Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Debugging Tools for Windows supports kernel debugging over a network cable using multiple Physical Functions (PFs) on the supported NICs by partitioning the PCI configuration space.
With 2PF debugging, each PF can be connected to a single network port, so it allows the kernel debugging functionality to be connected to one PF while the standard network stack talks to the other PF. Because of this, KDNIC doesn't need to route the Windows networking traffic via KDNET, and KDNET will only be responsible for routing the host kernel debugger traffic. This results in a dramatic performance increase.
This topic describes how to set up 2PF debugging using the kdnet.exe utility.
Network card vendors are encouraged to enable support for this feature. For more information, see Debugger 2PF KDNET Miniport Network Driver Support.
Two drivers will run over the partitioned PCI configuration space
The Windows inbox driver will run out of the primary network port at bus.dev.fun0.0 PCI location.
The KDNET-Ext. module will run out of the added PF at bus.dev.fun0.1, This technique ensures that the Windows inbox NIC driver does not get impacted by sharing the NIC with KDNET.
The computer that runs the debugger is called the host computer, and the computer being debugged is called the target computer.
Kernel-Mode 2PF device requirements
The following is required:
On the target computer, a supported 2PF network card.
On the host computer, a network card.
A network connection between the target and host.
Windows 10 Build 21313 and later.
Supported 2PF Network Cards
Vendors such as NVIDIA Mellanox and Cisco provide NICs that support 2PF network debugging. Check with the network card vendor to see which models of the network card are supported. Note that some vendors support 2PF on a sub-set of network cards that share the same PnP ID.
Use kdnet.exe to confirm device support and view the busparams value
Use the kdnet.exe utility to display the parameter information for controllers that support KDNET 2PF transport debugging.
Confirm that the Windows Debugging Tools are installed on the host system. For information on downloading and installing the debugger tools, see Debugging Tools for Windows.
Locate the kdnet.exe and VerifiedNICList.xml files. By default, they are located here.
C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Debuggers\x64On the host computer, copy the two files to a network share or thumb drive, so that they will be available on the target computer.
On the target computer, create a
C:\KDNETdirectory and copy the kdnet.exe and VerifiedNICList.xml files to that directory.On the target computer, open a Command Prompt window as Administrator. Enter this command to verify that the target computer has a supported network adapter and to view the busparams value.
C:\KDNET>kdnet.exe Network debugging is supported on the following NICs: busparams=141.0.0, Mellanox ConnectX-4 Lx Ethernet Adapter #2, Plugged in, Primary function, multiple physical functions are supported. Network debugging is supported on the following USB controllers: busparams=128.15.0, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft) busparams=0.15.0, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft) busparams=128.15.1, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft) busparams=0.15.1, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft)Because the output shown above does not include "KDNET is running on this NIC.", this indicates that traditional KDNET debugging is not enabled on any of the adapters.
If the NIC does not support the multiple PF feature, then the PF status notification of "multiple physical functions are supported" will be omitted (blank) from the displayed information.
If NIC supports multiple PF, then the actual displayed information will depend on the combination of the Network port (root port/PF added port), as well as the cable connected/disconnected status to/from the NIC physical port.
This table summarizes different PF notifications for the primary NIC.
NIC adapter bus.dev.fun corresponds to Cable status PF Status original (primary) PF cable connected Primary function, multiple physical functions are enabled original (primary) PF cable disconnected Primary function, multiple physical functions are supported This table summarizes different PF notifications for the secondary NIC.
NIC adapter bus.dev.fun corresponds to Cable status PF Status new (secondary) PF port Kdnet is running Secondary function new (secondary) PF port cable disconnected or unknown status Primary function, multiple physical functions are enabled, but secondary function is not used If the output from kdnet.exe indicates that a supported NIC controller is available, we can proceed.
Setting Up the Target Computer for 2PF
Use the kdnet.exe utility to configure the debugger settings on the target PC for 2PF, by following these steps.
