Configure sensors for AD FS, AD CS, and Microsoft Entra Connect
Install Defender for Identity sensors on Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS), and Microsoft Entra Connect servers to help protect them from on-premises and hybrid attacks. This article describes the installation steps.
These considerations apply:
- For AD FS environments, Defender for Identity sensors are supported only on the federation servers. They're not required on Web Application Proxy (WAP) servers.
- For AD CS environments, you don't need to install sensors on any AD CS servers that are offline.
- For Microsoft Entra Connect servers, you need to install the sensors on both active and staging servers.
Prerequisites
Prerequisites for installing Defender for Identity sensors on AD FS, AD CS, or Microsoft Entra Connect servers are the same as for installing sensors on domain controllers. For more information, see Microsoft Defender for Identity prerequisites.
A sensor installed on an AD FS, AD CS, or Microsoft Entra Connect server can't use the local service account to connect to the domain. Instead, you need to configure a Directory Service Account.
In addition, the Defender for Identity sensor for AD CS supports only AD CS servers with Certification Authority Role Service.
Configure event collection
If you're working with AD FS, AD CS, or Microsoft Entra Connect servers, make sure that you configured auditing as needed. For more information, see:
AD FS:
AD CS:
Microsoft Entra Connect:
Configure read permissions for the AD FS database
For sensors running on AD FS servers to have access to the AD FS database, you need to grant read (db_datareader) permissions for the relevant Directory Service Account.
If you have more than one AD FS server, make sure to grant this permission across all of them. Database permissions aren't replicated across servers.
Configure the SQL server to allow the Directory Service Account with the following permissions to the AdfsConfiguration database:
- connect
- log in
- read
- select
Note
If the AD FS database runs on a dedicated SQL server instead of the local AD FS server, and you're using a group Managed Service Account (gMSA) as the Directory Service Account, make sure that you grant the SQL server the required permissions to retrieve the gMSA's password.
Grant access to the AD FS database
Grant access to the AD FS database by using SQL Server Management Studio, Transact-SQL (T-SQL), or PowerShell.
For example, the following commands might be helpful if you're using the Windows Internal Database (WID) or an external SQL server.
In these sample codes:
[DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01]is the directory services user of the workspace. If you're working with a gMSA, append$to the end of the username. For example:[DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01$].AdfsConfigurationV4is an example of an AD FS database name and might vary.server=\.\pipe\MICROSOFT##WID\tsql\queryis the connection string to the database if you're using WID.
Tip
If you don't know your connection string, follow the steps in the Windows Server documentation.
To grant the sensor access to the AD FS database by using T-SQL:
USE [master]
CREATE LOGIN [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01] FROM WINDOWS WITH DEFAULT_DATABASE=[master]
USE [AdfsConfigurationV4]
CREATE USER [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01] FOR LOGIN [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01]
ALTER ROLE [db_datareader] ADD MEMBER [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01]
GRANT CONNECT TO [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01]
GRANT SELECT TO [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01]
GO
To grant the sensor access to the AD FS database by using PowerShell:
$ConnectionString = 'server=\\.\pipe\MICROSOFT##WID\tsql\query;database=AdfsConfigurationV4;trusted_connection=true;'
$SQLConnection= New-Object System.Data.SQLClient.SQLConnection($ConnectionString)
$SQLConnection.Open()
$SQLCommand = $SQLConnection.CreateCommand()
$SQLCommand.CommandText = @"
USE [master];
CREATE LOGIN [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01] FROM WINDOWS WITH DEFAULT_DATABASE=[master];
USE [AdfsConfigurationV4];
CREATE USER [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01] FOR LOGIN [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01];
ALTER ROLE [db_datareader] ADD MEMBER [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01];
GRANT CONNECT TO [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01];
GRANT SELECT TO [DOMAIN1\mdiSvc01];
"@
$SqlDataReader = $SQLCommand.ExecuteReader()
$SQLConnection.Close()
Configure permissions for the Microsoft Entra Connect (ADSync) database
Note
This section is applicable only if the Entra Connect database is hosted on an external SQL server instance.
Sensors running on Microsoft Entra Connect servers need to have access to the ADSync database, and have execute permissions for the relevant stored procedures. If you have more than one Microsoft Entra Connect server, make sure to run this across all of them.
