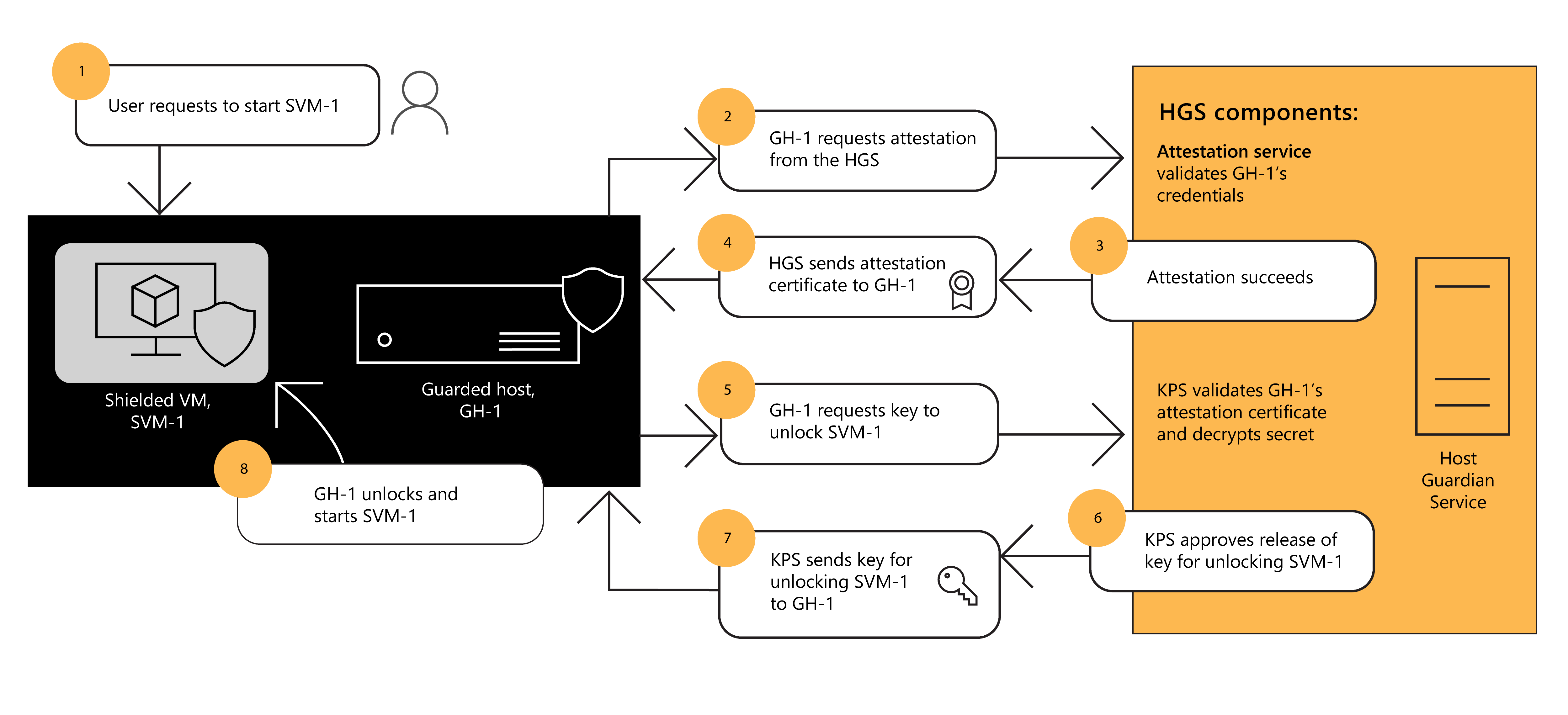
The following steps and supplemental diagram provide an overview of how HGS is used to start a shielded VM in a guarded fabric:
- A user requests to start the shielded VM SVM-1.
- Before SVM-1 is started, the guarded host GH-1 requests attestation from the HGS.
- The HGS Attestation service validates GH-1's credentials.
- The HGS Attestation service sends an attestation certificate to GH-1.
