SaaS vs. traditional software
This unit addresses the differences between the traditional, transactional license-based software model and SaaS. Major differences include:
- Emphasis on service vs. software.
- New consumption model.
- The importance of adoption.
Software vs. service
To sell software as a service instead of just software, focus on how effectively and smoothly your organization can deliver the service. Shift the mindset from what you deliver to how you can better align the solution to the customer's problems and return on investment (ROI).
Move away from long lists of product features and descriptions of what the product can do. Instead, focus on challenges and how your solutions can address those problems.
SaaS changes everything about the way your company operates. SaaS companies follow a customer-centric design, where the focus is on the value customers can get from using the service. Not only billing, but also branding, marketing messages, and sales processes are different from license-based software.
In the SaaS model, software providers must ensure the maintenance, updates, support, and security of the solution. In the traditional model, this responsibility is on customers. The next units cover this difference in more detail.
Consumption model
To start, understand how the consumption model differs from the transaction based model. The following diagram illustrates the four phases of the consumption model: Land, Adopt, Expand, Renew (LAER), as introduced in a book called Technology-as-a-Service Playbook.
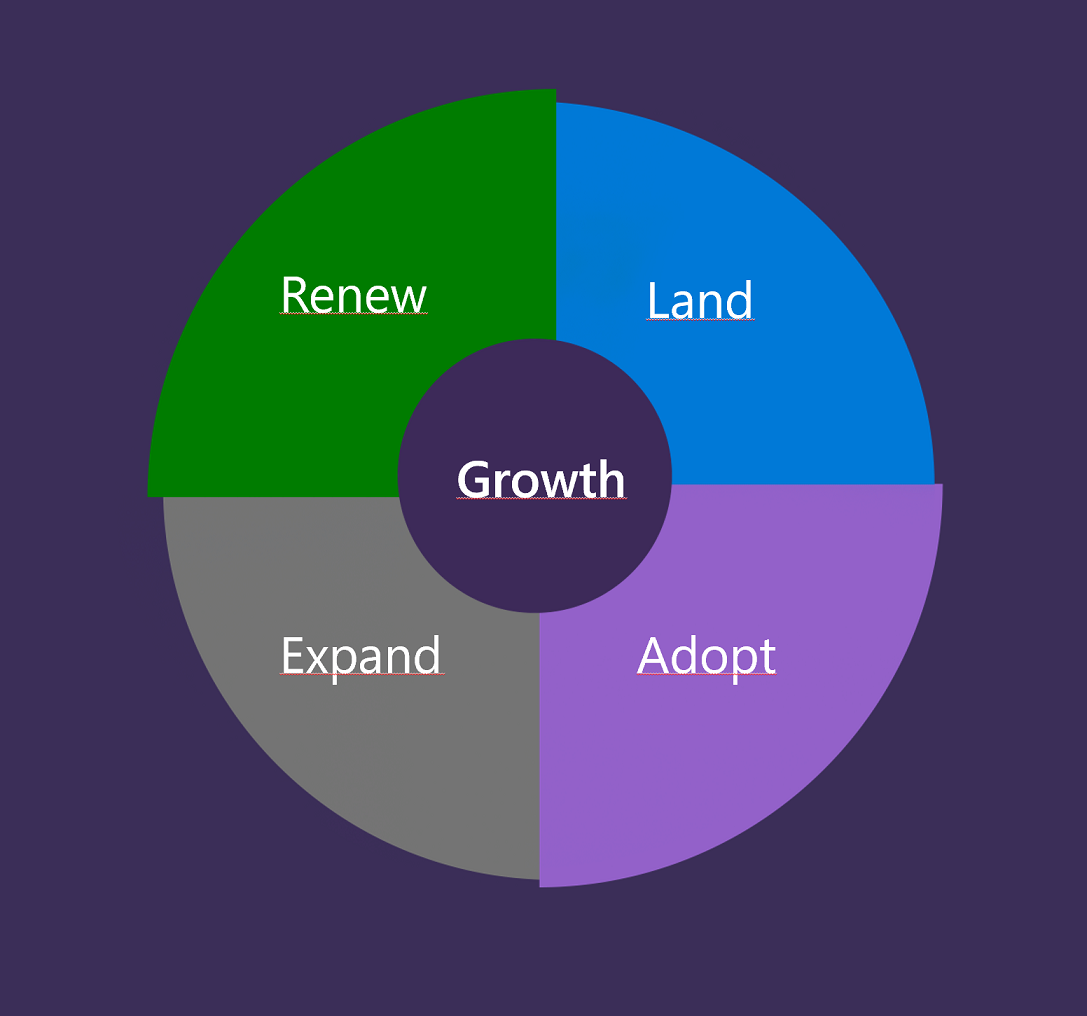
- The Land phase, which is familiar from selling traditional license-based software, is the first phase of acquiring a customer for your solution.
