Troubleshooting BitLocker with the Intune encryption report
Microsoft Intune provides a built-in encryption report that gives details about encryption status across all managed devices. The Intune encryption report is a useful starting point for troubleshooting encryption failure. You can use the report to identify and isolate BitLocker encryption failures, and see the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) status and encryption status of Windows devices.
This article explains how to use the Intune encryption report to help troubleshoot encryption for BitLocker. For additional troubleshooting guidance, see Troubleshooting BitLocker policies from the client side.
Note
To take full advantage of this troubleshooting method and the error details available in the encryption report, you will need to configure a BitLocker policy. If you are currently using a device configuration policy, consider migrating the policy. For more information, see Manage BitLocker policy for Windows devices with Intune and Disk encryption policy settings for endpoint security in Intune.
Encryption prerequisites
By default, the BitLocker setup wizard prompts users to enable encryption. You can also configure a BitLocker policy that silently enables BitLocker on a device. This section explains the different prerequisites for each method.
Note
Automatic encryption is not the same thing as silent encryption. Automatic encryption is performed during the Windows out-of-the-box experience (OOBE) mode on modern standby or on Hardware Security Test Interface (HSTI)-compliant devices. In silent encryption, Intune suppresses the user interaction through BitLocker configuration service provider (CSP) settings.
Prerequisites for user-enabled encryption:
- The hard disk must be partitioned into an operating system drive formatted with NTFS and a system drive of at least 350 MB formatted as FAT32 for UEFI and NTFS for BIOS.
- The device must be enrolled in Intune through Microsoft Entra hybrid join, Microsoft Entra registration, or Microsoft Entra join.
- A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) chip is not required, but highly recommended for increased security.
Prerequisites for BitLocker silent encryption:
- A TPM chip (version 1.2 or 2.0) that must be unlocked.
- Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) must be enabled.
- The hard disk must be partitioned into an operating system drive formatted with NTFS and a system drive of at least 350 MB must be formatted as FAT32 for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) and NTFS for BIOS. UEFI BIOS is required for TPM version 2.0 devices. (Secure boot is not required but will provide more security.)
- The Intune-enrolled device is connected to Microsoft Azure hybrid services or Microsoft Entra ID.
Identifying encryption status and failures
BitLocker encryption failures on Intune enrolled Windows 10 devices can fall into one of the following categories:
- The device hardware or software does not meet the prerequisites for enabling BitLocker.
- The Intune BitLocker policy is misconfigured, causing Group Policy Object (GPO) conflicts.
- The device is already encrypted, and the encryption method doesn't match policy settings.
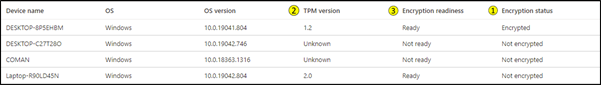
To identify the category of a device encryption failure, sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center and select Devices > Monitor > Encryption report. The report will show a list of enrolled devices and show if a device is encrypted or ready to be encrypted, and if it has a TPM chip.
Note
If a Windows 10 device displays a Not ready status, it might still support encryption. For a Ready status, the Windows 10 device must have TPM activated. TPM devices aren't required to support encryption but are highly recommended for increased security.
The above example shows that a device with TPM version 1.2 has been successfully encrypted. Additionally, you can see two devices not ready for encryption that will not be able to be encrypted silently, as well as one TPM 2.0 device that is ready for encryption but not yet encrypted.
Common failure scenarios
The following sections describe common failure scenarios that you can diagnose with details from the encryption report.
Scenario 1 – Device is not ready for encryption and not encrypted
When you click on a device that is not encrypted, Intune displays a summary of its status. In the example below, there are multiple profiles targeting the device: an endpoint protection policy, a Mac operating system policy (which is not applicable to this device), and a Microsoft Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) baseline.
