Rule set actions
An Azure Front Door rule set consist of rules with a combination of match conditions and actions. This article provides a detailed description of actions you can use in a rule set. An action defines the behavior that gets applied to a request type that a match condition(s) identifies. In a rule set, a rule can have up to five actions. Front Door also supports server variable in a rule set action.
The following actions are available for use in a rule set:
Route configuration override
The route configuration override action is used to override the origin group or the caching configuration for the request. You can choose to override or honor the origin group configurations specified in the route. However, when you override the route configuration, you must configure caching. Otherwise, caching gets disabled for the request.
You can also override how files get cached for specific requests, including:
- Override the caching behavior specified by the origin.
- How query string parameters are used to generate the request's cache key.
- The time to live (TTL) value to control how long contents stay in cache.
Properties
| Property | Supported values |
|---|---|
| Override origin group |
|
| Caching |
|
When Override origin group is set to Yes, set the following properties:
| Property | Supported values |
|---|---|
| Origin group | The origin group that the request should be routed to. This setting overrides the configuration specified in the Front Door endpoint route. |
| Forwarding protocol | The protocol for Front Door to use when forwarding the request to the origin. Supported values are HTTP only, HTTPS only, Match incoming request. This setting overrides the configuration specified in the Front Door endpoint route. |
When Caching is set to Enabled, set the following properties:
| Property | Supported values |
|---|---|
| Query string caching behavior |
|
| Query parameters | The list of query string parameter names, separated by commas. This property is only set when Query string caching behavior is set to Ignore Specified Query Strings or Include Specified Query Strings. |
| Compression |
|
| Cache behavior |
|
| Cache duration | When Cache behavior is set to Override always or Override if origin missing, these fields must specify the cache duration to use. The maximum duration is 366 days. This property is only set when Cache behavior is set to Override always or Override if origin missing.
|
Examples
In this example, we route all matched requests to an origin group named MyOriginGroup, regardless of the configuration in the Front Door endpoint route.
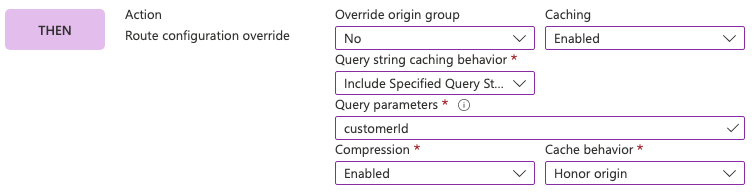
In this example, we set the cache key to include a query string parameter named customerId. Compression is enabled, and the origin's caching policies are honored.
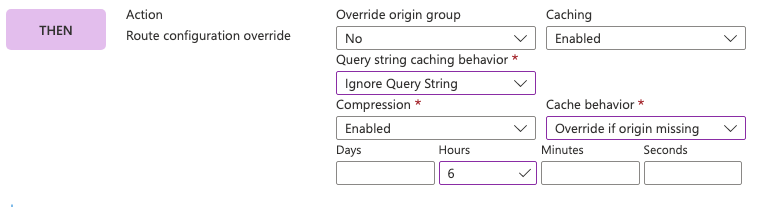
In this example, we override the cache expiration to 6 hours for matched requests that don't specify a cache duration already. Front Door ignores the query string when it determines the cache key, and compression is enabled.
Modify request header
Use the modify request header action to modify the headers in the request when it's sent to your origin.
Properties
| Property | Supported values |
|---|---|
| Operator |
|
| Header name | The name of the header to modify. |
| Header value | The value to append or overwrite. |
Example
In this example, we append the value AdditionalValue to the MyRequestHeader request header. If the origin set the response header to a value of ValueSetByClient, then after this action is applied, the request header would have a value of ValueSetByClientAdditionalValue.
Note
Certain Azure Front Door reserved headers can't be modified using rules engine actions, including the actions to modify request headers and response headers. The following list of reserved headers can't be modified, along with any headers prefixed with x-ec and x-fd.
