Märkus.
Juurdepääs sellele lehele nõuab autoriseerimist. Võite proovida sisse logida või kausta vahetada.
Juurdepääs sellele lehele nõuab autoriseerimist. Võite proovida kausta vahetada.
Natural language understanding (NLU) is at the core of how Copilot Studio agents make sense of user queries and provide relevant, contextual responses. A well-defined approach to intent recognition, entity extraction, and fallback handling ensures that agents deliver efficient, natural conversations that align with business needs.
When a user enters something to an agent, it's known as an utterance. The agent needs to break that utterance into intent and entities, making the agent's response feel both natural and efficient.
What is language understanding?
Language understanding (LU) is a subfield of Natural Language Processing (NLP) focused on enabling machines to comprehend the meaning, intent, and context behind human language.
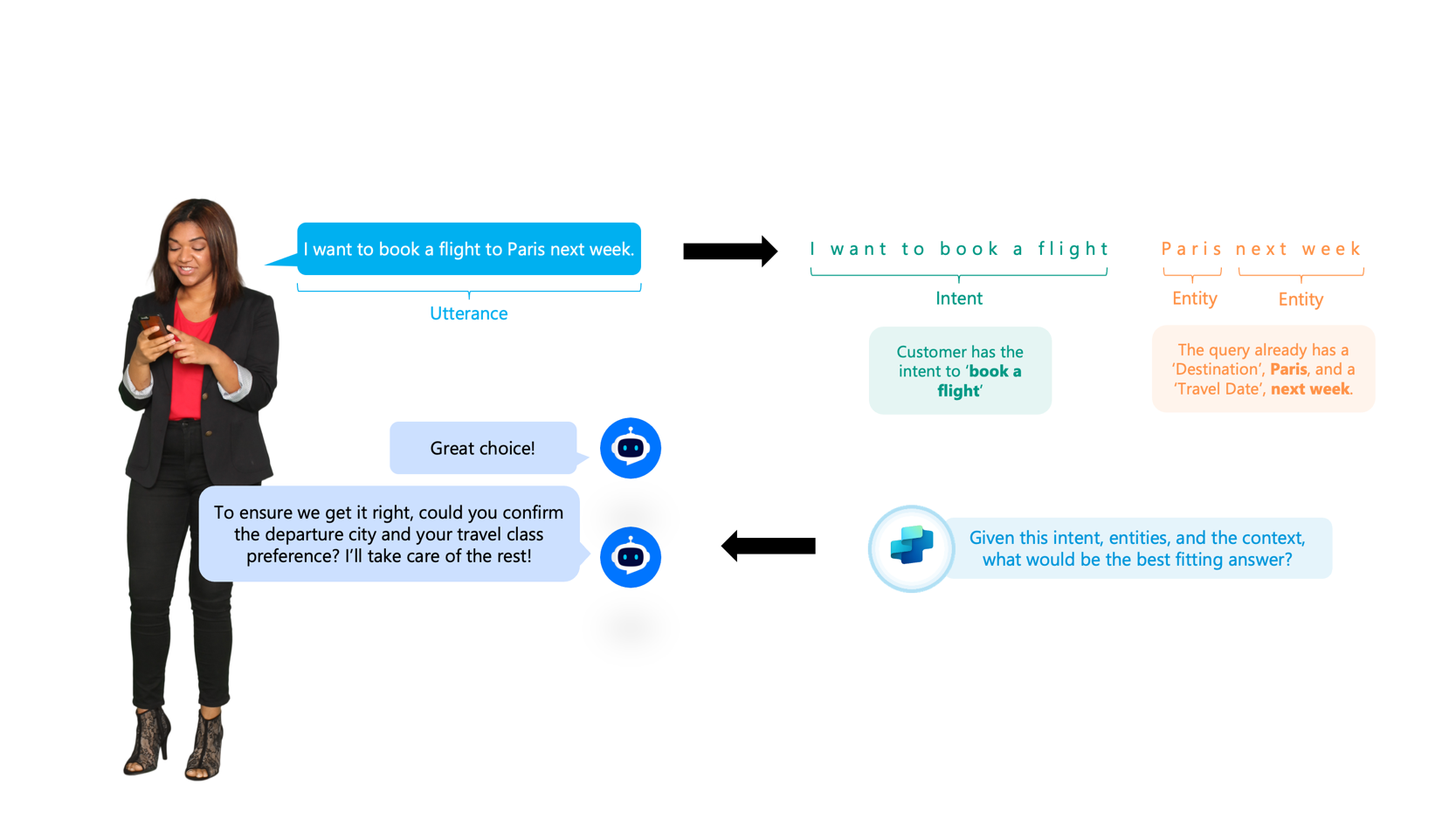
Diagram showing how a user's message is broken down into intent and entities. A person types, "I want to book a flight to Paris next week." The message is labeled as an utterance. The phrase "I want to book a flight" is identified as the intent, and "Paris" and "next week" are identified as entities. The system then asks for more details like departure city and travel class. The diagram illustrates how the agent uses intent, entities, and context to determine the best response.
Language understanding involves:
- Intent recognition: Identifying what the user wants to achieve (for example, "Book a flight to Paris next week" maps to the intent to book a flight).
- Entity extraction: Extracting key details such as dates, locations, or names (for example, "Paris" as the destination, "next week" as the travel date).
- Context awareness: Maintaining continuity and resolving ambiguities in conversation (for example, understanding pronouns or references).
- Handling ambiguities: Using context to resolve words with multiple meanings (for example, "bank" as a financial institution or river bank).
Language understanding in Copilot Studio
Copilot Studio has a flexible model for language understanding, with multiple configuration options.
Generative orchestration
Generative orchestration uses language models to intelligently chain together topics, actions, and knowledge. This capability enables multi-intent recognition, advanced entity extraction, and dynamic plan generation for complex queries.
