Understand hyperparameter tuning
Building machine learning solutions involves testing many different models. Let's explore two concepts that can help with finding the optimal model:
- Hyperparameter tuning
- Cross-validation
Hyperparameter tuning
A hyperparameter is a parameter used in a machine learning algorithm that is set before the learning process begins. In other words, a machine learning algorithm can't learn hyperparameters from the data itself. Hyperparameters are tested and validated by training multiple models. Common hyperparameters include the number of iterations and the complexity of the model. Hyperparameter tuning is the process of choosing the hyperparameter that has the best result on our loss function, or the way we penalize an algorithm for being wrong.
Cross-validation
When you train and evaluate a model on the same data, it can lead to overfitting. Overfitting is where the model performs well on data it has already seen but fails to predict anything useful on data it has not already seen. To avoid overfitting, you can use the train/test split where the dataset is divided between a training set used to train the model and a test set to evaluate the model's performance on unseen data.
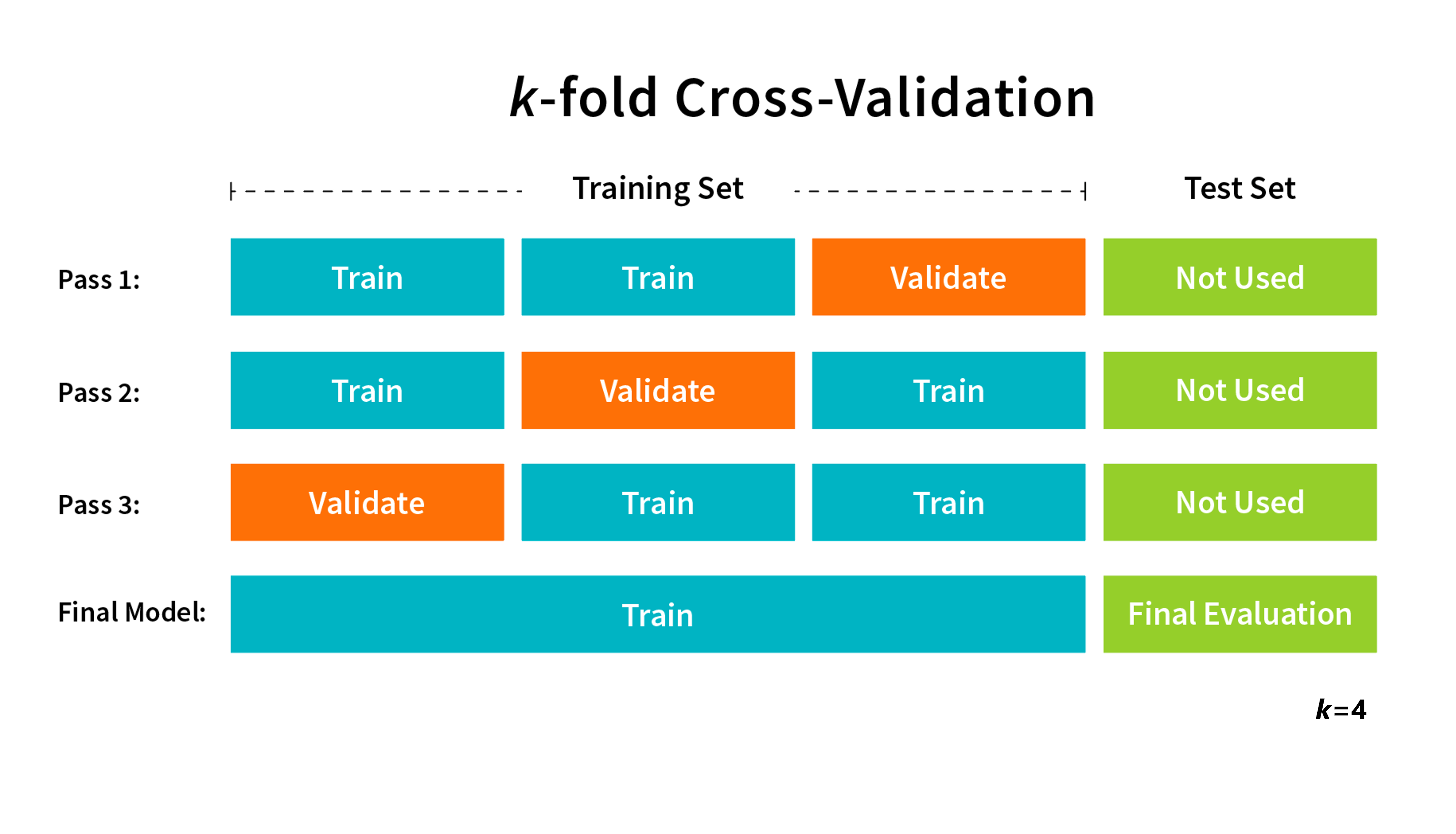
If you train many different models with different hyperparameters and then evaluate their performance on the test set, you would still risk overfitting because you may choose the hyperparameter that just so happens to perform the best on the data you have in your dataset. To solve overfitting when using hyperparameters, you can use k subsets of your training set to train the model, a process called k-fold cross-validation. A model is then trained on k-1 folds of the training data and the last fold is used to evaluate its performance.
Within Azure Databricks, there are two approaches to tune hyperparameters, which will be discussed in the next units:
- Automated MLflow tracking.
- Hyperparameter tuning with Hyperopt.