Boot integrity monitoring overview
To help Azure Trusted Launch better prevent malicious rootkit attacks on virtual machines (VMs), guest attestation through an Azure Attestation endpoint is used to monitor the boot sequence integrity. This attestation is critical to provide the validity of a platform's states.
Your Trusted Launch VM needs Secure Boot and virtual Trusted Platform Module (vTPM) to be enabled so that the attestation extensions can be installed. Microsoft Defender for Cloud offers reports based on Guest Attestation verifying status and that the boot integrity of your VM is set up correctly. To learn more about Microsoft Defender for Cloud integration, see Trusted Launch integration with Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Important
Automatic Extension Upgrade is now available for the Boot Integrity Monitoring - Guest Attestation extension. For more information, see Automatic Extension Upgrade.
Prerequisites
You need an active Azure subscription and a Trusted Launch VM.
Enable integrity monitoring
To enable integrity monitoring, follow the steps in this section.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select the resource (Virtual Machines).
Under Settings, select Configuration. On the Security type pane, select Integrity monitoring.
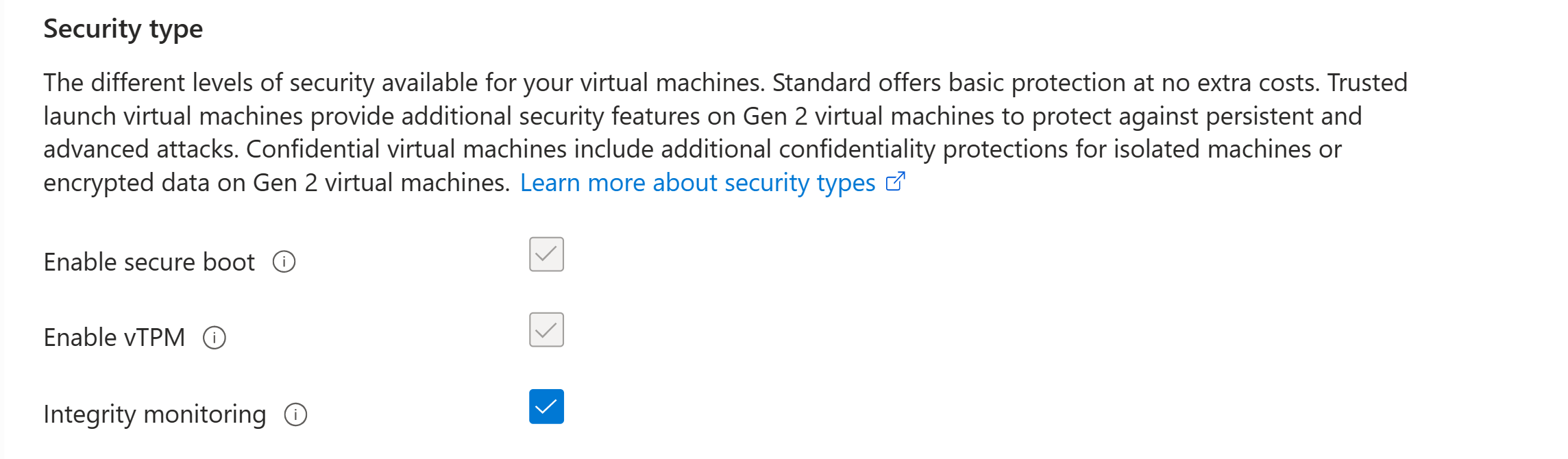
Save the changes.
On the VM Overview page, the security type for integrity monitoring should appear as Enabled.
This action installs the Guest Attestation extension, which you can refer to via the settings on the Extensions + Applications tab.
Troubleshooting guide for Guest Attestation extension installation
This section addresses attestation errors and solutions.
Symptoms
The Azure Attestation extension won't work properly when you set up a network security group (NSG) or a proxy. An error appears that looks similar to "Microsoft.Azure.Security.WindowsAttestation.GuestAttestation provisioning failed."
Solutions
In Azure, NSGs are used to help filter network traffic between Azure resources. NSGs contain security rules that either allow or deny inbound network traffic, or outbound network traffic from several types of Azure resources. The Azure Attestation endpoint should be able to communicate with the Guest Attestation extension. Without this endpoint, Trusted Launch can't access guest attestation, which allows Microsoft Defender for Cloud to monitor the integrity of the boot sequence of your VMs.
