CTaskDialog, classe
Boîte de dialogue contextuelle qui fonctionne comme une boîte de message mais peut afficher des informations supplémentaires pour l'utilisateur. CTaskDialog inclut également les fonctionnalités nécessaires pour recueillir des informations auprès de l'utilisateur.
Syntaxe
class CTaskDialog : public CObject
Membres
Constructeurs
| Nom | Description |
|---|---|
| CTaskDialog ::CTaskDialog | Construit un objet CTaskDialog. |
Méthodes
| Nom | Description |
|---|---|
| CTaskDialog ::AddCommandControl | Ajoute un contrôle de bouton de commande au CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::AddRadioButton | Ajoute une case d’option au CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::ClickCommandControl | Cliquez sur un contrôle de bouton de commande ou un bouton courant par programmation. |
| CTaskDialog ::ClickRadioButton | Clique sur une case d’option par programmation. |
| CTaskDialog ::D oModal | Affiche la CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::GetCommonButtonCount | Récupère le nombre de boutons courants disponibles. |
| CTaskDialog ::GetCommonButtonFlag | Convertit un bouton Windows standard en type de bouton commun associé à la CTaskDialog classe. |
| CTaskDialog ::GetCommonButtonId | Convertit l’un des types de boutons courants associés à la CTaskDialog classe en bouton Windows standard. |
| CTaskDialog ::GetOptions | Retourne les indicateurs d’option pour ce CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::GetSelectedCommandControlID | Retourne le contrôle de bouton de commande sélectionné. |
| CTaskDialog ::GetSelectedRadioButtonID | Retourne la case d’option sélectionnée. |
| CTaskDialog ::GetVerificationCheckboxState | Récupère l’état de la case à cocher de vérification. |
| CTaskDialog ::IsCommandControlEnabled | Détermine si un contrôle de bouton de commande ou un bouton commun est activé. |
| CTaskDialog ::IsRadioButtonEnabled | Détermine si une case d’option est activée. |
| CTaskDialog ::IsSupported | Détermine si l’ordinateur qui exécute l’application prend en charge le CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::LoadCommandControls | Ajoute des contrôles de bouton de commande à l’aide de données de la table de chaînes. |
| CTaskDialog ::LoadRadioButtons | Ajoute des cases d’option à l’aide de données de la table de chaînes. |
| CTaskDialog ::NavigateTo | Transfère le focus vers un autre CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::OnCommandControlClick | L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur clique sur un contrôle de bouton de commande. |
| CTaskDialog ::OnCreate | L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode après avoir créé le CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::OnDestroy | L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode immédiatement avant de détruire le CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::OnExpandButtonClick | L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur clique sur le bouton d’extension. |
| CTaskDialog ::OnHelp | L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur demande de l’aide. |
| CTaskDialog ::OnHyperlinkClick | L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur clique sur un lien hypertexte. |
| CTaskDialog ::OnInit | L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lors de l’initialisation CTaskDialog . |
| CTaskDialog ::OnNavigatePage | L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur déplace le focus en ce qui concerne les contrôles sur le CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::OnRadioButtonClick | L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur sélectionne un contrôle de case d’option. |
| CTaskDialog ::OnTimer | L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque le minuteur expire. |
| CTaskDialog ::OnVerificationCheckboxClick | L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur clique sur la case à cocher de vérification. |
| CTaskDialog ::RemoveAllCommandControls | Supprime tous les contrôles de commande de l’objet CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::RemoveAllRadioButtons | Supprime toutes les cases d’option du CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetCommandControlOptions | Met à jour un contrôle de bouton de commande sur le CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetCommonButtonOptions | Met à jour un sous-ensemble de boutons courants à activer et nécessite une élévation DAC. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetCommonButtons | Ajoute des boutons courants au CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetContent | Met à jour le contenu du CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetDefaultCommandControl | Spécifie le contrôle de bouton de commande par défaut. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetDefaultRadioButton | Spécifie la case d’option par défaut. