Tampering - changing data without authorization
Tampering occurs when a malicious attacker reads, modifies, deletes, or inserts data in your system without authorization.
Examples include:
- Modifying data temporarily stored in cache, sent over-the-wire, or permanently stored in databases to compromise data integrity.
- Inserting malicious payloads into browser caches to cause erratic behavior in processes and data stores.
- Modifying memory through weak API call handling to cause crashes and disclosure of sensitive error messages.
- Redirecting data to compromised machines to take over the system.
- Tricking users into joining a network or downloading a file, which grants them traffic and device access (used in combination with spoofing).
Elements and interactions at risk from tampering attacks
Element
| Name | Shape | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Process | 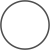 |
Activity that modifies or redirects input to an output |
| Data store |  |
Permanent or temporary data storage |
| Data-flow | 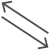 |
Data movement between elements |
Interaction
| Name | Interaction | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Process <-> Data store |  |
A task sends or receives data to or from a data store |
| Data-flow <-> Trust boundary | 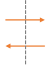 |
Data is transmitted from a trusted environment to someone over the internet (and vice-versa) |
How to prevent tampering
Integrity prevents data from being maliciously modified. Examples include:
- Validating input to prevent the processing of malicious payloads and mishandling of unexpected behavior
- Signing messages with digital signatures to ensure messages aren't tampered with
- Using access-control lists to apply permissions
- Using SSL/TLS to secure transmission
- Creating an IPSec tunnel to secure communication between endpoints
Common security controls to reduce or eliminate risk
- Operating system integrity controls
- Access control lists (ACL)
- Digital signatures
- Message authentication codes
Tip
Good question to ask: How do I know someone can't change my data in transit or at rest?