What is SaaS?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is one of the most popular forms of cloud computing, and is used daily by consumers and businesses. SaaS allows organizations to quickly get up and running with apps at minimal upfront cost.
SaaS is a complete software solution that customers purchase from a service provider. Customers rent the use of an app for their organization, and users connect to the app over the internet, usually with a web browser or mobile app.
All the underlying infrastructure, middleware, app software, and app data are in the service provider's datacenter. The service provider manages the hardware and software, and with the appropriate service agreement, ensures the availability and security of the app and data.
The term economies of scale, also called subtractive manufacturing in production scenarios, describes the idea of success underlying the SaaS model. This idea isn't new, and means that the more you produce, the higher margins you can achieve. Economies of scale apply to SaaS because you reuse infrastructure and don't produce customized software for each customer.
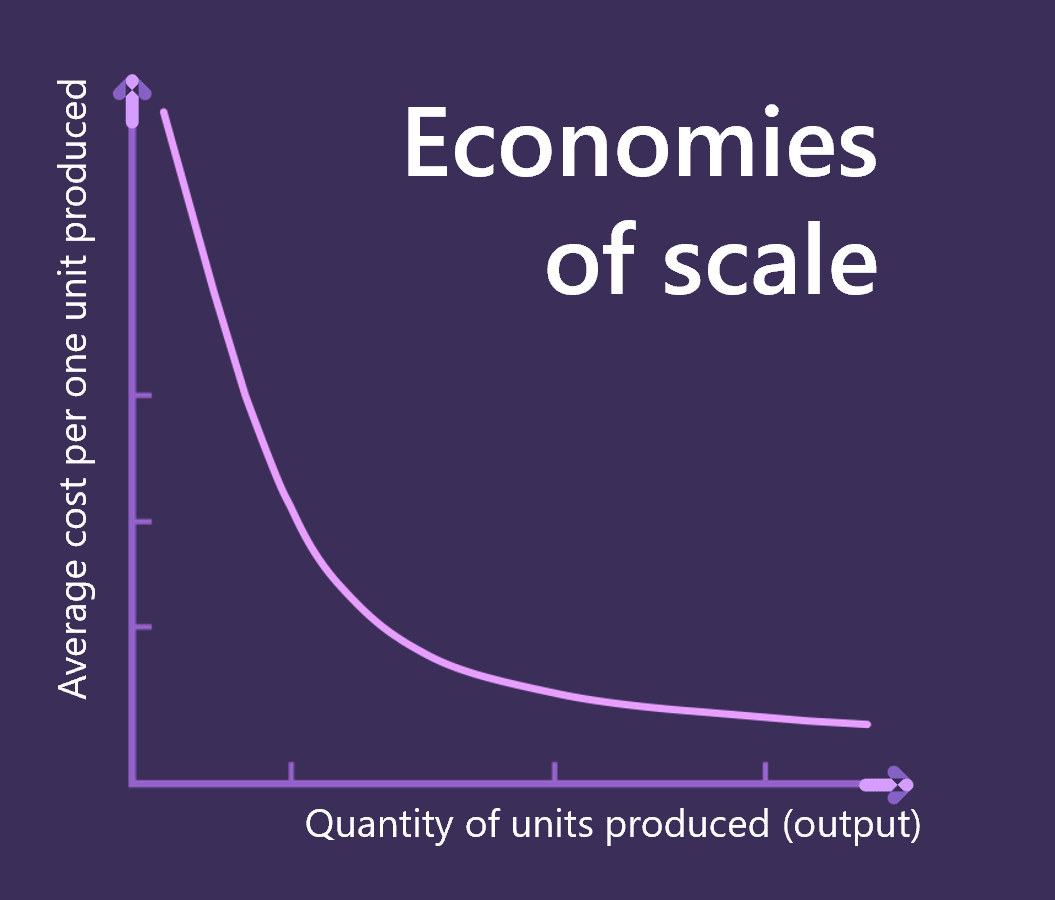
Some dedicated or isolated SaaS service tiers do have their own infrastructure. For example, the Microsoft special offer called Azure Government can be sold only to government. Because of government security standards and requirements, the infrastructure is completely isolated from the Azure public cloud.
SaaS business models
There are two high-level SaaS business models:
- Business-to-Business (B2B) companies provide software and services to other businesses.
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C) companies sell and operate software directly to individual consumers.
The main difference is the audience for products. A company might have a product that suits both business and individual consumers, but the audience still has the most direct influence on the company's implemented solution.
Some other differences between B2B and B2C include:
- Pricing models.
- Sales processes.
- Customer service or account management.
It's possible to serve both B2B and B2C customers. For example, there are different models of Microsoft Azure subscriptions tailored for enterprise-size customers (enterprise agreements) or individual consumers (pay-as-you-go).
Both B2B and B2C models can provide your company with sales and revenue, but you should create a strategy that suits your company best. When starting with a new solution, it's a good idea to begin with one customer segment.
As you work on defining the business model for your SaaS solution, you need to identify the market you're targeting. You can then gather insights about your customers and their problems, so you can define clearer requirements for the tech team that builds your solution.