- GH-1 submits its attestation certificate to the KPS and requests a key to unlock SVM-01 by using an encrypted secret.
- The KPS determines the validity of GH-1's attestation certificate and decrypts the secret to retrieve the key for unlocking SVM-1.
- The KPS sends the key to GH-1.
- GH-1 uses the key to unlock and start SVM-1.
Requirements for a HGS server
The requirements for a HGS server are listed in the following table.
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Hardware | The HGS can run on both physical and virtual machines. However, for higher availability, three physical servers with similar hardware are recommended for running the HGS as a three-node cluster. For TPM trusted attestation, the HGS server hardware must support TPM 2.0 and Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) 2.3.1 with Secure Boot enabled. A mid-sized (8 core/4 GB) HGS server node can manage approximately 1,000 Hyper-V hosts. |
| OS | Host Key attestation requires Windows Server 2019 Standard or Datacenter edition operating with v2 attestation. For TPM-based attestation, HGS can run Windows Server 2019 or Windows Server 2016, Standard or Datacenter edition. |
| Encryption certificates | When you deploy HGS, you must provide signing and encryption certificates. The certificates never leave the HGS and are only used to protect sensitive information that's needed to start shielded VMs. You should configure your fabric to obtain certificates from an internal certificate authority or from a trusted external authority. |
| Server Roles | The HGS and supporting server roles must be installed on the HGS server. |
| User account and resource management | To help compartmentalize the user accounts and resources in your fabric, you can choose to install HGS in a new and dedicated Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forest or to an existing bastion forest. |
| Network | You must configure your network to allow DNS forwarding between the fabric AD DS forest and the HGS AD DS forest. |
Note
A bastion environment is a single-directory AD DS forest, which acts as a dedicated administrative forest. It is separate from other production AD DS forests which might exist. This single function provides a reduced attack surface. The separation provides a security boundary between any security compromises which might occur in other AD DS forests in your environment.
Considerations for planning HGS servers
To ensure the security, availability, and reliability of your guarded fabric, consider the factors listed in the following table when you're planning to implement a HGS server.
| Consideration | Details |
|---|---|
| Management | To reduce the risk from an attacker or malicious administrators, designate specific people who will manage the HGS. Your HGS administrators should be separate from the administrators of your Hyper-V environments. |
| Recovery and backup | Depending on your requirements, you can install a separate HGS in each datacenter location (for failover clustering) or stretch a single HGS across multiple datacenters (for resiliency). You can also register a Hyper-V host with more than one HGS as failover. Back up every HGS by exporting its configuration so that you can always recover locally. |
| Generate HGS keys | You can generate security keys using your own internal certificate authority, or you can obtain keys from a publicly-trusted certificate authority. |
| Store HGS keys | For the strongest possible security, HGS keys should be created and stored exclusively in a Hardware Security Module (HSM). If you're not using HSMs, use BitLocker encryption on HGS servers. |
| Performance implications | There's roughly a 5% density-difference between hosts running shielded VMs and non-shielded VMs. This means that if a given Hyper-V host can run 20 non-shielded VMs, you can expect that it can run 19 shielded VMs. |
| Branch office considerations | You can specify a fallback URL for a virtualized HGS server that's running locally as a shielded VM in the branch office. The fallback URL can be used to power on or live migrate the shielded VM whenever the branch office loses connectivity to HGS servers in the datacenter. |
Demonstration
The following video demonstrates how to:
- Install the HGS role by using the Add Roles and Features wizard.
- Install the HGS role by using Windows PowerShell.
The main steps in the process are:
Install the HGS role and management tools by using the Add Roles and Features wizard.
Open a Windows PowerShell console with elevated permissions, and then use the following cmdlet to install the HGS role:
Install-WindowsFeature HostGuardianServiceRole -IncludeManagementTools -Restart
Note
There are two feature names available to use when installing HGS by using Windows PowerShell. The HostGuardianServiceRole feature name installs the HGS role on the Host Guardian server. The HostGuardian feature name installs the Host Guardian feature on the Hyper-V server, which enables the Hyper-V server to interact with the Host Guardian server.