Create a custom consumer for service hooks
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
With service hooks, you can notify third-party systems about events that occur in your project. You can use a custom consumer to send an HTTP message to the endpoint that’s defined in the extension's manifest.
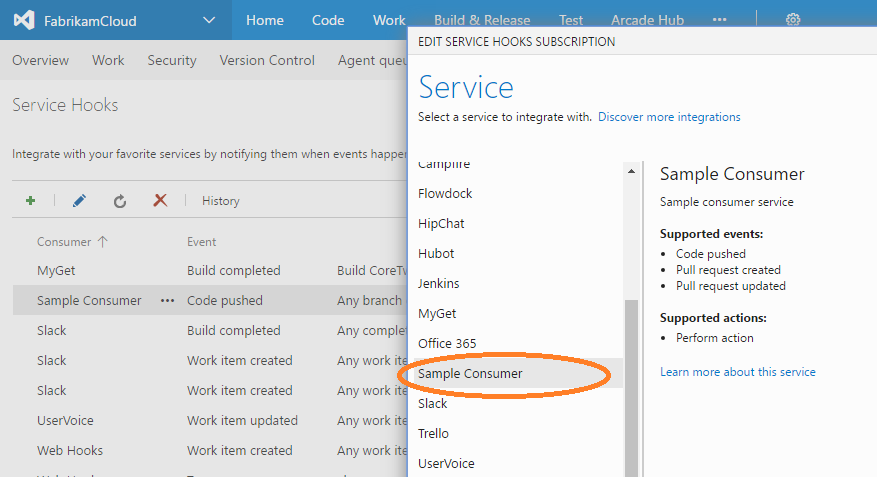
This article walks through developing an extension that implements a sample consumer service, which includes the following events and actions.
- Supported events that trigger the following actions:
- Code pushed
- Pull request created
- Pull request updated
- Supported actions to take when events occur:
- Do action (Send HTTP message)
Note
In this article, we refer to the home directory for your project as "home".
For more information, see the Extension example GitHub repo. For a list of all supported events you can use as triggers for your custom consumer extension, see List of event types.
Tip
Check out our newest documentation on extension development using the Azure DevOps Extension SDK.
How service hooks work
Service hook publishers define a set of events. Subscriptions listen and wait for the events and define actions for when the event is triggered.

This is a general description of how all our service hook implementations work. For our case, we specify our consumer defined by an extension, as well as the specified action for when an event occurs.
Create the extension
Add the specific contribution for custom consumer implementation to your basic manifest file. See the following example of how your manifest should look after you add the contribution.
{
"manifestVersion": 1,
"id": "samples-service-hooks-consumer",
"version": "0.1.2",
"name": "Service Hooks Sample",
"description": "A simple extension that demonstrates how to contribute a consumer service into service hooks.",
"publisher": "fabrikam",
"public": false,
"icons": {
"default": "images/logo.png"
},
"scopes": [],
"files": [
{
"path": "images",
"addressable": true
}
],
"content": {
"details": {
"path": "readme.md"
}
},
"categories": [
"Developer samples"
],
"targets": [
{
"id": "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Services"
}
],
"contributions": [
{
"id": "consumer",
"type": "ms.vss-servicehooks.consumer",
"targets": [
"ms.vss-servicehooks.consumers"
],
"properties": {
"id": "consumer",
"name": "Sample Consumer",
"description": "Sample consumer service",
"informationUrl": "https://aka.ms/vsoextensions",
"inputDescriptors": [
{
"id": "url",
"isRequired": true,
"name": "URL",
"description": "URL to post event payload to",
"inputMode": "textbox"
}
],
"actions": [
{
"id": "performAction",
"name": "Perform action",
"description": "Posts a standard event payload",
"supportedEventTypes": [
"git.push",
"git.pullrequest.created",
"git.pullrequest.updated"
],
"publishEvent": {
"url": "{{{url}}}",
"resourceDetailsToSend": "all",
"messagesToSend": "all",
"detailedMessagesToSend": "all"
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
Note
Remember to update the publisher property.
For each contribution in your extension, the manifest defines the following items.
- Type of contribution - consumer service (ms.vss-servicehooks.consumer) in this case
- Contribution target - consumer services (ms.vss-servicehooks.consumers) in this case
- Properties that are specific to each type of contribution
Consumers have the following properties.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| id | Unique ID for your consumer service. |
| name | Name of the custom consumer, which is visible during service hook subscription creation. |
| description | Describes your consumer service. |
| informationUrl | Find more info about your extension. |
| inputDescriptors | Inputs to be used by users that are creating subscriptions with the consumer service. |
| actions | Describes the actions to take and which events trigger those actions. |
Actions for your consumer have the following properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| id | ID for your action service. |
| name | Name of the action. |
| description | Detailed description of the action. |
| supportedEventTypes | Array of trigger types for which this action can be used. For more information, see List of event types. |
| publishEvent.url | URL where HTTP message gets sent to. It can be templated by values provided by inputDescriptors. Their actual values get defined by the user when the subscription gets created. |
- Deploy your extension to your Azure DevOps organization and test it.