Märkus.
Juurdepääs sellele lehele nõuab autoriseerimist. Võite proovida sisse logida või kausta vahetada.
Juurdepääs sellele lehele nõuab autoriseerimist. Võite proovida kausta vahetada.
When you publish a Copilot Studio agent, you deploy it to the channels you select. A channel is the integration point where an end-user can interact with a Copilot Studio agent. The client is the interface through which users interact with the agent, such as a chat window in Microsoft Teams or a custom application.
Deploy agents to channels and clients
You can deploy an agent to a channel after you publish it. Copilot Studio natively deploys agents to many channels, such as Teams, Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat, SharePoint, Power Pages, and more. You can use advanced scenarios such as custom applications or web clients by using the Direct Line API.
The Direct Line API enables communication with a Copilot Studio agent through a REST API. It supports both HTTP GET requests to explicitly request messages and WebSocket for real-time delivery of messages without requiring client-side requests. When multiple conversations occur between Azure Bot Service channels and a Direct Line connection to the Copilot Studio agent, each external conversation must be mapped and relayed so both entities remain synchronized.
You can choose from many clients, including React Web Chat and WebChat JS. You need to select a client when you deploy to the web or custom application channels because these channels don't have a built-in client. Native channels that Copilot Studio deploys to already have a client.
Depending on the client and channel, support for Markdown, Adaptive Cards, and other message formats might not be available.
Hand off a conversation to a live agent
Copilot Studio agents can escalate to a live agent who takes over the conversation. Hand-off requires Dynamics 365 Omnichannel or another engagement hub solution.
A full handoff to an engagement hub follows this pattern:
- An end user interacts with the engagement hub's chat canvas.
- The engagement hub routes the incoming chat through its routing capabilities.
- A custom adapter relays the incoming chat messages to the Copilot Studio agent.
- Once the end user triggers a handoff, Copilot Studio initiates the handoff with full chat context.
- The custom adapter intercepts the handoff message and context, and seamlessly routes the conversation to an agent.
- The end user's chat is handed off to an agent, who can resume the conversation.
Choosing an approach to enable hand-off to a live agent
You can use two approaches to connect Copilot Studio with an engagement hub so they work together to handle conversations.
Pattern 1: Bot-as-an-Agent—Engagement hub at the front, Copilot Studio at the back
Use the Engagement Hub Chat Canvas at the front to handle conversation hand-offs to a live agent. Most standard integrations with first-party or third-party contact centers use this approach.
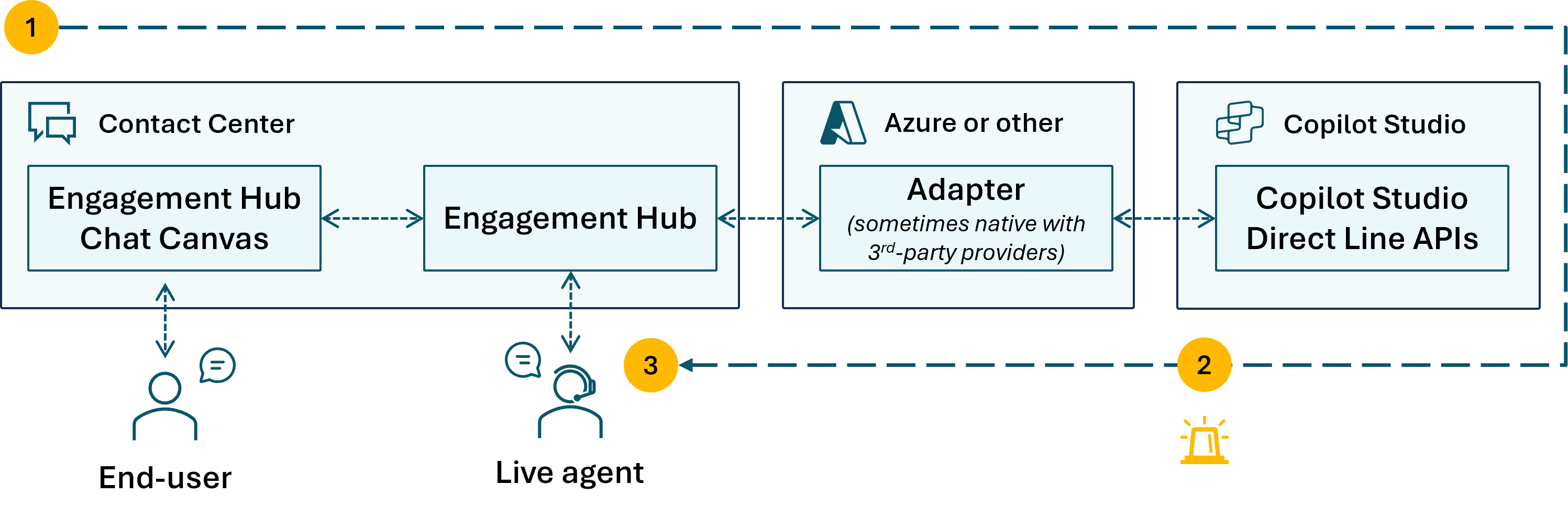
- The user chats by using the Engagement Hub Chat Canvas. An adapter relays messages between the user and a Copilot Studio agent through the Direct Line APIs.