Important
Before using bcdedit to change boot information you may need to temporarily suspend Windows security features such as BitLocker and Secure Boot on the test PC. You can re-enable Bit Locker and Secure Boot once you’re done using BCDEdit to update the boot information. Appropriately manage the test PC, when the security features are disabled.
This process will add a new physical function (PF) to the NIC, specified by bus.device.function. The new PF can be used only by KDNET since the Windows inbox driver is set up to not run on an added, secondary PF. Follow these steps to add a new PF that will be used by the debug device.
Confirm that debugging is disabled before adding the new physical function
- Use the BCDEdit command to confirm that the KD is disabled on the target before adding a new PF on the NIC. This is needed to make sure the standard vendor NIC driver is loaded so that it can be used to add the new PF.
C:\> bcdedit /enum
...
debug No
As an alternative, use kdnet.exe without parameters to see if debugging is enabled. The output below shows KDNET running on a system with debugging enabled on one NIC. This is the lower-performance legacy setup.
c:\Debuggers>kdnet
Network debugging is supported on the following NICs:
busparams=141.0.0, Mellanox ConnectX-4 Lx Ethernet Adapter #2, KDNET is running on this NIC.
Network debugging is supported on the following USB controllers:
busparams=128.15.0, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft)
busparams=0.15.0, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft)
busparams=128.15.1, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft)
busparams=0.15.1, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft)
- If the debug value is set to Yes, use the set command to disable debugging.
C:\> bcdedit.exe /debug off
C:\> bcdedit.exe /set {default} bootdebug off
C:\> bcdedit.exe /set {bootmgr} bootdebug off
- Use the
shutdown -r -t 0command from an administrator's command prompt to reboot.
After the target PC restarts, and debugging is disabled, we can add the new physical function.
Add the new physical function
- Open an elevated command prompt and run the following command to add a second PF. All values are provided using decimal values.
C:\KDNET> kdnet -addpf 141.0.0 198.51.100.1 50001
Succeeded adding a Pci PF on :141.0.1. Please power off or reboot the machine.
Enabling network debugging on Mellanox ConnectX-4 Lx Ethernet Adapter #2.
Manage-bde.exe not present. Bitlocker presumed disabled.
To debug this machine, run the following command on your debugger host machine.
windbg -k net:port=50001,key=2steg4fzbj2sz.23418vzkd4ko3.1g34ou07z4pev.1sp3yo9yz874p
Then reboot this machine by running shutdown -r -t 0 from this command prompt.
bus.dev.fun is the PCI location port of the NIC adapter that supports the multiple PF feature, so the new PF will be added/attached to this network device.
-addpf option enables automatically kernel debugging over KDNET transport on the added PF port.
[host name/host ip address] is the TCP/IP address of the host computer. Use the ipconfig command on the host computer to determine this address.
[port number] is the TCP/IP port number. You can choose any port number from 49152 through 65535. The recommended range is between 50000 and 50039. The port that you choose will be opened for exclusive access by the debugger running on the host computer. Pick a unique port address for each target/host pair that you work with, within the recommended range of 50000-50039. 50005 is shown in the example.
Note that -addpf will also add the NO_KDNIC attribute to the OS installation {default} loadoptions. This is because KDNIC is no longer required to run on top of KDNET.
The loadoptions = NO_KDNIC is added to {default} OS tag to ensure that kdnic.sys won't run out of the newly added pf (141.0.1)
Use the bcdedit command to confirm that NO_KDNIC has been set.
C:\KDNET> bcdedit /enum {default}
Windows Boot Loader
-------------------
identifier {current}
device partition=C:
path \Windows\system32\winload.efi
description Windows Server
locale en-US
loadoptions NO_KDNIC
inherit {bootloadersettings}
recoverysequence {c23c4005d-12ae-11eb-9399-ac9840c152e7}
displaymessageoverride Recovery
recoveryenabled Yes
bootdebug No
testsigning Yes
isolatedcontext Yes
flightsigning Yes
allowedinmemorysettings 0x15000075
osdevice partition=C:
systemroot \Windows
resumeobject {c23c4005d-12ae-11eb-9399-ac9840c152e7}
nx OptOut
debug Yes
hypervisordebug No
2. Run the bcdedit /enum command to display the generated key.
```console
C:\KDNET> bcdedit /dbgsettings
busparams 141.0.1
key 2steg4fzbj2sz.23418vzkd4ko3.1g34ou07z4pev.1sp3yo9yz874p
debugtype NET
hostip 198.51.100.1
port 50001
dhcp Yes
The operation completed successfully.
