Troubleshoot direct routing issues
Microsoft Phone System Direct Routing connects on-premises telephony systems to Microsoft Teams. In this unit, you will learn how to troubleshoot some of the common issues with direct routing.
When troubleshooting direct routing issues, first check:
- The user has a Teams license.
- The user has a phone system license.
- The user is enabled for Enterprise Voice.
- Optionally, the user may require an Audio-Conferencing license.
You can also run Direct Routing-specific diagnostics by describing your issue. Log in to the Microsoft 365 admin center as an administrator, and in the navigation, pane select Show all > Support > New service request. Describe the issue in natural language and you will be prompted to enter more information to help diagnose the problem. As you enter the issue, possible matches are displayed together with recommended articles for you to read. After the diagnostic tool has finished searching, it displays steps you can take to resolve the problem. Direct routing is one of several scenarios currently supported in Teams diagnostics.
Troubleshoot dial pad is missing
If a user has reported that the dial pad is missing from the Calls screen and they cannot make outbound calls, check the following:
- Does the user have a Teams license?
- Does the user have a Calling plan assigned?
- Is Enterprise Voice enabled for the user?
- Is the user in Islands mode?
- Is the OnlineVoiceRoutingPolicy value set correctly for this user?
If the OnlineVoiceRoutingPolicy value is set incorrectly, administrators should set the correct value for the policy to force an update, as in the following PowerShell example:
Grant-CsOnlineVoiceRoutingPolicy -Identity "Ken Myer" -PolicyName $Null Grant-CsOnlineVoiceRoutingPolicy -Identity "Ken Myer" -PolicyName "RedmondPolicy"
After a few hours, the user should see the dial pad on the Calls screen.
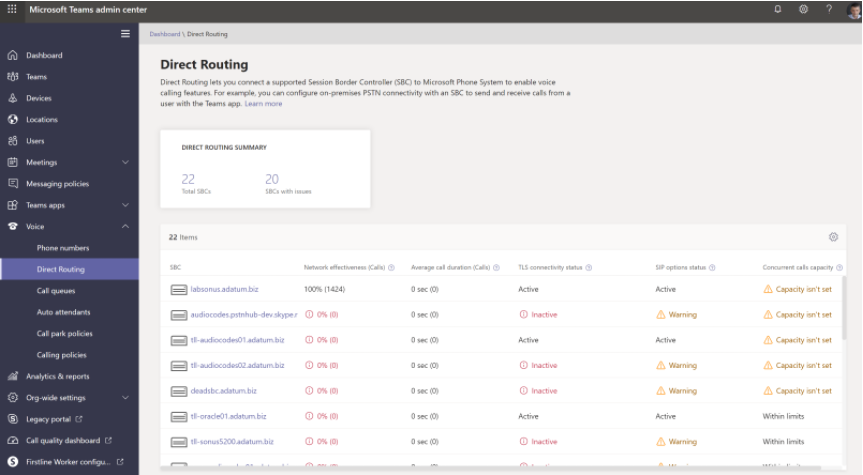
Health dashboard for Direct Routing
The Health Dashboard for Direct Routing allows you to monitor the interface between the Session Border Controller (SBC) and Direct Routing. The Health Dashboard provides both high-level information about the connected SBCs and detailed information. You must be logged in as an administrator with permission to access the health dashboard.
Troubleshoot SBC phone numbers
When you connect your on-premises telephony infrastructure to Microsoft Teams, an on-premises Session Border Controller (SBC) is used to connect to Phone System Direct Routing. One or more SBCs may be installed depending on the volume of calls within your organization.
Verify that the SBC is on the list of paired SBCs, and validate the SIP options. This will verify that the SBC connection has been made. Also see PowerShell script to test Direct Routing Session Border Controller connections In the Learn More section.
To ensure interoperability between the SBC and Phone System Direct Routing, create a Number Translation Rules policy using PowerShell. This translates numbers to the correct format. Number Translation Rules policies convert inbound calls from a caller to a Teams client, or to convert outbound calls from a Teams client to a PSTN endpoint (the person being called). Each policy can include multiple translation rules, which are applied in sequence.
Troubleshoot Number Translation Rules
- The rules in a Number Translation Rule policy are applied in sequence. Check the sequence of your rules and if necessary, change of the order in the policy.
- Check the format of your rules using the examples in Translate phone numbers for Direct Routing - Microsoft Teams.
Troubleshoot dial plans
A dial plan translates a shortened version of a number, such as an extension number, into a unique number that adheres to an international dialing standard usually E.164. Dial plans are implemented in the Microsoft Teams admin center using regular expressions to create a set of normalization rules. These rules allow users to keep numbers they are familiar with, which are then translated into internationally unique numbers.
Tip
Before creating dial plans and normalization rules, decide on an organization-wide naming convention. This will reduce errors and improve understanding when troubleshooting problems. Names should be descriptive so that anyone can understand their purpose.
There are three different types of dial plan, which are used in order. That means that if you haven’t modified any dial plan, then the service dial plan will be used. If you modify the tenant global dial plan, that will be used in combination with the service country dial plan. Finally, the user dial plan is used.
| Dial plan | Scope | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Service | Everyone within the country/region assigned to a user record. | The service dial plan contains common normalization rules and cannot be changed. |
| Global | All users in your organization. | Contains organization-wide rules, customized to your organization. |
| User | Group of users. | Normalization rules customized for a specific group of users. |
Normalization rules
Each dial plan must have one or more normalization rules, which are created using regular expressions. See the Learn More section for how regular expressions work.