This method is the default for Copilot Studio. This approach recognizes multiple intents or topics in a single utterance, automatically chains actions and knowledge sources, and generates unified responses. It's especially useful for handling complex conversations that span multiple business areas. Generative orchestration has limits, such as five messages per topic or action chain, and 128 topics or actions per orchestration, but it provides a powerful way to scale conversational breadth.
Learn more in Apply generative orchestration capabilities.
Classic orchestration
Classic orchestration uses trigger phrases and deterministic topic routing. If a user's utterance matches a trigger phrase, the corresponding topic runs. If there's no match, fallback mechanisms search knowledge sources or prompt the user for clarification.
Built-in NLU
This approach was the default but is now the fallback approach. Copilot Studio provides an out-of-the-box NLU model that supports trigger phrases, predefined entities, and custom entities. This model enables agents to identify user intent and extract key details like dates, destinations, or quantities directly from a query.
NLU+
For high accuracy, use the NLU+ option. The NLU+ option is ideal for large enterprise-grade applications. These types of applications typically consist of a large number of topics and entities, and use a large number of training samples. Also, if you have a voice-enabled agent, your NLU+ training data is also used to optimize your speech recognition capabilities.
Azure CLU integration
For more advanced scenarios where you can't use the default generative orchestration, you can integrate Azure Conversational Language Understanding (CLU). CLU provides greater customization, multilingual support, and complex entity extraction (for example, multiple "from" entities). You must map CLU intents to Copilot Studio topics to keep them in sync. This option is especially valuable for industry-specific vocabularies, non-English languages, or scenarios that require higher accuracy.
Key features and limitations
This table compares the three language-understanding approaches in Copilot Studio. It highlights their key features and limitations to help you choose the right model for your agent's complexity, scale, and accuracy needs.
| Features and limitations | Generative orchestration | Built-in NLU model | Custom Azure CLU model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Features |
|
|
|
| Limits |
|
|
|
Learn more in Natural language understanding (NLU) overview.
Topic structure and fallback
Topics have shifted away from a rigid, intent-based path into a more flexible, orchestration-first approach. Rather than relying solely on predefined triggers and paths, topics now act as modular instructions that the agent can call upon when orchestrating a conversation. Generative orchestration handles most routing by interpreting user input dynamically, and topics provide structured fallback when precision is needed.
The more traditional structured topic design makes conversations feel natural and efficient. Topics can be entry points triggered by user utterances or reusable subtopics called by redirects or system events. Disambiguation topics help avoid confusion when multiple topics could be triggered, while fallback and conversational boosting topics provide safety nets when the agent can't confidently match intent. You can also layer on generative answers to pull from external knowledge sources, ensuring users rarely go without a response.
Learn more in Apply best practices to authoring topics.
Localization and languages
The language used by a Copilot Studio agent is determined by the value of the system variable: System.User.Language.
This variable acts as the central control point for all language-related behavior in the agent. You can set its value manually, programmatically, or detect it automatically.
How does it work?
Search knowledge in the user's language: Copilot Studio uses the value of
System.User.Languageto search knowledge sources in the specified language. This approach means that even if a user asks a question in one language, the agent translates the search query to the language set inSystem.User.Language(auto translation for search query).Respond in the user's language: The agent generates answers in the language specified by
System.User.Language, regardless of the language used in the question or the original documents (auto translation for answer generation).Manual override: You can manually set the value of
System.User.Languageto force the agent to operate in a specific language. This feature is useful for testing or for scenarios where you must explicitly control the language. Learn more in Configure and create multilingual agents.
Auto detect spoken language
You can configure Copilot Studio to automatically detect the user's spoken or written language and set the System.User.Language variable accordingly. This feature enables seamless multilingual experiences without requiring users to specify their language preference.
How auto-detection works
- Trigger-based detection: When the bot receives a message, a trigger starts a language detection flow.
- Set system variable: The bot assigns the detected language to
System.User.Language. - Dynamic response: The agent continues the conversation in the detected language, both searching knowledge and generating responses accordingly.
Benefits
- Personalized experience: Users interact in their preferred language without manual configuration.
- Consistent experience: All responses and knowledge retrievals align with the detected or set language.
- Scalable solution: Supports global deployments with minimal configuration.
Tip
Review the sample solution that demonstrates how to enable Copilot Studio agents to automatically detect a user's spoken language and switch to one of the maker‑approved languages for the agent: Auto-detect language for generative responses
Best practices for localization
- Configure supported languages: Define primary and secondary languages for your agent. Use localization files (JSON or ResX) to provide translations for prompts, messages, and topics.
- Test multilingual scenarios: Simulate user interactions in different languages to ensure smooth transitions and accurate responses.
- Use auto-translation: Rely on Copilot Studio's built-in translation for knowledge search and answer generation, but provide custom translations for critical or nuanced content.
- Monitor and refine: Use analytics to track language usage and improve localization coverage over time.
Copilot Studio agent language approaches:
- Separate agents per language.
- Single multilingual agents with pre-authored translations.
- Real-time multilingual agents, using translation services between user and agent.
The right approach depends on use, concerns of separation, scale, update cadence, and available resources.
Identified technical challenges
Typical challenges include ensuring that Azure CLU and Copilot Studio topics stay synchronized, handling ambiguous utterances, and scaling multilingual deployments. Early identification of these roadblocks lets you plan mitigation strategies, such as fallback configurations, bulk testing of trigger phrases, or relay-based translation services.
The goal of language understanding is to ensure that every agent can interpret user queries accurately, adapt to diverse languages and scenarios, and gracefully handle the unexpected. This goal creates a strong foundation for building reliable, engaging, and efficient Copilot Studio conversations.