Muistiinpano
Tämän sivun käyttö edellyttää valtuutusta. Voit yrittää kirjautua sisään tai vaihtaa hakemistoa.
Tämän sivun käyttö edellyttää valtuutusta. Voit yrittää vaihtaa hakemistoa.
This tutorial shows how to create and run a .NET console application in Visual Studio 2026.
Prerequisites
Visual Studio 2026 or later with the .NET desktop development workload installed. The .NET SDK is automatically installed when you select this workload.
For more information, see Install the .NET SDK with Visual Studio.
Create the app
Create a .NET console app project named "HelloWorld".
Start Visual Studio.
On the start page, choose Create a new project.
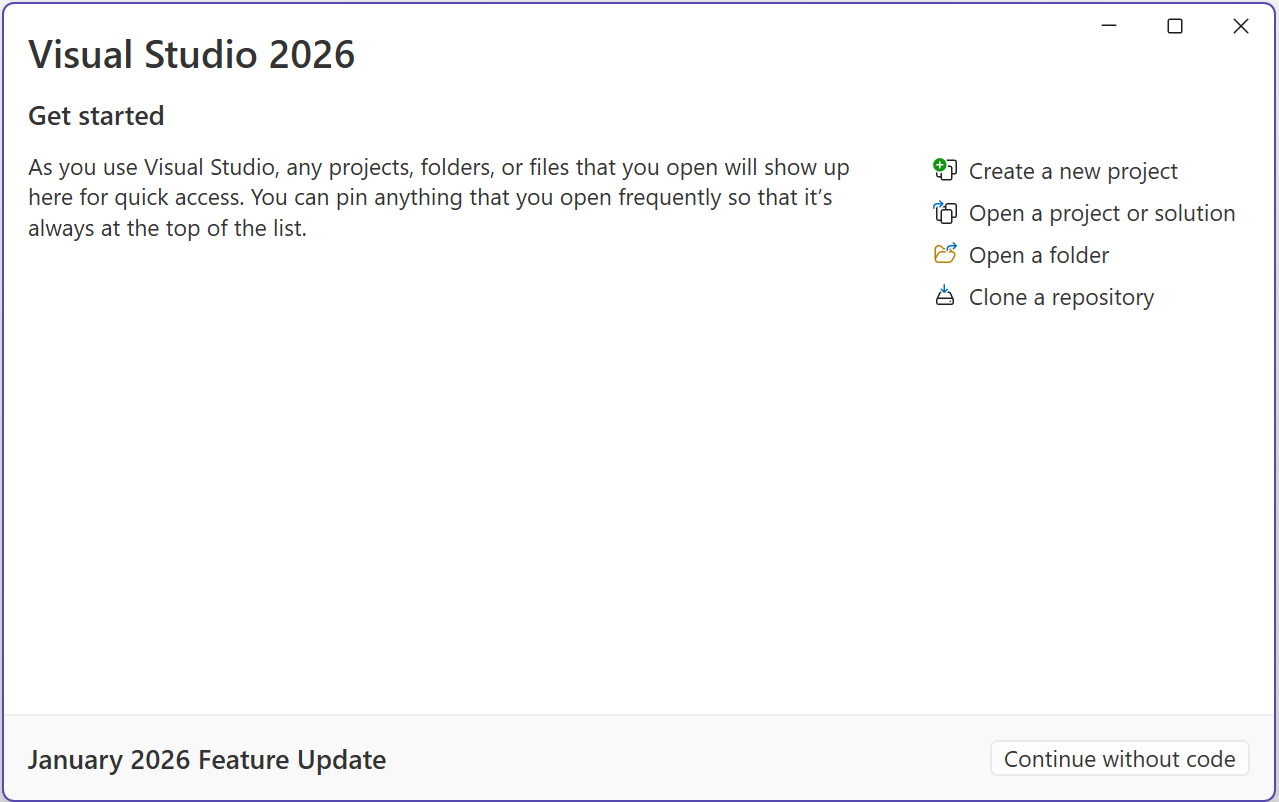
On the Create a new project page, enter console in the search box. Next, choose C# or Visual Basic from the language list, and then choose All platforms from the platform list. Choose the Console App template, and then choose Next.
Tip
If you don't see the .NET templates, you're probably missing the required workload. Under the Not finding what you're looking for? message, choose the Install more tools and features link. The Visual Studio Installer opens. Make sure you have the .NET desktop development workload installed.