Contoso scenario
This example considers a fictitious UK company, Contoso, that wants to develop a subscription-based service to generate and improve website designs. Contoso created an AI model that can generate user interfaces for websites, track the performance of the design over time, and suggest improvements.
The technical capability of this service isn't much different for private users or large corporations, but from a business perspective it makes sense to focus on only one segment at a time. Marketing and business development efforts are different for individual consumers and business segments, and might bring different technical requirements for the solution itself.
Contoso decides to focus initially on the B2B model, in particular small companies who can't afford their own in-house designers. It's important to offer attractive designs that aren't too complex, so AI can provide high-quality service. Contoso discovered through market and user research that lawyers were the most willing to pay for these services.
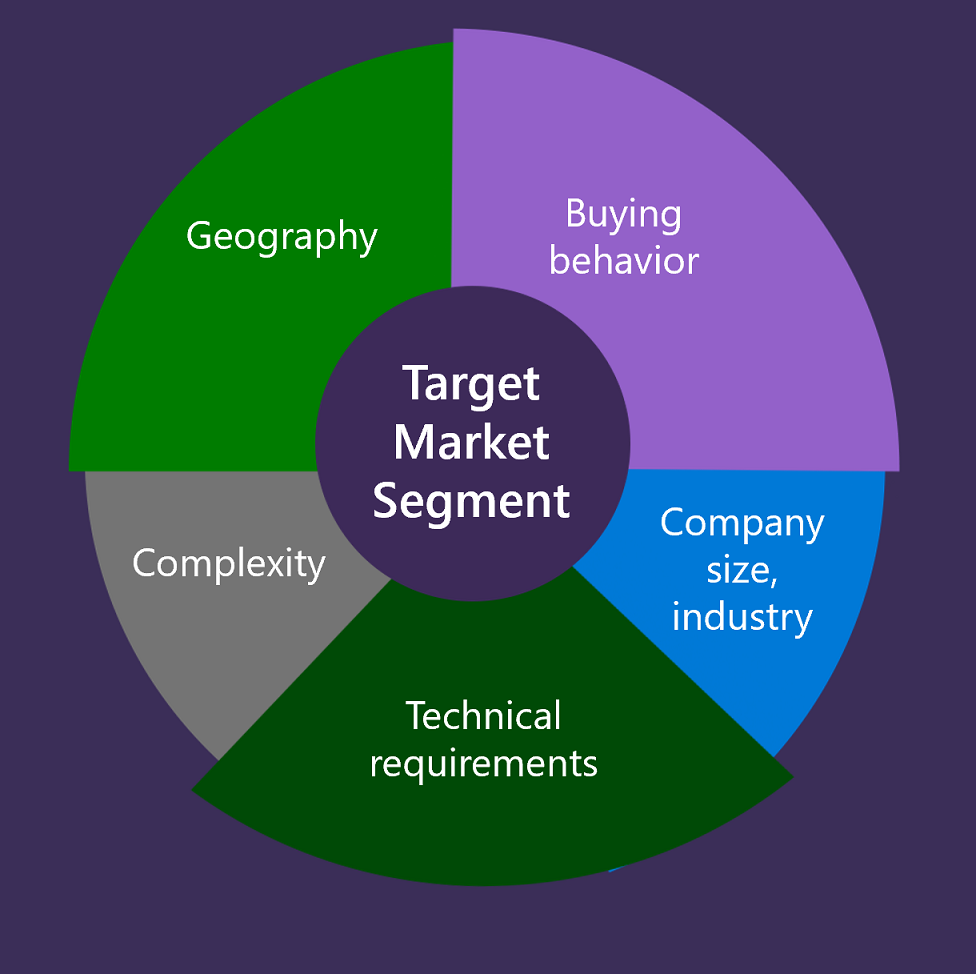
The identified market segment looks something like this:
Buying behaviors
- Customers search for service online and purchase online.
- A free trial lets users try out the product to decide if it's suitable.
Company size and industry
- Small size companies.
- Legal industry.
Technical requirements
The example is simplified, but here are some general requirements:
- Must allow collecting website usage data and analyzing this data to improve the design of the website.
- Due to the collection of sensitive data, must comply with several regulations, such as UK GDPR.
- Must provide capability for customers to book appointments with lawyers.
Complexity
- The AI model was trained on a set of simple landing pages, and can handle website designs that aren't too complex and are mostly informational or used for booking time slots.
- Complexity of customers' business should be low.
Geography
Initially, Contoso is focusing on the UK region due to its origins, preferred language, and the financial capabilities of companies that provide legal services within the UK. After Contoso establishes a stable business within the UK region, they plan to go into other markets.
Each geographical region adds more challenges in terms of technical delivery of the service and overall market strategies and activities. If Contoso decides their next market is Europe, they have to create a strategy for marketing the product in countries/regions where English isn't the default language, and account for specifics of the local legal industry.
With a clear understanding of the requirements for the service and which customers to focus on, Contoso understands why SaaS is the preferred model instead of just selling AI-generated designs.