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetDialogWidth | Ajuste la largeur du CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetExpansionArea | Met à jour la zone d’expansion du CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetFooterIcon | Met à jour l’icône de pied de page pour le CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetFooterText | Met à jour le texte sur le pied de page du CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetMainIcon | Met à jour l’icône principale du CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetMainInstruction | Met à jour l’instruction principale du CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetOptions | Configure les options pour le CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarMarquee | Configure une barre de marque pour la CTaskDialog boîte de dialogue et l’ajoute à la boîte de dialogue. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarPosition | Ajuste la position de la barre de progression. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarRange | Ajuste la plage de la barre de progression. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarState | Définit l’état de la barre de progression et l’affiche sur le CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetRadioButtonOptions | Active ou désactive une case d’option. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetVerificationCheckbox | Définit l’état activé de la case à cocher de vérification. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetVerificationCheckboxText | Définit le texte sur le côté droit de la case à cocher de vérification. |
| CTaskDialog ::SetWindowTitle | Définit le titre du CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::ShowDialog | Crée et affiche un CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog ::TaskDialogCallback | L’infrastructure appelle ceci en réponse à différents messages Windows. |
Données membres
| Nom | Description |
|---|---|
m_aButtons |
Tableau de contrôles de bouton de commande pour le CTaskDialog. |
m_aRadioButtons |
Tableau de contrôles de case d’option pour le CTaskDialog. |
m_bVerified |
TRUE indique que la case à cocher de vérification est cochée ; FALSE indique qu’elle n’est pas. |
m_footerIcon |
Icône dans le pied de page du CTaskDialog. |
m_hWnd |
Handle vers la fenêtre pour le CTaskDialog. |
m_mainIcon |
Icône principale du CTaskDialog. |
m_nButtonDisabled |
Masque qui indique quels boutons courants sont désactivés. |
m_nButtonElevation |
Masque qui indique quels boutons courants nécessitent une élévation de contrôle d’utilisateur. |
m_nButtonId |
ID du contrôle de bouton de commande sélectionné. |
m_nCommonButton |
Masque qui indique quels boutons courants sont affichés sur le CTaskDialog. |
m_nDefaultCommandControl |
ID du contrôle de bouton de commande sélectionné lors de l’affichage CTaskDialog . |
m_nDefaultRadioButton |
ID du contrôle de case d’option sélectionné lors de l’affichage CTaskDialog . |
m_nFlags |
Masque qui indique les options pour le CTaskDialog. |
m_nProgressPos |
Position actuelle de la barre de progression. Cette valeur doit être comprise entre m_nProgressRangeMin et m_nProgressRangeMax. |
m_nProgressRangeMax |
Valeur maximale de la barre de progression. |
m_nProgressRangeMin |
Valeur minimale de la barre de progression. |
m_nProgressState |
État de la barre de progression. Pour plus d’informations, consultez CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarState. |
m_nRadioId |
ID du contrôle de case d’option sélectionné. |
m_nWidth |
Largeur du CTaskDialog en pixels. |
m_strCollapse |
Chaîne affichée CTaskDialog à droite de la zone d’expansion lorsque les informations développées sont masquées. |
m_strContent |
Chaîne de contenu du CTaskDialog. |
m_strExpand |
Chaîne affichée CTaskDialog à droite de la zone d’expansion lorsque les informations développées sont affichées. |
m_strFooter |
Pied de page du CTaskDialog. |
m_strInformation |
Informations développées pour le CTaskDialog. |
m_strMainInstruction |
L’instruction principale du CTaskDialog. |
m_strTitle |
Le titre du CTaskDialog. |
m_strVerification |
Chaîne affichée CTaskDialog à droite de la case à cocher de vérification. |
Notes
La CTaskDialog classe remplace la boîte de message Windows standard et dispose de fonctionnalités supplémentaires telles que de nouveaux contrôles pour collecter des informations auprès de l’utilisateur. Cette classe se trouve dans la bibliothèque MFC dans Visual Studio 2010 et versions ultérieures. Il CTaskDialog est disponible à partir de Windows Vista. Les versions antérieures de Windows ne peuvent pas afficher l’objet CTaskDialog . Permet CTaskDialog::IsSupported de déterminer au moment de l’exécution si l’utilisateur actuel peut afficher la boîte de dialogue de tâche. La boîte de message Windows standard est toujours prise en charge.
Il CTaskDialog est disponible uniquement lorsque vous générez votre application à l’aide de la bibliothèque Unicode.
Il CTaskDialog a deux constructeurs différents. Un constructeur vous permet de spécifier deux boutons de commande et un maximum de six contrôles de bouton standard. Vous pouvez ajouter d’autres boutons de commande après avoir créé le CTaskDialog. Le deuxième constructeur ne prend pas en charge les boutons de commande, mais vous pouvez ajouter un nombre illimité de contrôles de bouton standard. Pour plus d’informations sur les constructeurs, consultez CTaskDialog ::CTaskDialog.
L’image suivante montre un exemple CTaskDialog pour illustrer l’emplacement de certains contrôles.
