Understand environments
In an enterprise machine learning solution, where experiments may be run in various compute contexts, it can be important to be aware of the environments in which your experiment code is running. You can use Azure Machine Learning environments to create environments and specify runtime configuration for an experiment.
When you create an Azure Machine Learning workspace, curated environments are automatically created and made available to you. Alternatively, you can create and manage your own custom environments and register them in the workspace. Creating and registering custom environments makes it possible to define consistent, reusable runtime contexts for your experiments - regardless of where the experiment script is run.
What is an environment in Azure Machine Learning?
Python code runs in the context of a virtual environment that defines the version of the Python runtime to be used as well as the installed packages available to the code. In most Python installations, packages are installed and managed in environments using conda or pip.
To improve portability, you usually create environments in Docker containers that are in turn hosted on compute targets, such as your development computer, virtual machines, or clusters in the cloud.
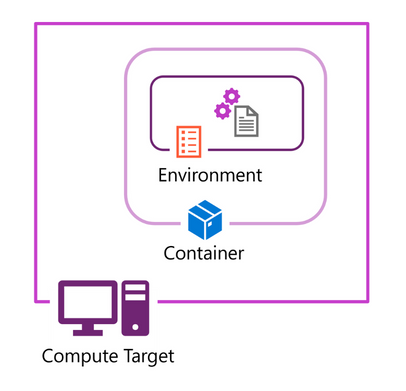
Azure Machine Learning builds environment definitions into Docker images and conda environments. When you use an environment, Azure Machine Learning builds the environment on the Azure Container registry associated with the workspace.
Tip
When you create an Azure Machine Learning workspace, you can choose whether to use an existing Azure Container registry, or whether to let the workspace create a new registry for you when needed.
To view all available environments within the Azure Machine Learning workspace, you can list the environments in the studio, using the Azure CLI, or the Python SDK.
For example, to list the environments using the Python SDK:
envs = ml_client.environments.list()
for env in envs:
print(env.name)
To review the details of a specific environment, you can retrieve an environment by its registered name:
env = ml_client.environments.get(name="my-environment", version="1")
print(env)