Recover workspace data while soft deleted
The soft delete feature for Azure Machine Learning workspace provides a data protection capability that enables you to attempt recovery of workspace data after accidental deletion. Soft delete introduces a two-step approach in deleting a workspace. When a workspace is deleted, it's first soft deleted. While in soft-deleted state, you can choose to recover or permanently delete a workspace and its data during a data retention period.
How workspace soft delete works
When a workspace is soft deleted, data and metadata stored service-side get soft deleted, but some configurations get hard deleted. The following table provides an overview of which configurations and objects get soft deleted, and which are hard deleted.
| Data / configuration | Soft deleted | Hard deleted |
|---|---|---|
| Run History | ✓ | |
| Models | ✓ | |
| Data | ✓ | |
| Environments | ✓ | |
| Components | ✓ | |
| Notebooks | ✓ | |
| Pipelines | ✓ | |
| Designer pipelines | ✓ | |
| AutoML jobs | ✓ | |
| Data labeling projects | ✓ | |
| Datastores | ✓ | |
| Queued or running jobs | ✓ | |
| Role assignments | ✓* | |
| Internal cache | ✓ | |
| Compute instance | ✓ | |
| Compute clusters | ✓ | |
| Inference endpoints | ✓ | |
| Linked Databricks workspaces | ✓* |
* Microsoft attempts recreation or reattachment when a workspace is recovered. Recovery isn't guaranteed, and a best effort attempt.
After soft deletion, the service keeps necessary data and metadata during the recovery retention period. When the retention period expires, or in case you permanently delete a workspace, data and metadata are actively deleted.
Soft delete retention period
A default retention period of 14 days holds for deleted workspaces. The retention period indicates how long workspace data remains available after deletion. The clock starts on the retention period as soon as a workspace is soft deleted.
During the retention period, soft deleted workspaces can be recovered or permanently deleted. Any other operations on the workspace, like submitting a training job, fail.
Important
You can't reuse the name of a workspace that has been soft deleted until the retention period has passed or the workspace is permanently deleted. Once the retention period elapses, a soft deleted workspace automatically gets permanently deleted.
Deleting a workspace
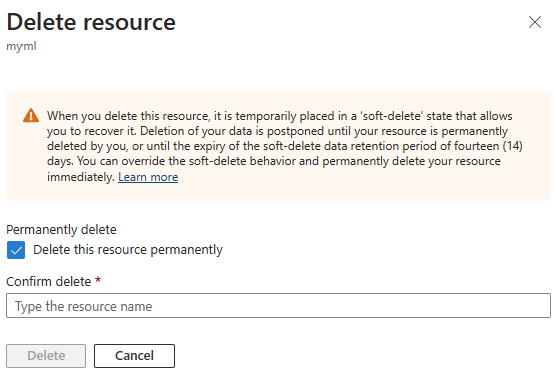
The default deletion behavior when deleting a workspace is soft delete. Optionally, you might override the soft delete behavior by permanently deleting your workspace. Permanently deleting a workspace ensures workspace data is immediately deleted. Use this option to meet related compliance requirements, or whenever you require a workspace name to be reused immediately after deletion. Overriding the default behavior might be useful in dev/test scenarios where you want to create and later delete a workspace.
When deleting a workspace from the Azure portal, check Delete the workspace permanently. You can permanently delete only one workspace at a time, and not using a batch operation.
Tip
The v1 SDK and CLI don't provide functionality to override the default soft-delete behavior. To override the default behavior from SDK or CLI, use the v2 versions. For more information, see the CLI & SDK v2 article or the v2 version of this article.
If you're using the Azure Machine Learning SDK or CLI, you can set the permanently_delete flag.
from azure.ai.ml import MLClient
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
ml_client = MLClient(
DefaultAzureCredential(),
subscription_id="<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>",
resource_group_name="<RESOURCE_GROUP>"
)
result = ml_client.workspaces.begin_delete(
name="myworkspace",
permanently_delete=True,
delete_dependent_resources=False
).result()
print(result)
Once permanently deleted, workspace data can no longer be recovered. Permanent deletion of workspace data is also triggered when the soft delete retention period expires.