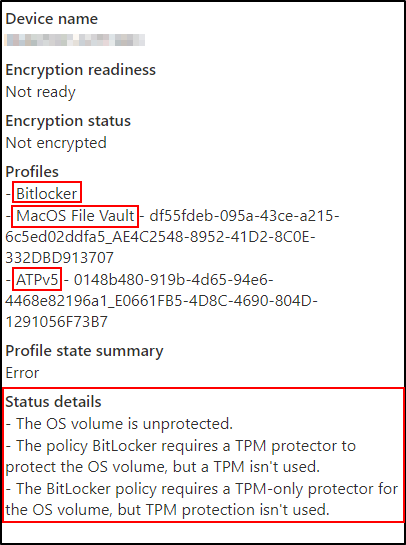
Encryption status explained:
The messages under Status details are codes returned by the BitLocker CSP status node from the device. The encryption status is in an error state because the OS volume is not encrypted. Additionally, the BitLocker policy has requirements for a TPM, which the device does not satisfy.
The messages mean that the device is not encrypted because it doesn't have a TPM present and the policy requires one.
Scenario 2 – Device is ready but not encrypted
This example shows that the TPM 2.0 device is not encrypted.
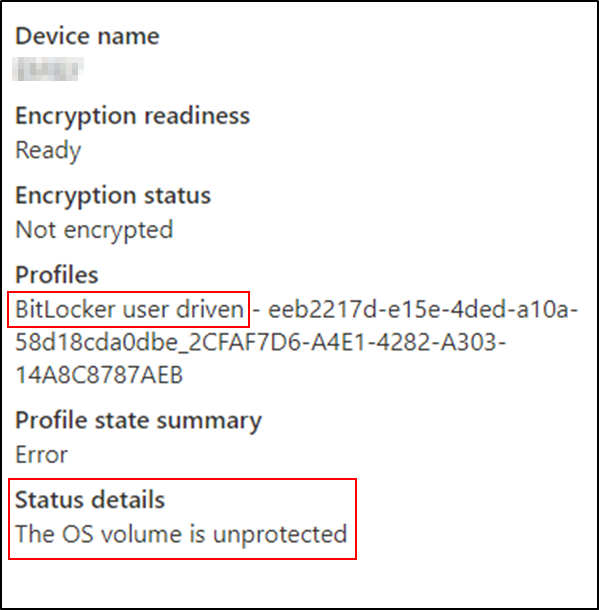
Encryption status explained:
This device has a BitLocker policy that is configured for user interaction rather than silent encryption. The user has not started or completed the encryption process (the user receives a notification message), so the drive remains unencrypted.
Scenario 3 – Device is not ready and will not encrypt silently
If an encryption policy is configured to suppress user interaction and encrypt silently and the encryption report Encryption readiness state is Not applicable or Not ready, it is likely the TPM is not ready for BitLocker.

Device status details reveal the cause:
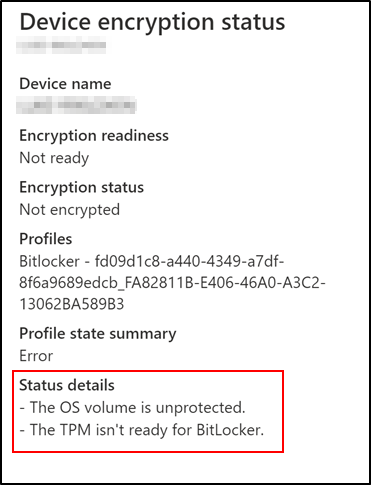
Encryption status explained:
If the TPM is not ready on the device, it could be because it is disabled in the firmware or needs to be cleared or reset. Running the TPM management console (TPM.msc) from the command line on the affected device will help you understand and resolve the TPM state.
Scenario 4 – The device is ready but not encrypted silently
There are several reasons that a device targeted with silent encryption is ready but not yet encrypted.
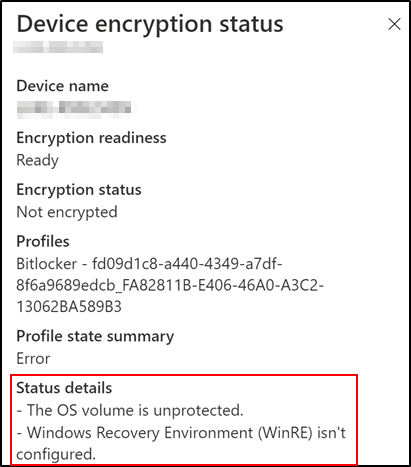
Encryption status explained:
One explanation is that WinRE is not enabled on the device, which is a prerequisite. You can validate the status of WinRE on the device using the reagentc.exe/info command as an administrator.