To unblock Azure Attestation traffic in NSGs by using service tags:
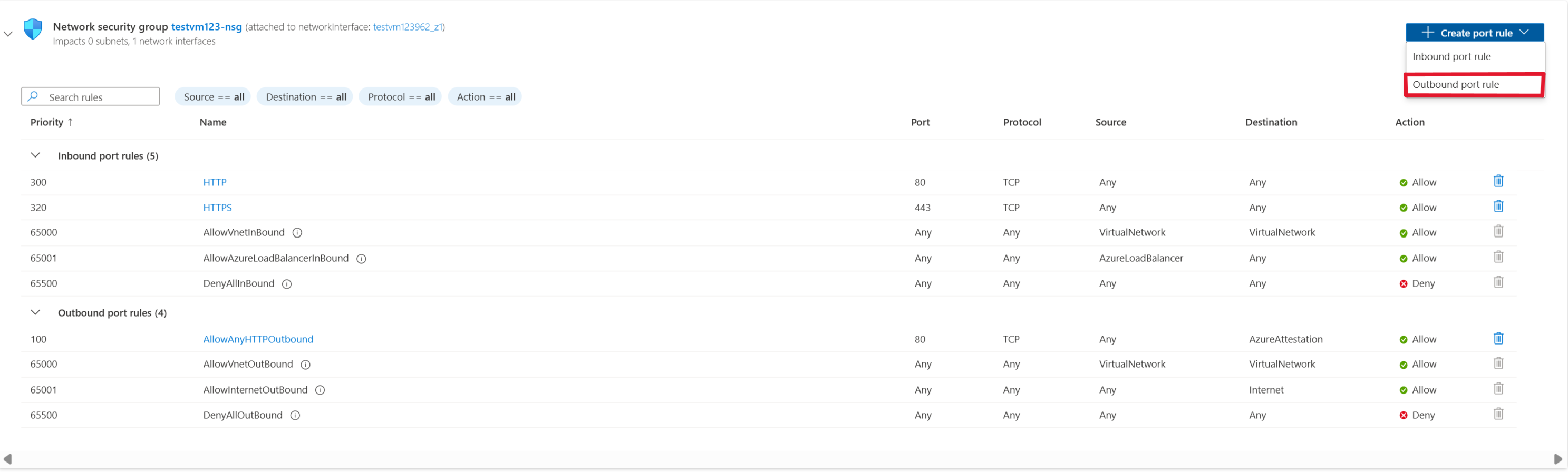
Go to the VM that you want to allow outbound traffic.
On the leftmost pane, under Networking, select Networking settings.
Then select Create port rule > Outbound port rule.
To allow Azure Attestation, you make the destination a service tag. This setting allows for the range of IP addresses to update and automatically set rules that allow Azure Attestation. Set Destination service tag to AzureAttestation and set Action to Allow.
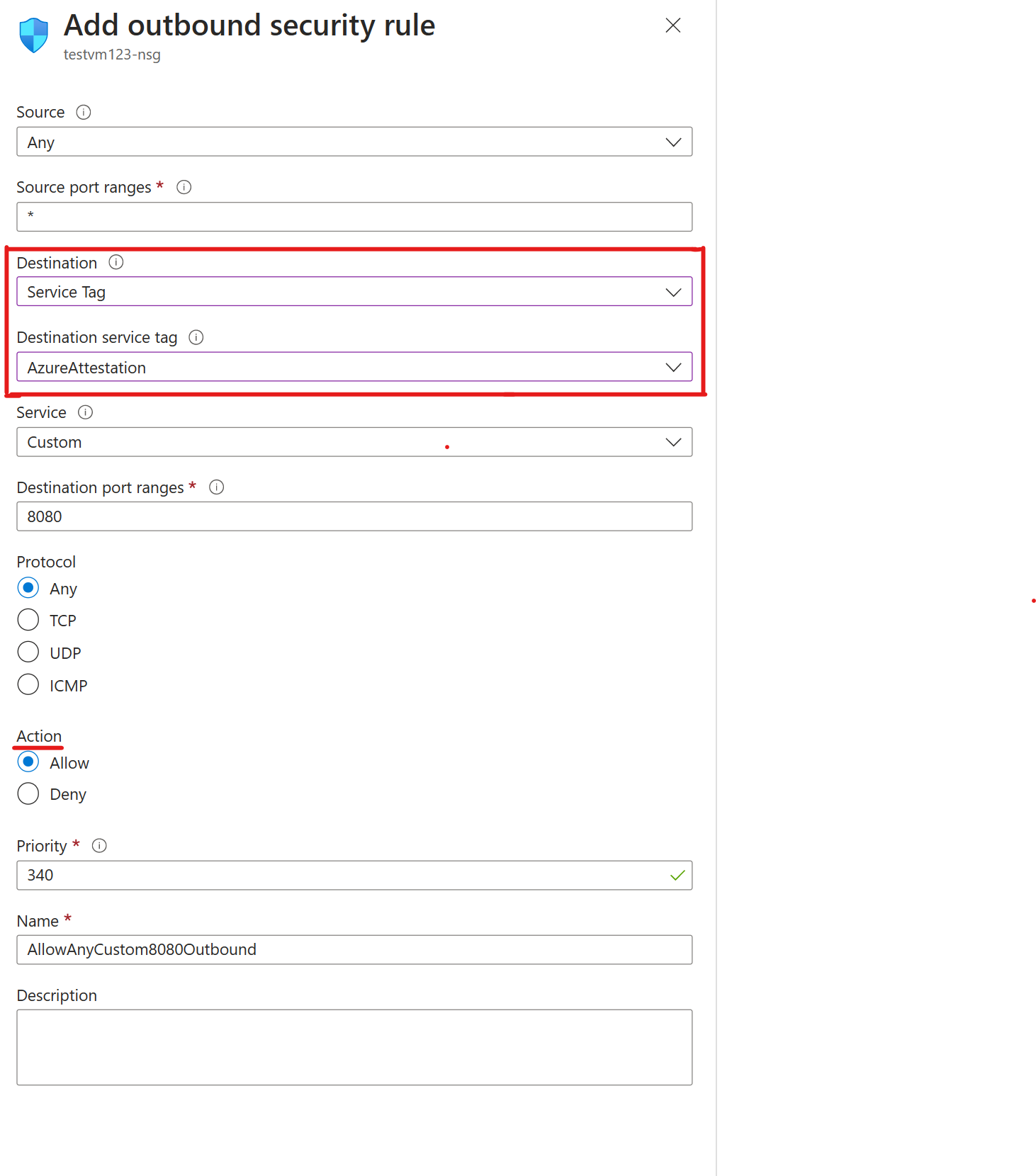
Firewalls protect a virtual network, which contains multiple Trusted Launch VMs. To unblock Azure Attestation traffic in a firewall by using an application rule collection:
Go to the Azure Firewall instance that has traffic blocked from the Trusted Launch VM resource.
Under Settings, select Rules (classic) to begin unblocking guest attestation behind the firewall.
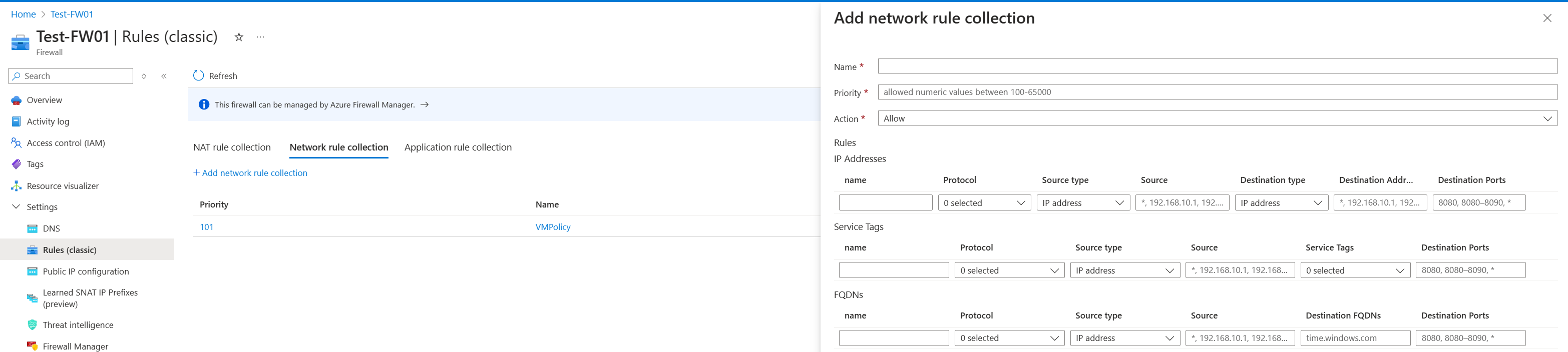
Under Network rule collection, select Add network rule collection.
Configure the name, priority, source type, and destination ports based on your needs. Set Service tag name to AzureAttestation and set Action to Allow.
To unblock Azure Attestation traffic in a firewall by using an application rule collection:
Go to the Azure Firewall instance that has traffic blocked from the Trusted Launch VM resource.
The rules collection must contain at least one rule that targets fully qualified domain names (FQDNs).
Select the application rule collection and add an application rule.
Select a name and a numeric priority for your application rules. Set Action for the rule collection to Allow.
Configure the name, source, and protocol. The source type is for a single IP address. Select the IP group to allow multiple IP addresses through the firewall.
Regional shared providers
Azure Attestation provides a regional shared provider in each available region. You can choose to use the regional shared provider for attestation or create your own providers with custom policies. Any Microsoft Entra user can access shared providers. The policy associated with it can't be changed.
Note
You can configure the source type, service, destination port ranges, protocol, priority, and name.
Related content
Learn more about Trusted Launch and deploying a Trusted Launch VM.