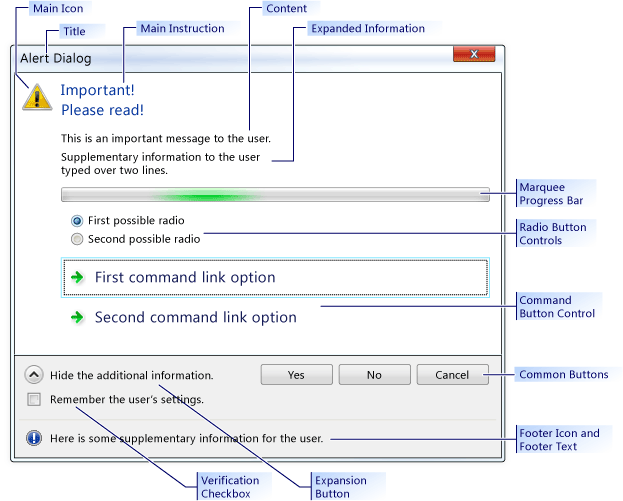
Exemple CTaskDialog
Spécifications
Système d’exploitation minimum requis : Windows Vista
En-tête : afxtaskdialog.h
CTaskDialog ::AddCommandControl
Ajoute un nouveau contrôle de bouton de commande au CTaskDialog.
void AddCommandControl(
int nCommandControlID,
const CString& strCaption,
BOOL bEnabled = TRUE,
BOOL bRequiresElevation = FALSE);
Paramètres
nCommandControlID
[in] Numéro d’identification du contrôle de commande.
strCaption
[in] Chaîne affichée CTaskDialog à l’utilisateur. Utilisez cette chaîne pour expliquer l’objectif de la commande.
bEnabled
[in] Paramètre booléen qui indique si le nouveau bouton est activé ou désactivé.
bRequiresElevation
[in] Paramètre booléen qui indique si une commande nécessite une élévation.
Notes
Le CTaskDialog Class bouton peut afficher un nombre illimité de contrôles de bouton de commande. Toutefois, si un bouton de commande affiche des CTaskDialog contrôles de bouton de commande, il peut afficher un maximum de six boutons. Si aucun CTaskDialog contrôle de bouton de commande n’est disponible, il peut afficher un nombre illimité de boutons.
Lorsque l’utilisateur sélectionne un contrôle de bouton de commande, la CTaskDialog fermeture est terminée. Si votre application affiche la boîte de dialogue à l’aide de CTaskDialog ::D oModal, DoModal retourne le nCommandControlID du contrôle de bouton de commande sélectionné.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::AddRadioButton
Ajoute une case d’option au CTaskDialog.
void CTaskDialog::AddRadioButton(
int nRadioButtonID,
const CString& strCaption,
BOOL bEnabled = TRUE);
Paramètres
nRadioButtonID
[in] Numéro d’identification de la case d’option.
strCaption
[in] Chaîne affichée CTaskDialog en regard de la case d’option.
bEnabled
[in] Paramètre booléen qui indique si la case d’option est activée.
Notes
Les cases d’option de la classe CTaskDialog vous permettent de recueillir des informations à partir de l’utilisateur. Utilisez la fonction CTaskDialog ::GetSelectedRadioButtonID pour déterminer la case d’option sélectionnée.
Les CTaskDialog paramètres nRadioButtonID ne sont pas obligatoires pour chaque case d’option. Toutefois, vous pouvez rencontrer un comportement inattendu si vous n’utilisez pas d’identificateur distinct pour chaque case d’option.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::ClickCommandControl
Cliquez sur un contrôle de bouton de commande ou un bouton courant par programmation.
protected:
void ClickCommandControl(int nCommandControlID) const;
Paramètres
nCommandControlID
[in] ID de commande du contrôle à cliquer.
Notes
Cette méthode génère le message Windows TDM_CLICK_BUTTON.
CTaskDialog ::ClickRadioButton
Clique sur une case d’option par programmation.
protected:
void ClickRadioButton(int nRadioButtonID) const;
Paramètres
nRadioButtonID
[in] ID de la case d’option à cliquer.
Notes
Cette méthode génère le message Windows TDM_CLICK_RADIO_BUTTON.
CTaskDialog ::CTaskDialog
Crée une instance de la classe CTaskDialog.