Accept-RangesHostConnectionContent-LengthTransfer-EncodingTELast-ModifiedKeep-AliveExpectUpgradeIf-Modified-SinceIf-Unmodified-SinceIf-None-MatchIf-MatchRangeIf-RangeX-Ms-ViaX-Ms-Force-RefreshX-MSEdge-RefWarningForwardedViaX-Forwarded-ForX-Forwarded-ProtoX-Forwarded-HostX-Azure-RequestChainX-Azure-FDIDX-Azure-RequestChainv2X-Azure-Ref
Modify response header
Use the modify response header action to modify headers that are present in responses before they're returned to your clients.
Properties
| Property | Supported values |
|---|---|
| Operator |
|
| Header name | The name of the header to modify. |
| Header value | The value to append or overwrite. |
Example
In this example, we delete the header with the name X-Powered-By from the responses before they're returned to the client.
Note
Certain Azure Front Door reserved headers can't be modified using rules engine actions, including the actions to modify request headers and response headers. The following list of reserved headers can't be modified, along with any headers prefixed with x-ec and x-fd.
Accept-RangesHostConnectionContent-LengthTransfer-EncodingTELast-ModifiedKeep-AliveExpectUpgradeIf-Modified-SinceIf-Unmodified-SinceIf-None-MatchIf-MatchRangeIf-RangeX-Ms-ViaX-Ms-Force-RefreshX-MSEdge-RefWarningForwardedViaX-Forwarded-ForX-Forwarded-ProtoX-Forwarded-HostX-Azure-RequestChainX-Azure-FDIDX-Azure-RequestChainv2X-Azure-Ref
URL redirect
Use the URL redirect action to redirect clients to a new URL. Clients are sent a redirection response from Front Door. Azure Front Door supports dynamic capture of URL path with {url_path:seg#} server variable, and converts URL path to lowercase or uppercase with {url_path.tolower} or {url_path.toupper}. For more information, see Server variables.
Properties
| Property | Supported values |
|---|---|
| Redirect type | The response type to return to the requestor.
|
| Redirect protocol |
|
| Destination host | The host name you want the request to be redirected to. Leave blank to preserve the incoming host. |
| Destination path | The path to use in the redirect. Include the leading /. Leave blank to preserve the incoming path. |
| Query string | The query string used in the redirect. Don't include the leading ?. Leave blank to preserve the incoming query string. |
| Destination fragment | The fragment to use in the redirect. Leave blank to preserve the incoming fragment. |
Example
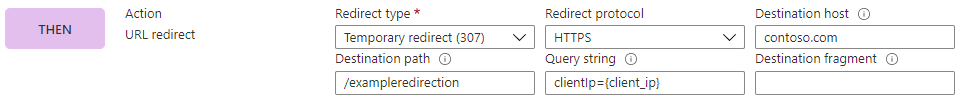
In this example, we redirect the request to https://contoso.com/exampleredirection?clientIp={client_ip}, while preserving the fragment. An HTTP Temporary Redirect (307) is used. The IP address of the client is used in place of the {client_ip} token within the URL by using the client_ip server variable.
URL rewrite
Use the URL rewrite action to rewrite the path of a request that's en route to your origin. Azure Front Door supports dynamic capture of URL path with {url_path:seg#} server variable, and converts URL path to lowercase or uppercase with {url_path.tolower} or {url_path.toupper}. For more information, see Server variables.
Properties
| Property | Supported values |
|---|---|
| Source pattern | Define the source pattern in the URL path to replace. Currently, source pattern uses a prefix-based match. To match all URL paths, use a forward slash (/) as the source pattern value. |
| Destination | Define the destination path to use in the rewrite. The destination path overwrites the source pattern. |
| Preserve unmatched path | If set to Yes, the remaining path after the source pattern is appended to the new destination path. |
Example
In this example, we rewrite all requests to the path /redirection, and don't preserve the remainder of the path.
Important
Azure Front Door (classic) will be retired on March 31, 2027. To avoid any service disruption, it is important that you migrate your Azure Front Door (classic) profiles to Azure Front Door Standard or Premium tier by March 2027. For more information, see Azure Front Door (classic) retirement.
In Azure Front Door (classic), a Rules engine can consist up to 25 rules containing matching conditions and associated actions. This article provides a detailed description of each action you can define in a rule.