Normalization rules are used in sequence. When a number is dialed, the first matching rule will be used, and all other rules ignored. Create the most restrictive rules first, followed by less restrictive rules.
Tip
Create PowerShell scripts to create dial plans. Scripts allow more than one person to check the rules before the script is run. You can add comments to a script to make it more understandable. Scripts are also easier to update, without introducing other errors. To create dial plan scripts, you will need the Teams PowerShell module.
Troubleshoot normalization rules
- Check that the normalization rules are in the correct dial plan. Dial plans are used in sequence and merged with the plan above in the hierarchy. If you have modified the global dial plan, this will be merged with the service dial plan. If you have created one or more user dial plans, these will be merged with the global dial plan. You do not, for example, need to add a country code because that is already in the service dial plan.
- Test each dial plan by entering a phone number and selecting Test.
- Rarely, users are forced to type in five or more digits, even though a dial plan normalization rule is in place to allow short digit dialing. As a workaround, users should type the full number instead of the shortened number.
Review the SBC log
The SBC logs provide information about the issues related to the pairing of the SBCs and the Direct Routing service. In addition to the Call Quality Dashboard, you can also use SBC logs to view the descriptive error codes stored in the logs. These can help you identify root cause of direct-dialling call issues.
Issues with SBC pairing or where the SIP "Invite" was rejected (such as when the name of the trunk FQDN is misconfigured), can be identified from the SBC logs. Direct Routing sends a detailed description to the SBCs, which are recorded in the SBC logs. Refer to the SBC vendor instructions for further details.
Troubleshoot audio conferencing issues
Microsoft Teams Audio conferencing enables people to use a phone to join a meeting. Audio conferencing is only available in some countries/regions, and users must have a Teams Add-on license. Not all users will require audio conferencing capabilities; you only need to set up audio conferencing for people who schedule or lead meetings. Meeting attendees don’t need a Teams add-on license, or other setup.
To set up Audio Conferencing:
- Determine whether Audio Conferencing is availability in your region.
- Acquire and assign licenses for users who need them.
- Get service numbers for your conferencing bridges. These can be toll or toll-free numbers. In some regions you can get service numbers from the Microsoft Teams admin center. Or you can port your existing service numbers. In other cases, you may have to request a number from Microsoft.
- Assign a service number to the conferencing bridge.
- Set the default and alternate languages for a conferencing bridge.
- Set your conferencing bridge settings.
- Assign dial-in phone numbers for users who lead meetings.
- Optionally set up meeting invitations.
- Optionally, purchase Communications Credits.
Communications credits
Consider purchasing communications credits. Communications Credits are used to pay for Audio Conferencing and Calling Plan minutes and ensure users can always:
- Add toll-free numbers to use with Audio Conferencing meetings, auto attendants, or call queues. Toll-free calls are billed per minute and require a positive Communications Credits balance.
- Dial out from an Audio Conference meeting to add someone else from anywhere in the world.
- Dial out from an Audio Conference meeting to a mobile phone with the Microsoft Teams app or Skype for Business app installed to destinations that aren't already included in your subscription.
- Dial any international phone number when you have Domestic Calling Plan subscriptions.
- Dial international phone numbers beyond what is included in a Domestic and International Calling Plan subscription.
- Dial out and pay per minute once you have exhausted your monthly minute allotment.
If you do not set up Communications Credits, users may run out of minutes depending on your Calling Plan, Audio Conferencing plan, and country or region. This results in users not being able to make calls or dial out from online Audio Conferencing meetings.
See Learn More for links to provisioning Audio Conferencing and Communications Credits. There is also a link in the Learn More section for known issues with Audio Conferencing.
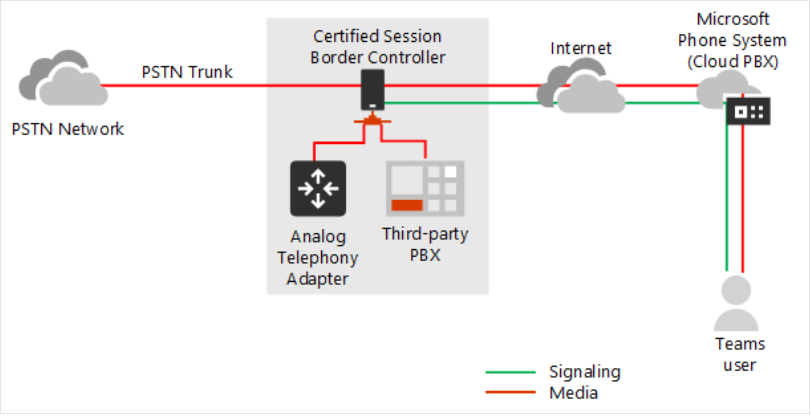
Media bypass with Direct Routing
Media bypass enables you to shorten the path of media traffic to improve performance. Media is kept between the Session Border Controller (SBC) and the client, instead of it being sent to the Microsoft Phone System. To configure media bypass, the SBC and the client must be in the same location or network. Without media bypass, media will flow to Microsoft data centers, and back to the SBC. With media bypass, the media is kept between the Teams user and SBC as shown in the following diagram:
To troubleshoot media bypass:
- Check that the Teams client has access to the public IP address of the SBC, including from the internal network. This is known as “hair-pinning”.
- If the Teams client does not have access to the public IP address of the SBC, media will be relayed by the Teams Transport Relay servers but still bypasses the Media Processors.
- To optimize media bypass for your configuration, consider the location of your SBCs, and how close your users are to the Microsoft Transport Relay servers. Where possible, allow internal users to connect directly to the SBC, but block external users.