Enhancements in SQL Server 2022 to help scalability
Now let's look at scalability, and how new features in SQL Server 2022 can help significantly improve the performance of your workloads. By upgrading to SQL Server 2022, you can see significant improvements just by using the default configurations and features that were added to help scalability.
In this unit, we go over:
- Buffer pool parallel scan
- System page latch concurrency enhancements
Buffer pool parallel scan
SQL Server 2022 introduces the buffer pool parallel scan feature that improves the performance of buffer pool scan operations that help customers as they scale their SQL Server environments. Many common operations benefit from buffer pool parallel scans. Such as, database startup or shutdown, creating a new database, file drop operations, backup and restore operations, and Always On failover events. Database consistency checkers (DBCC) CHECKDB and DBCC Check Table also benefit, as well as log restore operations and other internal operations.
What is a buffer pool and why does it affect performance?
A buffer is an 8-KB page in memory and the buffer pool (also known as the buffer cache) is divided into 8-KB pages. The buffer pool is the area in memory where SQL Server stores data pages that are read from disk. All pages must be copied into the buffer pool before they can be used in a query. Imagine that you have a 1-TB buffer space. With 1 TB, the buffer pool scan needs to iterate over 130 million buffers.
In SQL Server 2019 and earlier, scanning the buffer pool was always a serial operation. Meaning that the larger your environment or memory on your machine, the bigger performance effect you would see to scanning the buffer pool, as the scan would need to iterate over all the buffers serially. There was no way to eliminate this problem, and the issue wasn't necessarily correlated to how large of an operation you were doing. You would see a difference in performance versus a smaller system even when creating a new database, or shutting down SQL Server, as the bigger system would take longer to scan the buffer pool.
Solving scaling with buffer pool parallel scan
With buffer pool parallel scan, the buffer pool scan can be parallelized, and the scan can complete faster. This improvement is important for large-memory machines, as you can see the effect to performance when scaling your environment. Customers are seeing 10 to 30 times the improvement in operations that scan the buffer pool, just by using SQL Server 2022 as buffer pool parallel scan is enabled by default.
System page latch concurrency enhancements