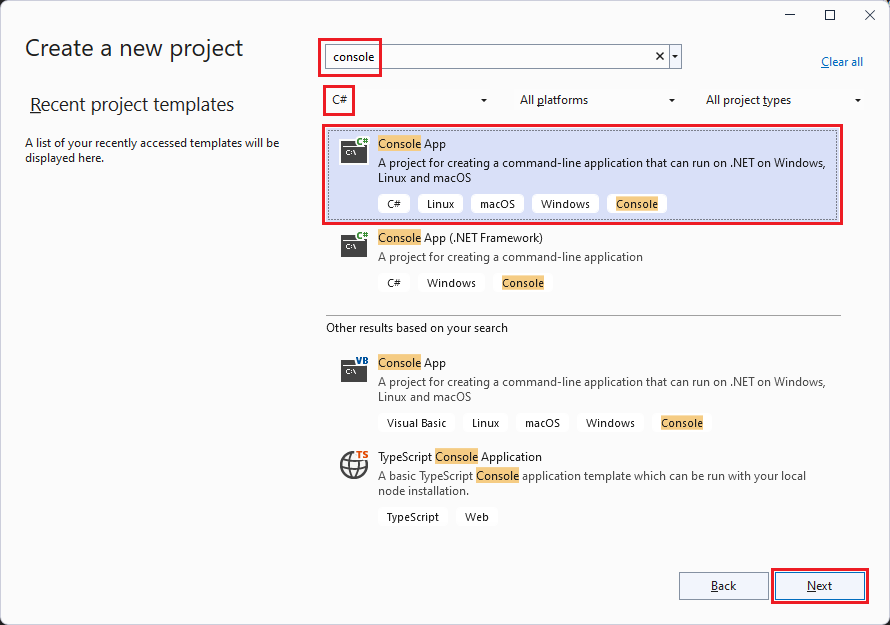
In the Configure your new project dialog, enter HelloWorld in the Project name box. Then choose Next.
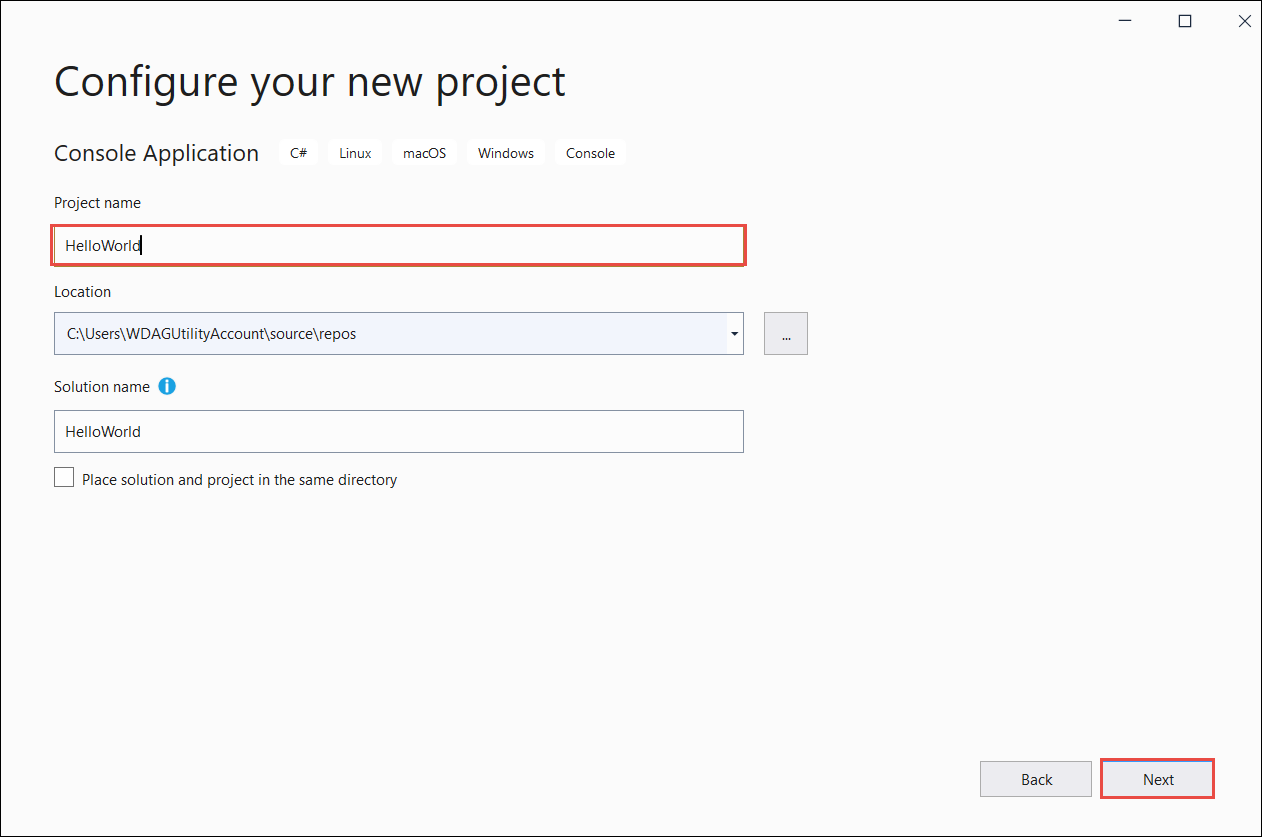
In the Additional information dialog:
- Select .NET 10.0 (Long Term Support).