CTaskDialog(
const CString& strContent,
const CString& strMainInstruction,
const CString& strTitle,
int nCommonButtons = TDCBF_OK_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON,
int nTaskDialogOptions = TDF_ENABLE_HYPERLINKS | TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS,
const CString& strFooter = _T(""));
CTaskDialog(
const CString& strContent,
const CString& strMainInstruction,
const CString& strTitle,
int nIDCommandControlsFirst,
int nIDCommandControlsLast,
int nCommonButtons,
int nTaskDialogOptions = TDF_ENABLE_HYPERLINKS | TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS,
const CString& strFooter = _T(""));
Paramètres
strContent
[in] Chaîne à utiliser pour le contenu du CTaskDialog.
strMainInstruction
[in] L’instruction principale du CTaskDialog.
strTitle
[in] Le titre du CTaskDialog.
nCommonButtons
[in] Masque des boutons courants à ajouter au CTaskDialog.
nTaskDialogOptions
[in] Ensemble d’options à utiliser pour le CTaskDialog.
strFooter
[in] Chaîne à utiliser comme pied de page.
nIDCommandControlsFirst
[in] ID de chaîne de la première commande.
nIDCommandControlsLast
[in] ID de chaîne de la dernière commande.
Notes
Il existe deux façons d’ajouter un CTaskDialog à votre application. La première façon consiste à utiliser l’un des constructeurs pour créer et CTaskDialog l’afficher à l’aide de CTaskDialog ::D oModal. La deuxième méthode consiste à utiliser la fonction statique CTaskDialog ::ShowDialog, qui vous permet d’afficher un CTaskDialog objet sans créer explicitement d’objet CTaskDialog .
Le deuxième constructeur crée des contrôles de bouton de commande à l’aide de données à partir du fichier de ressources de votre application. La table de chaînes du fichier de ressources comporte plusieurs chaînes avec des ID de chaîne associés. Cette méthode ajoute un contrôle de bouton de commande pour chaque entrée valide dans la table de chaînes entre nIDCommandControlsFirst et nCommandControlsLast, inclus. Pour ces contrôles de bouton de commande, la chaîne de la table de chaînes est la légende du contrôle et l’ID de chaîne est l’ID du contrôle.
Consultez CTaskDialog ::SetOptions pour obtenir la liste des options valides .
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::D oModal
Affiche et CTaskDialog le rend modal.
INT_PTR DoModal (HWND hParent = ::GetActiveWindow());
Paramètres
hParent
[in] Fenêtre parente pour le CTaskDialog.
Valeur de retour
Entier qui correspond à la sélection effectuée par l’utilisateur.
Notes
Affiche cette instance de CTaskDialog. L’application attend ensuite que l’utilisateur ferme la boîte de dialogue.
La CTaskDialog fermeture se ferme lorsque l’utilisateur sélectionne un bouton commun, un contrôle de lien de commande ou ferme le CTaskDialog. La valeur de retour est l’identificateur qui indique comment l’utilisateur a fermé la boîte de dialogue.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::GetCommonButtonCount
Récupère le nombre de boutons courants.
int GetCommonButtonCount() const;
Valeur de retour
Nombre de boutons courants disponibles.
Notes
Les boutons courants sont les boutons par défaut que vous fournissez à CTaskDialog ::CTaskDialog. La classe CTaskDialog affiche les boutons le long du bas de la boîte de dialogue.
La liste énumérée des boutons est fournie dans CommCtrl.h.
CTaskDialog ::GetCommonButtonFlag
Convertit un bouton Windows standard en type de bouton commun associé à la classe CTaskDialog.
int GetCommonButtonFlag(int nButtonId) const;
Paramètres
nButtonId
[in] Valeur de bouton Windows standard.
Valeur de retour
Valeur du bouton commun correspondant CTaskDialog . S’il n’existe aucun bouton commun correspondant, cette méthode retourne 0.
CTaskDialog ::GetCommonButtonId
Convertit l’un des types de boutons courants associés à la classe CTaskDialog en un bouton Windows standard.
int GetCommonButtonId(int nFlag);
Paramètres
nFlag
[in] Type de bouton commun associé à la CTaskDialog classe.
Valeur de retour
Valeur du bouton Windows standard correspondant. S’il n’existe aucun bouton Windows correspondant, la méthode retourne 0.
CTaskDialog ::GetOptions
Retourne les indicateurs d’option pour ce CTaskDialog.
int GetOptions() const;
Valeur de retour
Indicateurs pour le CTaskDialog.
Notes
Pour plus d’informations sur les options disponibles pour la classe CTaskDialog, consultez CTaskDialog ::SetOptions.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::GetSelectedCommandControlID
Retourne le contrôle de bouton de commande sélectionné.
int GetSelectedCommandControlID() const;
Valeur de retour
ID du contrôle de bouton de commande actuellement sélectionné.