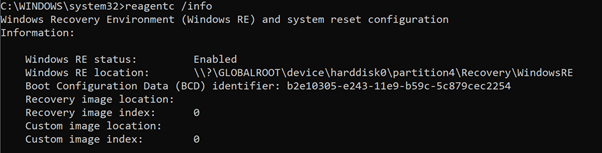
If WinRE is disabled, run the reagentc.exe/info command as administrator to enable WinRE.
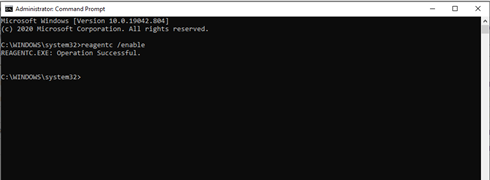
The Status details page will display the following message if WinRE is not configured correctly:
The user logged into the device does not have admin rights.
Another reason could be administrative rights. If your BitLocker policy is targeting a user who does not have administrative rights and Allow standard users to enable encryption during Autopilot is not enabled, you will see the following encryption status details.
Encryption status explained:
Set Allow standard users to enable encryption during Autopilot to Yes to resolve this issue for Microsoft Entra joined devices.
Scenario 5 – The device is in an error state but encrypted
In this common scenario, if the Intune policy is configured for XTS-AES 128-bit encryption but the targeted device is encrypted using XTS-AES 256-bit encryption (or the reverse), you will receive the error shown below.
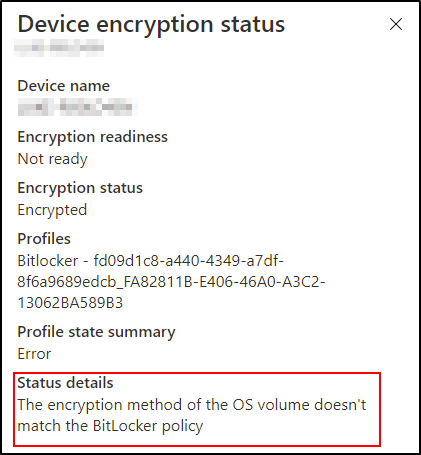
Encryption status explained:
This happens when a device that has already been encrypted using another method—either manually by the user, with Microsoft BitLocker Administration and Monitoring (MBAM), or by the Microsoft Configuration Manager before enrollment.
To correct this, decrypt the device manually or with Windows PowerShell. Then let the Intune BitLocker policy encrypt the device again the next time the policy reaches it.
Scenario 6 – The device is encrypted but the profile state is in error
Occasionally, a device appears encrypted but has an error state in the profile state summary.
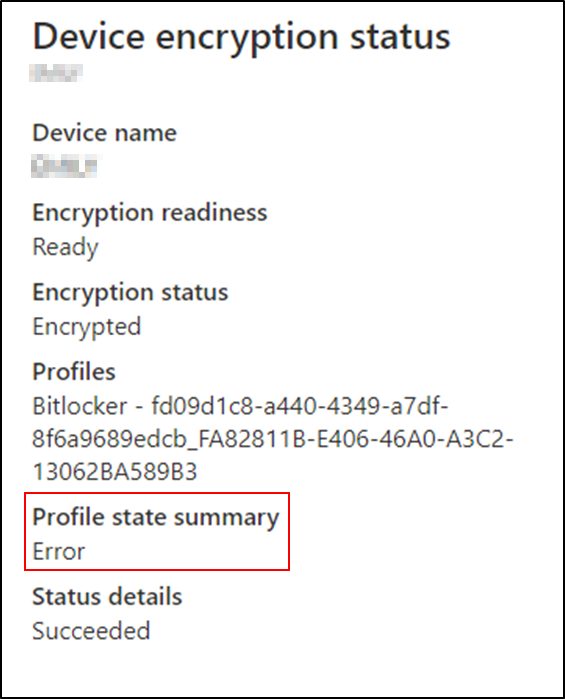
Encryption status explained:
This usually occurs when the device has been encrypted by another means (possibly manually). The settings match the current policy, but Intune has not initiated the encryption.