As in prior versions of SQL Server, SQL Server 2022 introduced further improvements to tempdb performance, and this time to address:
- Concurrent global allocation maps (GAM) updates
- Concurrent shared global allocation maps (SGAM) updates
The performance problem with tempdb
One of the biggest performance issues we see with scaling a SQL Server environment is with tempdb. tempdb is a system database that is used to store temporary objects such as global or local temporary tables, temporary stored procedures, table variables, table-valued functions, and cursors. tempdb is also used for row versioning, online index operations, snapshots, and triggers. tempdb is a shared resource, used for nearly every SQL Server workload, and all sessions in the SQL Server instance uses the one tempdb database.
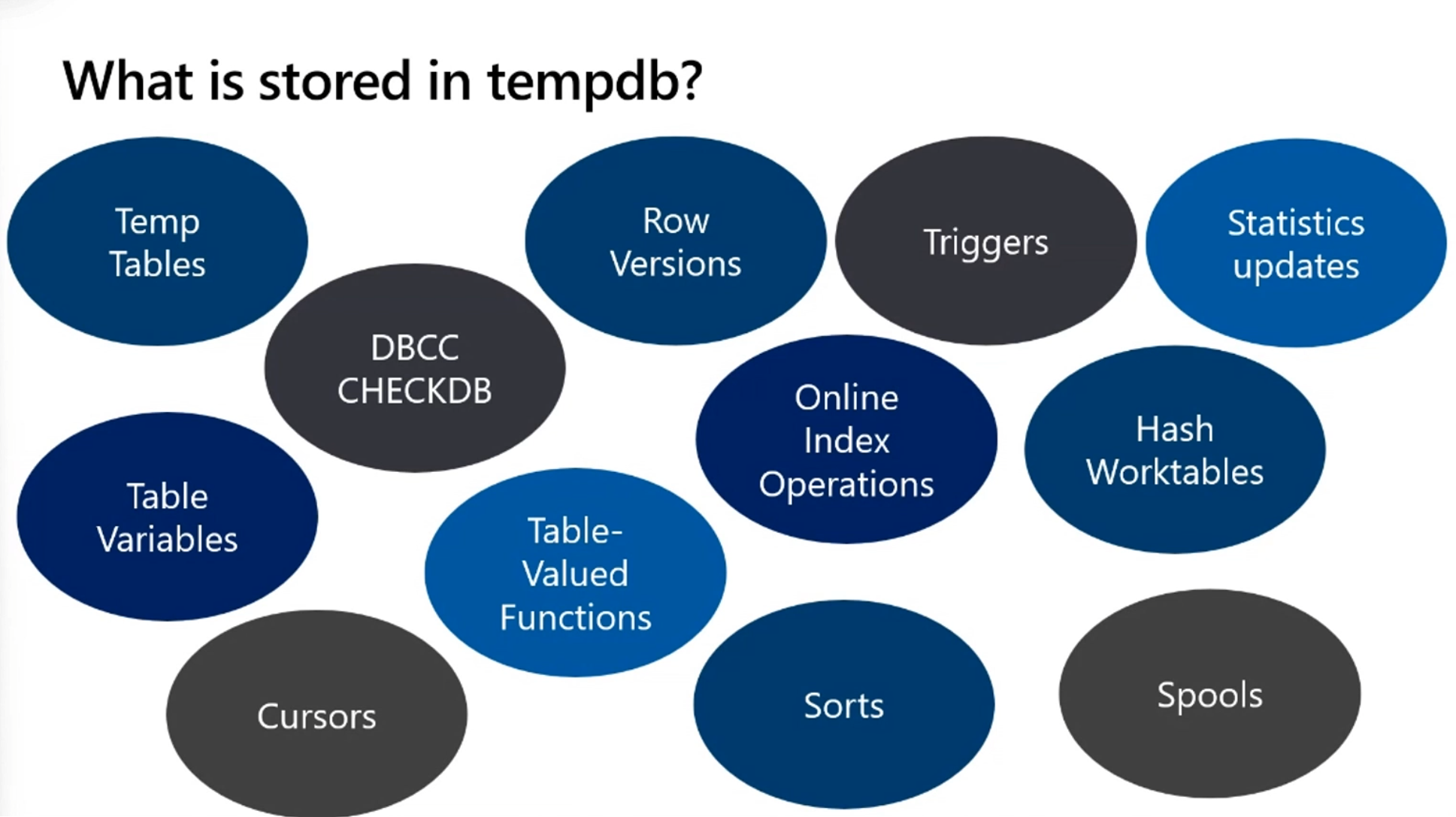
Another tempdb use is to internally spill to disk when there isn't enough memory available for a process or there's an inaccurate estimate that causes SQL Server to spill to tempdb. As we start pushing towards bigger machines with larger workloads, we start seeing concurrency issues emerge in the tempdb space in three key areas:
If you want more information on the types of contention and why they occur, explore these links.
Solving scaling issues with concurrent GAM and SGAM updates
If you're managing a large SQL Server environment, you're likely to run into issues with higher concurrent workloads, and one of the likely causes is with tempdb contentions. For a couple decades, we recommended a best practice of having multiple data files for tempdb to relieve contentions, including contentions to GAM and SGAM. You might discover SQL Server performance issues with high workloads but underutilized CPUs on your machine, and read about PAGELATCH waits, and followed guides troubleshooting tempdb.
Continuing the scaling enhancements with SQL Server 2022, we introduced concurrent GAM and SGAM updates to help address the performance bottleneck with tempdb with no application changes or configuration required. This improvement erases nearly all tempdb contention, allowing parallel threads to be able to modify the GAM and SGAM pages. With all of these enhancements, users should be able to use the defaults from SQL Server 2022 setup to configure tempdb files and no longer have to perform any other tuning for tempdb system page latch contention. This enhancement potentially enables you to have a hands-free approach to managing the tempdb.
If you want to see a performance demo of the scaling improvements introduced in SQL Server 2022, check out the following video:
Learn more about the scalability and performance improvements in What's new in SQL Server 2022 (16.x) - Performance.