Notes
Vous n’avez pas besoin d’utiliser cette méthode pour récupérer l’ID du bouton de commande sélectionné par l’utilisateur. Cet ID est retourné par CTaskDialog ::D oModal ou CTaskDialog ::ShowDialog.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::GetSelectedRadioButtonID
Retourne la case d’option sélectionnée.
int GetSelectedRadioButtonID() const;
Valeur de retour
ID de la case d’option sélectionnée.
Notes
Vous pouvez utiliser cette méthode une fois que l’utilisateur ferme la boîte de dialogue pour récupérer la case d’option sélectionnée.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::GetVerificationCheckboxState
Récupère l’état de la case à cocher de vérification.
BOOL GetVerificationCheckboxState() const;
Valeur de retour
TRUE si la case à cocher est cochée, FALSE si ce n’est pas le cas.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add the verification checkbox and set the default state.
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckboxText(L"Remember your selection.");
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckbox(false);
taskDialog.DoModal();
if (taskDialog.GetVerificationCheckboxState())
{
// TODO: Write settings of the task dialog to the registry
}
CTaskDialog ::IsCommandControlEnabled
Détermine si un contrôle de bouton de commande ou un bouton est activé.
BOOL IsCommandControlEnabled(int nCommandControlID) const;
Paramètres
nCommandControlID
[in] ID du contrôle de bouton de commande ou du bouton à tester.
Valeur de retour
TRUE si le contrôle est activé, FALSE s’il ne l’est pas.
Notes
Vous pouvez utiliser cette méthode pour déterminer la disponibilité des contrôles de bouton de commande et des boutons courants de la CTaskDialog classe*.
Si nCommandControlID n’est pas un identificateur valide pour un bouton commun CTaskDialog ou un contrôle de bouton de commande, cette méthode lève une exception.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::IsRadioButtonEnabled
Détermine si une case d’option est activée.
BOOL IsRadioButtonEnabled(int nRadioButtonID) const;
Paramètres
nRadioButtonID
[in] ID de la case d’option à tester.
Valeur de retour
TRUE si la case d’option est activée, FALSE si ce n’est pas le cas.
Notes
Si nRadioButtonID n’est pas un identificateur valide pour une case d’option, cette méthode lève une exception.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::IsSupported
Détermine si l’ordinateur qui exécute l’application prend en charge le CTaskDialog.
static BOOL IsSupported();
Valeur de retour
TRUE si l’ordinateur prend en charge le CTaskDialog; FALSE dans le cas contraire.
Notes
Utilisez cette fonction pour déterminer au moment de l’exécution si l’ordinateur qui exécute votre application prend en charge la CTaskDialog classe. Si l’ordinateur ne prend pas en charge, CTaskDialogvous devez fournir une autre méthode de communication des informations à l’utilisateur. Votre application se bloque si elle tente d’utiliser un CTaskDialog ordinateur qui ne prend pas en charge la CTaskDialog classe.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the string below with the actual message to the user
CString message("Important information to the user");
// TODO: Replace the string below with the title of this project
CString title("Project Title");
CString emptyString;
if (CTaskDialog::IsSupported())
{
CTaskDialog::ShowDialog(message, emptyString, title, 0, 0,
TDCBF_OK_BUTTON);
}
else
{
AfxMessageBox(message);
}
CTaskDialog ::LoadCommandControls
Ajoute des contrôles de bouton de commande à l’aide de données de la table de chaînes.
void LoadCommandControls(
int nIDCommandControlsFirst,
int nIDCommandControlsLast);
Paramètres
nIDCommandControlsFirst
[in] ID de chaîne de la première commande.
nIDCommandControlsLast
[in] ID de chaîne de la dernière commande.
Notes
Cette méthode crée des contrôles de bouton de commande à l’aide de données à partir du fichier de ressources de votre application. La table de chaînes du fichier de ressources comporte plusieurs chaînes avec des ID de chaîne associés. Les nouveaux contrôles de bouton de commande ajoutés à l’aide de cette méthode utilisent la chaîne pour la légende du contrôle et l’ID de chaîne de l’ID du contrôle. La plage de chaînes sélectionnées est fournie par nIDCommandControlsFirst et nCommandControlsLast, inclus. S’il existe une entrée vide dans la plage, la méthode n’ajoute pas de contrôle de bouton de commande pour cette entrée.