- During Adoption, you ensure that the customer is able to successfully use the software and gain value, so you can expand with other offerings.
- Expansion is the process of upselling extra functionality or upgrading the purchased plan.
- In the Renewal phase, customers decide to continue with your software.
This model is significantly different from the transactional model, where it didn't really matter what happened after the software was sold. In a SaaS model, the sales costs are often higher than the revenue from the first billing period. If customers don't recognize the value, they don't use the service.
Importance of adoption
Low adoption rates lead to high customer churn rates. Investments in sales and marketing don't pay off if customers don't use and realize the value of the service.
- Adoption reduces churn.
- Churn reduces revenue growth.
- Expansion is possible only if the product is adopted.
The following diagram illustrates the impact of potential customer churn on the Adoption and Renew stages of the LAER model.
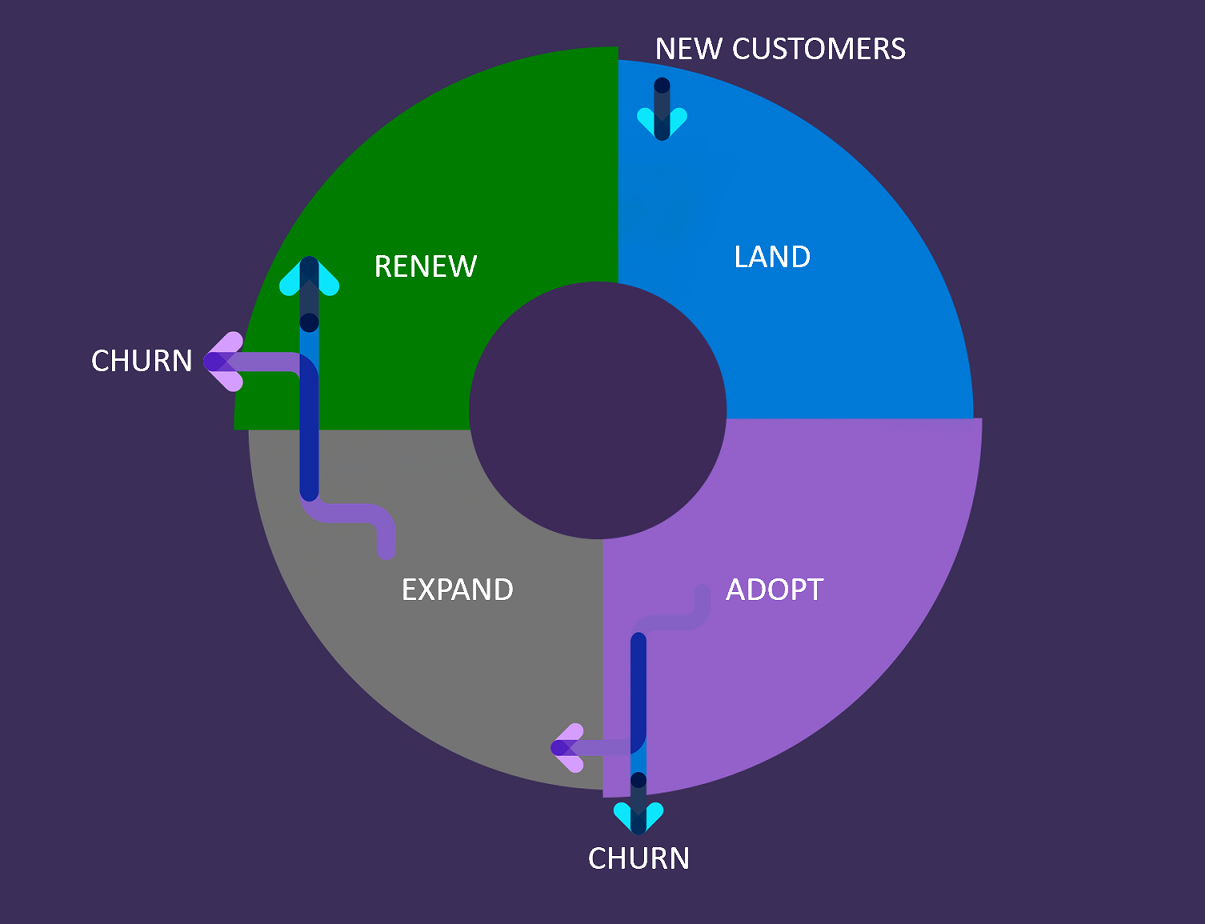
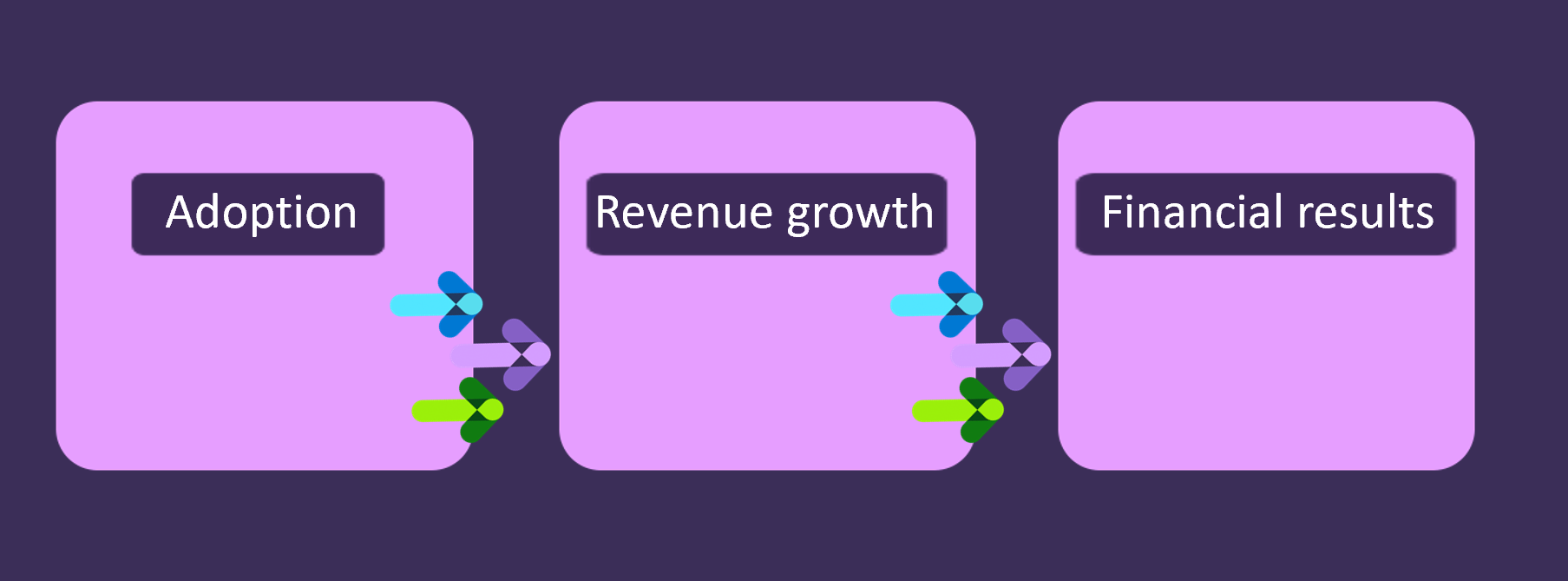
As you can see, in order for the LAER cycle to function, you need to make sure that the level of churn is low and level of adoption is high. Improving adoption improves revenue growth, and predictable revenue growth improves company financial results and valuation. Adoption plays a very important part in SaaS.
SaaS companies often establish a Customer Success department. The purpose of this department is to ensure that customers are realizing the value of the service and discovering new features that can help solve their problems. Successful organizations take charge and help customers understand and find the value of the services they provide.
Understanding customer success is crucial to the value generation of the company. Being able to define customer success is a prerequisite for proper execution of all other activities. The definition of customer success goes from the company delivering a tool, which really isn't success, to an X% improvement in some factor by using the service.

Based on the preceding definitions, you can set possible targets for a Customer Success organization. The main objective of this organization should be making sure that customers are adopting the service and getting value from using it. In larger organizations, these measures also become the basis for breaking down department and individual goals.
Contoso scenario
Here's how Contoso shifted their mindset from the tool towards the value their service provides to customers:
- Contoso delivers the service, which provides a tool for lawyers to generate and track website design performance.
- Contoso delivers a service that helps lawyers create user-friendly and attractive designs and provide improvements based on customer interaction. This service allows the lawyers to attract more customers and save time and money by focusing more on what they know best, the law.
- Contoso customers increase their customer base by 5% by improving their website designs.
- Contoso customers on average increased their customer base by 5% by improving website design, while Contoso's top customers increased their customer base by 15%.