- When the Copilot Studio agent APIs send an escalation event, the Engagement Hub takes over the conversation.
- A live agent resumes the chat with the user.
Benefits
- Easier to set up front-end configuration without much overhead.
- Agent messaging and capabilities are maintained in full fidelity.
- Existing engagement hub capabilities (agent takeover, sentiment analysis, supervisory, and so on) continue to work as-is.
Limitations
- No ability to intercept human agent messages upon escalation unless the engagement hub supports an API.
- No whisper mode unless the engagement hub supports it.
- No control over user experience of responses (messages, Adaptive Cards) emitted from the bot.
- Some specific features, like thumbs up and thumbs down, aren't supported.
Pattern 2: Bot-in-the-Loop—Copilot Studio at the front, engagement hub at the back
An alternative approach to enable hand-off to a live agent is to use Copilot Studio at the front and integrate through engagement hub APIs with a skill. This approach is more complex and requires heavy customization.
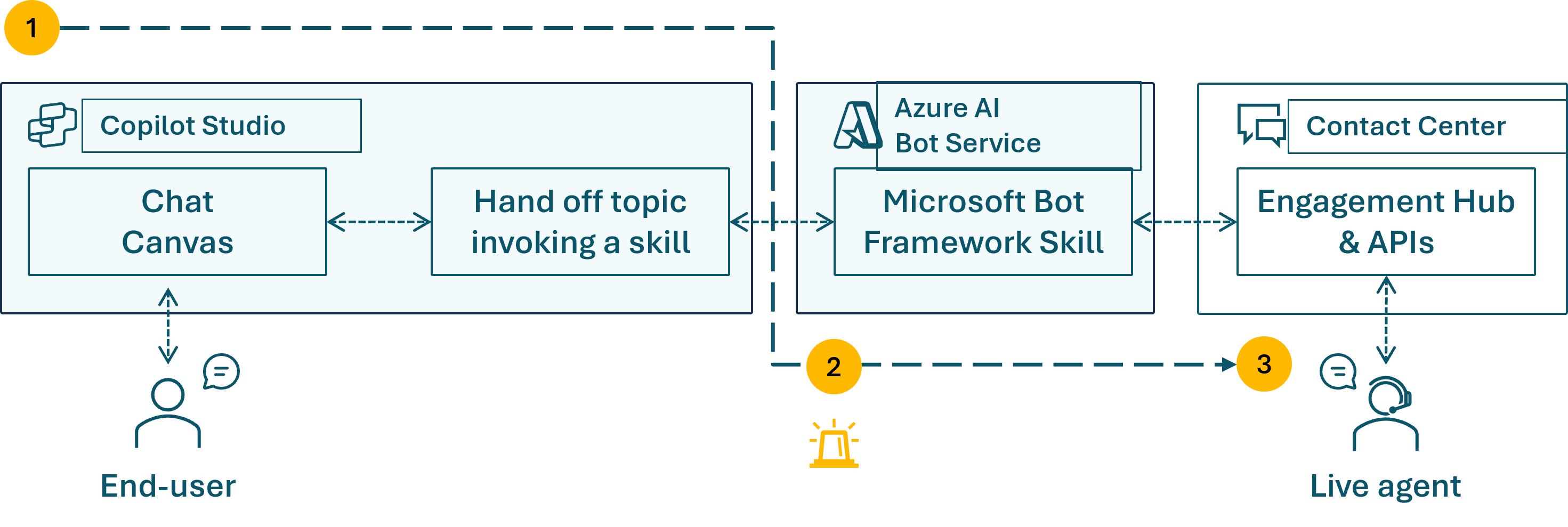
- The user chats with the Copilot Studio agent through the Chat Canvas (the standard one or a custom one that integrates with Copilot Studio standard endpoints).
- When an escalation event occurs, Copilot Studio triggers a Microsoft 365 Agent SDK skill, which is routed through the Microsoft Bot Framework Skill in Azure AI Bot Service.
- The skill relays messages back and forth between the contact center live agent and the user through the Engagement Hub APIs.
Benefits
- Copilot Studio is always in the loop, including agent messages.
- You have full control over how responses (messages, Adaptive Cards, and more) that the bot sends show to the user.
- The agent can get help in whisper mode (also known as agent assist).
- The bot can route to the right agent based on skill.
Limitations
- The engagement hub must be extensible enough to support this pattern.
- Many hops between systems.
- Requires a pro-developer and Platform as a Service (PaaS) approach for the Bot Framework skill.
- Heavy overhead and integrations of the hub with Copilot Studio.
- The live agent is limited to using a compatible chat canvas.
- The channel provider can't customize their agent messages to show up in the canvas.
- Agent takeover and supervisor capabilities likely aren't possible.
- Credits continue to be consumed while chatting with a live agent.