- Select Create.
The template creates a simple application that displays "Hello, World!" in the console window. The code is in the Program.cs or Program.vb file:
// See https://aka.ms/new-console-template for more information Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!");Imports System Module Program Sub Main(args As String()) Console.WriteLine("Hello World!") End Sub End ModuleIf the language you want to use is not shown, change the language selector at the top of the page.
The C# template uses top-level statements to call the Console.WriteLine(String) method to display a message in the console window. The Visual Basic template defines a
Module Programwith aSub Mainmethod that calls the same method.
Run the app
Press Ctrl+F5 to run the program without debugging.
A console window opens with the text "Hello, World!" printed on the screen. (Or "Hello World!" without a comma in the Visual Basic project template.)
Press any key to close the console window.
Enhance the app
Enhance the application to prompt the user for their name and display it along with the date and time.
In Program.cs or Program.vb, replace the contents with the following code:
Console.WriteLine("What is your name?"); var name = Console.ReadLine(); var currentDate = DateTime.Now; Console.WriteLine($"{Environment.NewLine}Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}!"); Console.Write($"{Environment.NewLine}Press Enter to exit..."); Console.Read();Console.WriteLine("What is your name?") Dim name = Console.ReadLine() Dim currentDate = DateTime.Now Console.WriteLine($"{Environment.NewLine}Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}") Console.Write($"{Environment.NewLine}Press any key to exit...") Console.ReadKey(True)This code displays a prompt in the console window and waits until the user enters a string followed by the Enter key. It stores this string in a variable named
name. It also retrieves the value of the DateTime.Now property, which contains the current local time, and assigns it to a variable namedcurrentDate. And it displays these values in the console window. Finally, it displays a prompt in the console window and calls the Read() method to wait for user input.Environment.NewLine is a platform-independent and language-independent way to represent a line break. Alternatives are
\nin C# andvbCrLfin Visual Basic.The dollar sign (
$) in front of a string lets you put expressions such as variable names in curly braces in the string. The expression value is inserted into the string in place of the expression. This syntax is referred to as interpolated strings.Press Ctrl+F5 to run the program without debugging.
Respond to the prompt by entering a name and pressing the Enter key.
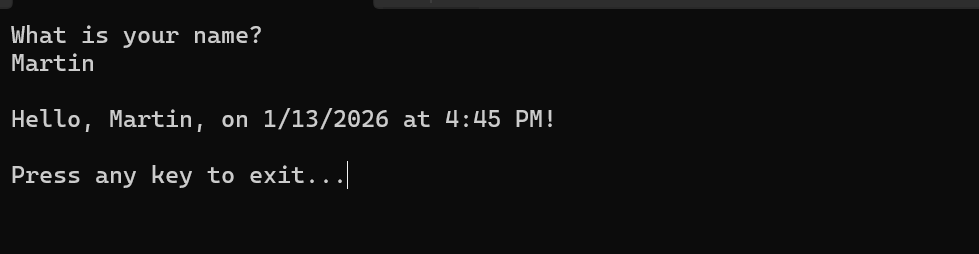
Press any key to close the console window.
Additional resources
Next steps
In this tutorial, you created a .NET console application. In the next tutorial, you debug the app.