Copy the returned key into a notepad .txt file. In the example shown, the generated key has a value of:
2steg4fzbj2sz.23418vzkd4ko3.1g34ou07z4pev.1sp3yo9yz874pOptionally use kdnet.exe to confirm that the multiple physical functions are enabled.
C:\KDNET> kdnet.exe
Network debugging is supported on the following NICs:
busparams=141.0.0, Mellanox ConnectX-4 Lx Ethernet Adapter #2, Plugged in, Primary function, multiple physical functions are enabled.
busparams=141.0.1, Mellanox ConnectX-4 Lx Ethernet Adapter, KDNET is running on this NIC, Secondary function.
Network debugging is supported on the following USB controllers:
busparams=128.15.0, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft)
busparams=0.15.0, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft)
busparams=128.15.1, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft)
busparams=0.15.1, Standard USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller - 1.0 (Microsoft)
Disable the firewall on the host
On the host, disable the firewall for the debugger port.
Connecting WinDbg to the target for kernel debugging
On the host computer, open WinDbg. On the File menu, choose Kernel Debug. In the Kernel Debugging dialog box, open the Net tab. Paste in your port number and key that you saved in the notepad .txt file earlier. Select OK.
You can also start a WinDbg session by opening a Command Prompt window and entering the following command, where is the port you selected above, and is the key that was returned by kdnet.exe above. Paste in the key that you saved in the notepad .txt file earlier.
windbg -k -d net:port=<YourDebugPort>,key=<YourKey>
Reboot the target computer
Once the debugger is connected, reboot the target computer. One way to do reboot the PC is to use the shutdown -r -t 0 command from an administrator's command prompt.
After the target PC restarts, the debugger should connect automatically.
Once the machine reboots, then the NIC firmware will assign a new MAC address to the newly added KDNET PF, and dbgsettings::busparams will point to the newly added PF.
Finding the MAC address for the 2PF adapter
Since the newly added PF is a PCI bus configured port, there will be a new MAC address value assigned to the newly added PF by the NIC firmware. The kdnet.exe tool does not currently support displaying the MAC address for the added 2PF.
There are two ways of finding the new MAC address:
Use WinDbg/KD with a local KD session
Run the local kernel debugger windbg.exe -kl on the target.
Make sure you have access to the kdnet.pdb symbol file by running .reload /f kdnet.dll
Run .kdtargetmac command to get the MAC address.
kd> .kdtargetmac
Force unload of kdnet.dll
ModLoad: fffff800`18510000 fffff800`18557000 kdnet.dll
Loading symbols for fffff800`18510000 kdnet.dll -> kdnet.dll
The target machine MAC address in open-device format is: DC9840C151E8
Run the vendor provided firmware tools
One way to locate the MAC address is to run the vendor-provided firmware tools. Refer to the NIC vendor for information on downloading, installing, and using the vendor's tools.
...
Base MAC: 98039baa757c 4
Find the MAC address field. Calculate the KDNET 2PF MAC address value by sequentially adding one to the last digit of the root MAC device. So for the root device with an address of 98039baa757c, the KDNET 2PF device would have an address of 98039baa757d.
Restoring the previous configuration state - Removing the second PCI PF
You can remove the previously added PF from a device by using the kdnet -removepf option and the original bus.device.function value. The PF will be detached from the NIC and the PF-assigned resource will be released by the NIC firmware.
To remove the KDNET PF from the device, open an elevated command prompt and run the following command.
kdnet -removepf [bus.dev.fun] [host name/host ip address] [port number]
Where bus.dev.fun is the PCI location port of the NIC adapter where the PF was originally attached. This is the same PCI location originally passed to kdnet -addpf.