Manage soft deleted workspaces
Soft deleted workspaces can be managed under the Azure Machine Learning resource provider in the Azure portal. To list soft deleted workspaces, use the following steps:
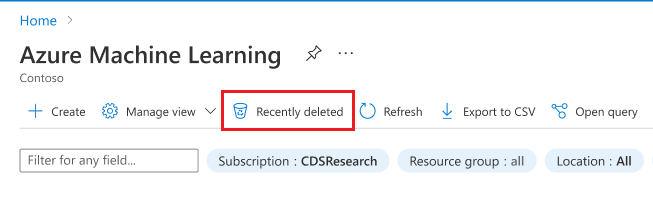
From the Azure portal, select More services. From the AI + machine learning category, select Azure Machine Learning.
From the top of the page, select Recently deleted to view workspaces that were soft-deleted and are still within the retention period.
From the recently deleted workspaces view, you can recover or permanently delete a workspace.
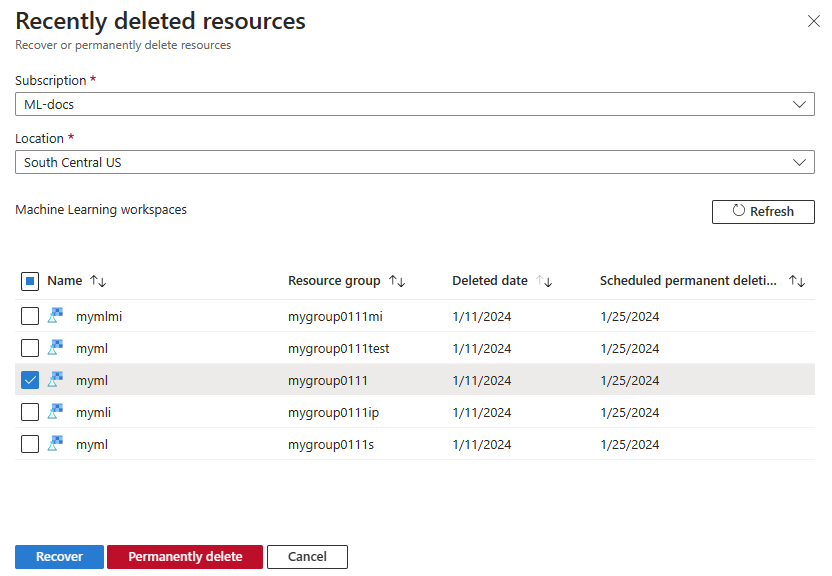
Recover a soft deleted workspace
When you select Recover on a soft deleted workspace, it initiates an operation to restore the workspace state. The service attempts recreation or reattachment of a subset of resources, including Azure RBAC role assignments. You must recreate hard-deleted resources, including compute clusters.
Azure Machine Learning recovers Azure RBAC role assignments for the workspace identity, but doesn't recover role assignments you added on the workspace. It might take up to 15 minutes for role assignments to propagate after workspace recovery.
Recovery of a workspace isn't always possible. Azure Machine Learning stores workspace metadata on other Azure resources associated with the workspace. In the event these dependent Azure resources were deleted, it might prevent the workspace from being recovered or correctly restored. Dependencies of the Azure Machine Learning workspace must be recovered first, before recovering a deleted workspace. The following table outlines recovery options for each dependency of the Azure Machine Learning workspace.
| Dependency | Recovery approach |
|---|---|
| Azure Key Vault | Recover a deleted Azure Key Vault instance |
| Azure Storage | Recover a deleted Azure storage account. |
| Azure Container Registry | Azure Container Registry isn't a hard requirement for workspace recovery. Azure Machine Learning can regenerate images for custom environments. |
| Azure Application Insights | First, recover your log analytics workspace. Then recreate an application insights with the original name. |
Billing implications
In general, when a workspace is in soft deleted state, there are only two operations possible: 'permanently delete' and 'recover'. All other operations fail. Therefore, even though the workspace exists, no compute operations can be performed, and hence no usage occurs. When a workspace is soft deleted, any cost-incurring resources including compute clusters are hard deleted.
Important
Workspaces that use customer-managed keys for encryption store additional service data in your subscription in a managed resource group. When a workspace is soft deleted, the managed resource group and resources in it will not be deleted and will incur cost until the workspace is hard-deleted.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) implications
After soft deletion, the service keeps necessary data and metadata during the recovery retention period. From a GDPR and privacy perspective, a request to delete personal data should be interpreted as a request for permanent deletion of a workspace and not soft delete.
When the retention period expires, or in case you permanently delete a workspace, data and metadata are actively deleted. You could choose to permanently delete a workspace at the time of deletion.
For more information, see the Export or delete workspace data article.