To grant the sensor permissions to the Microsoft Entra Connect ADSync database by using PowerShell:
$entraConnectServerDomain = $env:USERDOMAIN
$entraConnectServerComputerAccount = $env:COMPUTERNAME
$entraConnectDBName = (Get-ItemProperty 'registry::HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ADSync\Parameters' -Name 'DBName').DBName
$entraConnectSqlServer = (Get-ItemProperty 'registry::HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ADSync\Parameters' -Name 'Server').Server
$entraConnectSqlInstance = (Get-ItemProperty 'registry::HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ADSync\Parameters' -Name 'SQLInstance').SQLInstance
$ConnectionString = 'server={0}\{1};database={2};trusted_connection=true;' -f $entraConnectSqlServer, $entraConnectSqlInstance, $entraConnectDBName
$SQLConnection= New-Object System.Data.SQLClient.SQLConnection($ConnectionString)
$SQLConnection.Open()
$SQLCommand = $SQLConnection.CreateCommand()
$SQLCommand.CommandText = @"
USE [master];
CREATE LOGIN [{0}\{1}$] FROM WINDOWS WITH DEFAULT_DATABASE=[master];
USE [{2}];
CREATE USER [{0}\{1}$] FOR LOGIN [{0}\{1}$];
GRANT CONNECT TO [{0}\{1}$];
GRANT SELECT TO [{0}\{1}$];
GRANT EXECUTE ON OBJECT::{2}.dbo.mms_get_globalsettings TO [{0}\{1}$];
GRANT EXECUTE ON OBJECT::{2}.dbo.mms_get_connectors TO [{0}\{1}$];
"@ -f $entraConnectServerDomain, $entraConnectServerComputerAccount, $entraConnectDBName
$SqlDataReader = $SQLCommand.ExecuteReader()
$SQLConnection.Close()
Post-installation steps (optional)
During the sensor installation on an AD FS, AD CS, or Microsoft Entra Connect server, the closest domain controller is automatically selected. Use the following steps to check or modify the selected domain controller:
In Microsoft Defender XDR, go to Settings > Identities > Sensors to view all of your Defender for Identity sensors.
Locate and select the sensor that you installed on the server.
On the pane that opens, in the Domain controller (FQDN) box, enter the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the resolver domain controllers. Select + Add to add the FQDN, and then select Save.
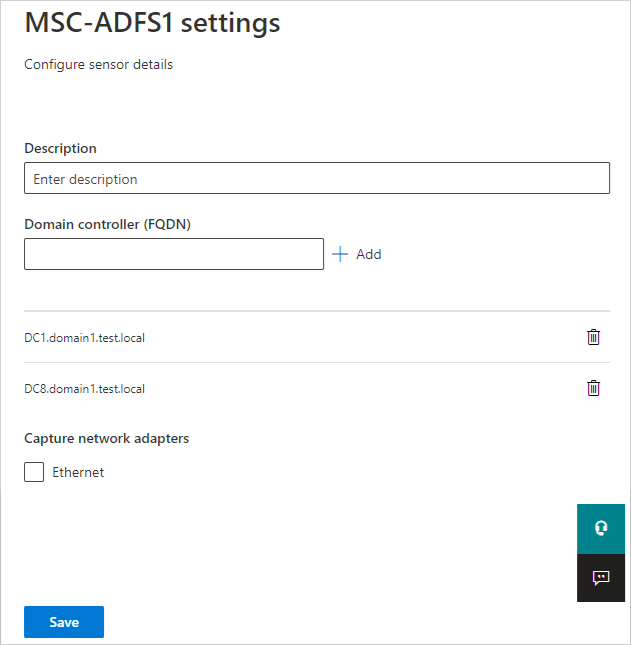
Initializing the sensor might take a couple of minutes. When it finishes, the service status of the AD FS, AD CS, or Microsoft Entra Connect sensor changes from stopped to running.
Validate successful deployment
To validate that you successfully deployed a Defender for Identity sensor on an AD FS or AD CS server:
Check that the Azure Advanced Threat Protection sensor service is running. After you save the Defender for Identity sensor settings, it might take a few seconds for the service to start.
If the service doesn't start, review the
Microsoft.Tri.sensor-Errors.logfile, located by default at%programfiles%\Azure Advanced Threat Protection sensor\Version X\Logs.Use AD FS or AD CS to authenticate a user to any application, and then verify that Defender for Identity observed the authentication.
For example, select Hunting > Advanced Hunting. On the Query pane, enter and run one of the following queries:
For AD FS:
IdentityLogonEvents | where Protocol contains 'Adfs'The results pane should include a list of events with a LogonType value of Logon with ADFS authentication.
For AD CS:
IdentityDirectoryEvents | where Protocol == "Adcs"The results pane shows a list of events of failed and successful certificate issuance. Select a specific row to see additional details on the Inspect record pane.
Related content
For more information, see:
