Rewrite a URL with Azure Application Gateway - Azure portal
This article describes how to use the Azure portal to configure an Azure Application Gateway v2 SKU instance to rewrite a URL.
Note
The URL Rewrite feature is available only for the Standard_v2 and Web Application Firewall_v2 SKU of Application Gateway. When URL Rewrite is configured on a Web Application Firewall-enabled gateway, Web Application Firewall evaluation takes place on the rewritten request headers and the URL. For more information, see Use URL rewrite or host header rewrite with Web Application Firewall (WAF_v2 SKU).
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Before you begin
You need to have an Application Gateway v2 SKU instance to finish the steps in this article. Rewriting a URL isn't supported in the v1 SKU. If you don't have the v2 SKU, create an Application Gateway v2 SKU instance before you begin.
Sign in to Azure
Sign in to the Azure portal with your Azure account.
Configure a URL rewrite
In the following example, whenever the request URL contains /article, the URL path and URL query string are rewritten. For example:
contoso.com/article/123/fabrikam -> contoso.com/article.aspx?id=123&title=fabrikam
Select All resources, and then select your application gateway.
In the service pane, select Rewrites.
Select Rewrite set.

Enter a name for the rewrite set and associate it with a routing rule:
In the Name box, enter the name for the rewrite set.
In the Associated routing rules list, select one or more of the rules. This step associates the rewrite configuration to the source listener via the routing rule. Select only those routing rules not already associated with other rewrite sets. The rules already associated with other rewrite sets are dimmed.
Select Next.

Create a rewrite rule:
Select Add rewrite rule.

In the Rewrite rule name box, enter a name for the rewrite rule.
In the Rule sequence box, enter a number.
In this example, we rewrite a URL path and a URL query string only when the path contains
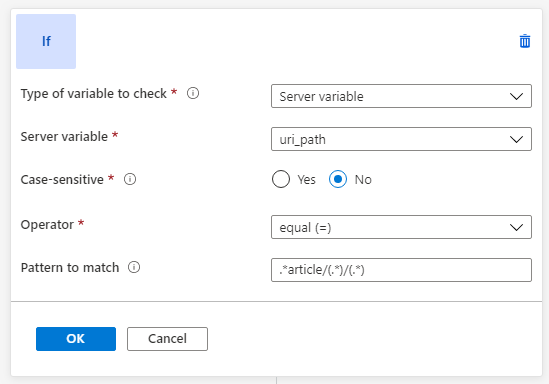
/article. To do this step, add a condition to evaluate whether the URL path contains/article:Select Add condition, and then select the box that contains the If instructions to expand it.
In the Type of variable to check list, select Server variable. In this example, we want to check the pattern
/articlein the URL path.In the Server variable list, select
uri_path.Under Case-sensitive, select No.
In the Operator list, select equal (=).
Enter a regular expression pattern. In this example, we use the pattern
.*article/(.*)/(.*)Parentheses ( ) are used to capture the substring for later use in composing the expression for rewriting the URL path. For more information, see Pattern matching and capturing.
Select OK.
Add an action to rewrite the URL and the URL path:
In the Rewrite type list, select URL.
In the Action type list, select Set.
Under Components, select Both URL path and URL query string.
In the URL path value, enter the new value of the path. In this example, we use
/article.aspx.In the URL query string value, enter the new value of the URL query string. In this example, we use
id={var_uri_path_1}&title={var_uri_path_2}.The
{var_uri_path_1}and{var_uri_path_2}paths are used to fetch the substrings captured while evaluating the condition in the expression.*article/(.*)/(.*)Select OK.

Select Create to create the rewrite set.
Verify that the new rewrite set appears in the list of rewrite sets.

Verify the URL rewrite through access logs
Observe the following fields in access logs to verify if the URL rewrite happened according to your expectations:
originalRequestUriWithArgs: This field contains the original request URL.requestUri: This field contains the URL after the rewrite operation on Application Gateway.
For more information on all the fields in the access logs, see Access log.
Related content
To learn more about how to set up rewrites for some common use cases, see Common rewrite scenarios.