Using the -removepf option also re-enables kernel debugging over KDNET on the original bus.dev.fun.
C:\KDNET> kdnet -removepf 141.0.0 198.51.100.1 50001
Succeeded removing a Pci PF on :141.0.0. Please power off or reboot the machine.
Enabling network debugging on Mellanox ConnectX-4 Lx Ethernet Adapter #2.
Manage-bde.exe not present. Bitlocker presumed disabled.
The kdnet.exe -removepf command also will remove the NO_KDNIC attribute from the OS installation {default} loadoptions, since KDNET will be enabled on the original bus.dev.fun, that is the dbgsettings::busparams will point to the original network port. This will cause KDNIC to be used again, providing a network connection again on top of KDNET.
Once the PF is removed the machine needs to be rebooted for the BCD changes to be applied.
shutdown -r -t 0
Troubleshooting host adapter configuration
Verify the 2PF adapter is present in device manager
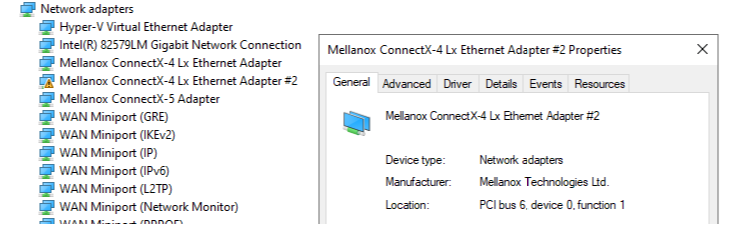
You can verify that the KDNET PF was added successfully by checking the new NIC adapter has a new bus.dev.fun port on the Windows Device Manager adapter list.
This diagram shows three different adapters, with Adapter #2 reserved for use by the kernel debugger.
Common error messages - adding a new PF
C:\KDNET> kdnet -addpf 28.0.0 192.168.137.1 50005
Device Name:\\.\Mlx5Util
Pci Bus:28.0.0
The PCI PF is already configured on this port: Error=(0x80004004) Failed PF operation on the debug device. The debug device is not configured for KDNET.
- Do not add/remove a PF on the root port where it is already added as a PF.
Common error messages - removing a PF
C:\KDNET> kdnet -removepf 28.0.1 192.168.137.1 50005
Adapter is not active: Error=(0x80070002)
Device Name:\\.\Mlx5Util
Pci Bus:28.0.1
Adapter is not active: Error=(0x80070002) Failed PF operation on the debug device. The debug device is not configured for KDNET
- Do not use an added PF port with the “-removepf/-addpf” command line parameter, because any operation on the added PF port will result in a failure (error: Adapter is not active on the port), since the vendor NIC inbox driver is set up to expressly not run on an added PF.
- Both command line options (-addpf/-removepf) must be used only on the root PCI device.
C:\KDNET> kdnet -removepf 28.0.0 192.168.137.1 50005
Device Name:\\.\Mlx5Util
Pci Bus:28.0.0
There is no PCI PF to remove on this port: Error=(0x80004005) Failed PF operation on the debug device. The debug device is not configured for KDNET
- If you add a new PF and then decide to remove it w/o rebooting it will result in a failure, since the vendor NIC firmware requires rebooting/resetting the NIC HW before it can recognize the newly added PF.
Common error messages - BCDEdit
NO_KDNIC is not present in the BCD OS {default} installation.
- It is not recommended to use bcdedit.exe to modify/change the debug device (dbgsettings) after adding a new PF. The kdnet -addpf/removepf command line options will configure the debug device and will also add/remove automatically the
NO_KDNICtoken to/from the{default}::loadoptions.
See also
Setting Up KDNET Network Kernel Debugging Automatically
Setting Up KDNET Network Kernel Debugging Manually
Setting up USB 3.0 xHCI-DBC kernel-mode debugging (KDUSB)
Setting Up USB KDNET EEM Kernel-Mode Debugging (KDNET-EEM-USB)