Par défaut, les nouveaux contrôles de bouton de commande sont activés et ne nécessitent pas d’élévation.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::LoadRadioButtons
Ajoute des contrôles de case d’option à l’aide de données de la table de chaînes.
void LoadRadioButtons(
int nIDRadioButtonsFirst,
int nIDRadioButtonsLast);
Paramètres
nIDRadioButtonsFirst
[in] ID de chaîne du premier bouton d’option.
nIDRadioButtonsLast
[in] ID de chaîne de la dernière case d’option.
Notes
Cette méthode crée des cases d’option à l’aide de données à partir du fichier de ressources de votre application. La table de chaînes du fichier de ressources comporte plusieurs chaînes avec des ID de chaîne associés. Les nouvelles cases d’option ajoutées à l’aide de cette méthode utilisent la chaîne pour la légende de la case d’option et l’ID de chaîne de l’ID de la case d’option. La plage de chaînes sélectionnées est fournie par nIDRadioButtonsFirst et nRadioButtonsLast, inclus. S’il existe une entrée vide dans la plage, la méthode n’ajoute pas de case d’option pour cette entrée.
Par défaut, les nouvelles cases d’option sont activées.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::NavigateTo
Transfère le focus vers un autre CTaskDialog.
protected:
void NavigateTo(CTaskDialog& oTaskDialog) const;
Paramètres
oTaskDialog
[in] Qui CTaskDialog reçoit le focus.
Notes
Cette méthode masque le courant CTaskDialog lorsqu’il affiche l’oTaskDialog. L’oTaskDialog est affiché dans le même emplacement que le fichier actif CTaskDialog.
CTaskDialog ::OnCommandControlClick
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur clique sur un contrôle de bouton de commande.
virtual HRESULT OnCommandControlClick(int nCommandControlID);
Paramètres
nCommandControlID
[in] ID du contrôle du bouton de commande sélectionné par l’utilisateur.
Valeur de retour
L’implémentation par défaut retourne S_OK.
Notes
Remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée pour implémenter un comportement personnalisé.
CTaskDialog ::OnCreate
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode après avoir créé le CTaskDialog.
virtual HRESULT OnCreate();
Valeur de retour
L’implémentation par défaut retourne S_OK.
Notes
Remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée pour implémenter un comportement personnalisé.
CTaskDialog ::OnDestroy
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode immédiatement avant de détruire le CTaskDialog.
virtual HRESULT OnDestroy();
Valeur de retour
L’implémentation par défaut retourne S_OK.
Notes
Remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée pour implémenter un comportement personnalisé.
CTaskDialog ::OnExpandButtonClick
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur clique sur le bouton d’extension.
virtual HRESULT OnExpandButtonClicked(BOOL bExpanded);
Paramètres
bExpanded
[in] Une valeur différente de zéro indique que les informations supplémentaires sont affichées ; 0 indique que les informations supplémentaires sont masquées.
Valeur de retour
L’implémentation par défaut retourne S_OK.
Notes
Remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée pour implémenter un comportement personnalisé.
CTaskDialog ::OnHelp
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur demande de l’aide.
virtual HRESULT OnHelp();
Valeur de retour
L’implémentation par défaut retourne S_OK.
Notes
Remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée pour implémenter un comportement personnalisé.
CTaskDialog ::OnHyperlinkClick
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur clique sur un lien hypertexte.
virtual HRESULT OnHyperlinkClick(const CString& strHref);
Paramètres
strHref
[in] Chaîne qui représente le lien hypertexte.
Valeur de retour
L’implémentation par défaut retourne S_OK.
Notes
Cette méthode appelle ShellExecute avant de renvoyer S_OK.
Remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée pour implémenter un comportement personnalisé.
CTaskDialog ::OnInit
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lors de l’initialisation CTaskDialog .
virtual HRESULT OnInit();
Valeur de retour
L’implémentation par défaut retourne S_OK.
Notes
Remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée pour implémenter un comportement personnalisé.
CTaskDialog ::OnNavigatePage
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode en réponse à la méthode CTaskDialog ::NavigateTo .
virtual HRESULT OnNavigatePage();
Valeur de retour
L’implémentation par défaut retourne S_OK.
Notes
Remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée pour implémenter un comportement personnalisé.
CTaskDialog ::OnRadioButtonClick
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur sélectionne un contrôle de case d’option.
virtual HRESULT OnRadioButtonClick(int nRadioButtonID);
Paramètres
nRadioButtonID
[in] ID du contrôle de case d’option sur lequel l’utilisateur a cliqué.