An action defines the behavior that gets applied to the request type that matches the condition or set of match conditions. In the Rules engine configuration, a rule can have up to 10 matching conditions and 5 actions. You can only have one Override Routing Configuration action in a single rule.
The following actions are available to use in Rules engine configuration.
Modify request header
Use these actions to modify headers that are present in requests sent to your backend.
Required fields
| Action | HTTP header name | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Append | When this option gets selected and the rule matches, the header specified in Header name gets added to the request with the specified value. If the header is already present, the value is appended to the existing value. | String |
| Overwrite | When this option is selected and the rule matches, the header specified in Header name gets added to the request with the specified value. If the header is already present, the specified value overwrites the existing value. | String |
| Delete | When this option gets selected with matching rules and the header specified in the rule is present, the header gets deleted from the request. | String |
Modify response header
Use these actions to modify headers that are present in responses returned to your clients.
Required fields
| Action | HTTP Header name | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Append | When this option gets selected and the rule matches, the header specified in Header name gets added to the response by using the specified Value. If the header is already present, Value is appended to the existing value. | String |
| Overwrite | When this option is selected and the rule matches, the header specified in Header name is added to the response by using the specified Value. If the header is already present, Value overwrites the existing value. | String |
| Delete | When this option gets selected with matching rules and the header specified in the rule is present, the header gets deleted from the response. | String |
Route configuration overrides
Route Type: Redirect
Use these actions to redirect clients to a new URL.
Required fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Redirect type | Redirect is a way to send users/clients from one URL to another. A redirect type sets the status code used by clients to understand the purpose of the redirect. You can select the following redirect status codes: Found (302), Moved (301), Temporary redirect (307), and Permanent redirect (308). |
| Redirect protocol | Retain the protocol as per the incoming request, or define a new protocol for the redirection. For example, select 'HTTPS' for HTTP to HTTPS redirection. |
| Destination host | Set this value to change the hostname in the URL for the redirection or otherwise retain the hostname from the incoming request. |
| Destination path | Either retain the path as per the incoming request, or update the path in the URL for the redirection. |
| Query string | Set this value to replace any existing query string from the incoming request URL or otherwise retain the original set of query strings. |
| Destination fragment | The destination fragment is the portion of URL after '#', normally used by browsers to land on a specific section on a page. Set this value to add a fragment to the redirect URL. |
Route Type: Forward
Use these actions to forward clients to a new URL. These actions also contain sub actions for URL rewrites and caching.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Backend pool | Select the backend pool to override and serve the requests, you see all your preconfigured backend pools currently in your Front Door profile. |
| Forwarding protocol | Protocol to use for forwarding request to backend or match the protocol from incoming request. |
| URL rewrite | Path to use when constructing the request for URL rewrite to forward to the backend. |
| Caching | Enable caching for this routing rule. When enabled, Azure Front Door caches your static content. |
URL rewrite
Use this setting to configure an optional Custom Forwarding Path to use when constructing the request to forward to the backend.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom forwarding path | Define a path for which requests get forwarded to. |
Caching
Use these settings to control how files get cached for requests that contain query strings. Whether to cache your content based on all parameters or on selected parameters. You can use these settings to overwrite the time to live (TTL) value to control how long contents stay in cache. To force caching as an action, set the caching field to "Enabled." When you force caching, the following options appear:
| Cache behavior | Description |
|---|---|
| Ignore Query String | Once the asset is cached, all ensuing requests ignore the query strings until the cached asset expires. |
| Use Query String | Each request with a unique URL, including the query string, is treated as a unique asset with its own cache. |
| Ignore Specified Query Strings | Request URL query strings listed in "Query parameters" setting are ignored for caching. |
| Include Specified Query Strings | Request URL query strings listed in "Query parameters" setting are used for caching. |
| Other fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Dynamic compression | Front Door can dynamically compress content on the edge, resulting in a smaller and faster response. |
| Query parameters | A comma-separated list of allowed or disallowed parameters to use as a basis for caching. |
| Use default cache duration | Set to use Azure Front Door default caching duration or define a caching duration that ignores the origin response directive. |
Next steps
- Learn how to configure your first Rule set.
- Learn more about Rule set match conditions.
- Learn more about Azure Front Door Rule sets.