Valeur de retour
L’implémentation par défaut retourne S_OK.
Notes
Remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée pour implémenter un comportement personnalisé.
CTaskDialog ::OnTimer
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque le minuteur expire.
virtual HRESULT OnTimer(long lTime);
Paramètres
lTime
[in] Durée en millisecondes depuis la CTaskDialog création ou la réinitialisation du minuteur.
Valeur de retour
L’implémentation par défaut retourne S_OK.
Notes
Remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée pour implémenter un comportement personnalisé.
CTaskDialog ::OnVerificationCheckboxClick
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode lorsque l’utilisateur clique sur la case à cocher de vérification.
virtual HRESULT OnVerificationCheckboxClick(BOOL bChecked);
Paramètres
bChecked
[in] TRUE indique que la case à cocher de vérification est cochée ; FALSE indique que ce n’est pas le cas.
Valeur de retour
L’implémentation par défaut retourne S_OK.
Notes
Remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée pour implémenter un comportement personnalisé.
CTaskDialog ::RemoveAllCommandControls
Supprime tous les contrôles du bouton de commande du CTaskDialog.
void RemoveAllCommandControls();
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::RemoveAllRadioButtons
Supprime toutes les cases d’option du CTaskDialog.
void RemoveAllRadioButtons();
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::SetCommandControlOptions
Met à jour un contrôle de bouton de commande sur le CTaskDialog.
void SetCommandControlOptions(
int nCommandControlID,
BOOL bEnabled,
BOOL bRequiresElevation = FALSE);
Paramètres
nCommandControlID
[in] ID du contrôle de commande à mettre à jour.
bEnabled
[in] Paramètre booléen qui indique si le contrôle de bouton de commande spécifié est activé ou désactivé.
bRequiresElevation
[in] Paramètre booléen qui indique si le contrôle de bouton de commande spécifié nécessite une élévation.
Notes
Utilisez cette méthode pour modifier si un contrôle de bouton de commande est activé ou nécessite une élévation une fois qu’il a été ajouté à la CTaskDialog classe.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::SetCommonButtonOptions
Met à jour un sous-ensemble de boutons courants à activer et pour exiger une élévation de contrôle d’accès utilisateur.
void SetCommonButtonOptions(
int nDisabledButtonMask,
int nElevationButtonMask = 0);
Paramètres
nDisabledButtonMask
[in] Masque pour les boutons courants à désactiver.
nElevationButtonMask
[in] Masque pour les boutons courants qui nécessitent une élévation.
Notes
Vous pouvez définir les boutons courants disponibles pour une instance de la classe CTaskDialog à l’aide du constructeur CTaskDialog ::CTaskDialog et de la méthode CTaskDialog ::SetCommonButtons. CTaskDialog::SetCommonButtonOptions ne prend pas en charge l’ajout de nouveaux boutons courants.
Si vous utilisez cette méthode pour désactiver ou élever un bouton commun qui n’est pas disponible pour cela CTaskDialog, cette méthode lève une exception à l’aide de la macro ENSURE .
Cette méthode active nDisabledButtonMask tous les boutons disponibles, CTaskDialog mais pas dans le fichier nDisabledButtonMask, même s’il a été précédemment désactivé. Cette méthode traite l’élévation de la même manière : elle enregistre les boutons courants comme ne nécessitant pas d’élévation si le bouton commun est disponible, mais n’est pas inclus dans nElevationButtonMask.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title);
// Create a button mask.
int buttons = TDCBF_OK_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON;
buttons |= TDCBF_RETRY_BUTTON | TDCBF_CLOSE_BUTTON;
taskDialog.SetCommonButtons(buttons);
// Disable the close button and make the retry button require
// elevation.
taskDialog.SetCommonButtonOptions(TDCBF_CLOSE_BUTTON,
TDCBF_RETRY_BUTTON);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetCommonButtons
Ajoute des boutons courants au CTaskDialog.
void SetCommonButtons(
int nButtonMask,
int nDisabledButtonMask = 0,
int nElevationButtonMask = 0);
Paramètres
nButtonMask
[in] Masque des boutons à ajouter au CTaskDialog.
nDisabledButtonMask
[in] Masque des boutons à désactiver.
nElevationButtonMask
[in] Masque des boutons qui nécessitent une élévation.
Notes
Vous ne pouvez pas appeler cette méthode après la création de la fenêtre d’affichage de cette instance de la CTaskDialog classe. Si vous le faites, cette méthode lève une exception.
Les boutons indiqués par nButtonMask remplacent tous les boutons courants précédemment ajoutés au CTaskDialogfichier . Seuls les boutons indiqués dans nButtonMask sont disponibles.
Si nDisabledButtonMask ou nElevationButtonMask contiennent un bouton qui n’est pas dans nButtonMask, cette méthode lève une exception à l’aide de la macro ENSURE.
Par défaut, tous les boutons courants sont activés et ne nécessitent pas d’élévation.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title);
// Create a button mask.
int buttons = TDCBF_OK_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON;
buttons |= TDCBF_RETRY_BUTTON | TDCBF_CLOSE_BUTTON;
taskDialog.SetCommonButtons(buttons);
// Disable the close button and make the retry button require
// elevation.
taskDialog.SetCommonButtonOptions(TDCBF_CLOSE_BUTTON,
TDCBF_RETRY_BUTTON);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetContent
Met à jour le contenu du CTaskDialog.
void SetContent(const CString& strContent);
Paramètres
strContent
[in] Chaîne à afficher à l’utilisateur.
Notes
Le contenu de la CTaskDialog classe est le texte affiché à l’utilisateur dans la section principale de la boîte de dialogue.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetDefaultCommandControl
Spécifie le contrôle de bouton de commande par défaut.
void SetDefaultCommandControl(int nCommandControlID);
Paramètres
nCommandControlID
[in] ID du contrôle de bouton de commande pour être la valeur par défaut.
Notes
Le contrôle de bouton de commande par défaut est le contrôle sélectionné lors de la CTaskDialog première affichage de l’utilisateur.
Cette méthode lève une exception si elle ne trouve pas le contrôle de bouton de commande spécifié par nCommandControlID.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::SetDefaultRadioButton
Spécifie la case d’option par défaut.
void SetDefaultRadioButton(int nRadioButtonID);
Paramètres
nRadioButtonID
[in] ID de la case d’option correspondant à la valeur par défaut.
Notes
La case d’option par défaut est le bouton sélectionné lors de la CTaskDialog première affichage de l’utilisateur.
Cette méthode lève une exception si elle ne trouve pas la case d’option spécifiée par nRadioButtonID.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::SetDialogWidth
Ajuste la largeur du CTaskDialog.
void SetDialogWidth(int nWidth = 0);
Paramètres
nWidth
[in] Largeur de la boîte de dialogue, en pixels.
Notes
Le paramètre nWidth doit être supérieur ou égal à 0. Sinon, cette méthode lève une exception.
Si nWidth est défini sur 0, cette méthode définit la boîte de dialogue sur la taille par défaut.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetExpansionArea
Met à jour la zone d’expansion du CTaskDialog.
void SetExpansionArea(
const CString& strExpandedInformation,
const CString& strCollapsedLabel = _T(""),
const CString& strExpandedLabel = _T(""));
Paramètres
strExpandedInformation
[in] Chaîne affichée CTaskDialog dans le corps principal de la boîte de dialogue lorsque l’utilisateur clique sur le bouton d’expansion.
strCollapsedLabel
[in] Chaîne affichée CTaskDialog en regard du bouton d’extension lorsque la zone développée est réduite.
strExpandedLabel
[in] Chaîne affichée CTaskDialog en regard du bouton d’expansion lorsque la zone développée est affichée.
Notes
La zone d’expansion de la CTaskDialog classe vous permet de fournir des informations supplémentaires à l’utilisateur. La zone d’expansion se trouve dans la partie principale du CTaskDialog, située immédiatement sous le titre et la chaîne de contenu.
Lorsque le CTaskDialog premier s’affiche, il n’affiche pas les informations développées et met strCollapsedLabel en regard du bouton d’extension. Lorsque l’utilisateur clique sur le bouton d’expansion, l’affichage CTaskDialog de strExpandedInformation et modifie l’étiquette en strExpandedLabel.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetFooterIcon
Met à jour l’icône de pied de page du CTaskDialog.
void SetFooterIcon(HICON hFooterIcon);
void SetFooterIcon(LPCWSTR lpszFooterIcon);
Paramètres
hFooterIcon
[in] Nouvelle icône pour le CTaskDialog.
lpszFooterIcon
[in] Nouvelle icône pour le CTaskDialog.
Notes
L’icône de pied de page s’affiche en bas de la classe CTaskDialog. Il peut avoir du texte de pied de page associé. Vous pouvez modifier le texte du pied de page avec CTaskDialog ::SetFooterText.
Cette méthode lève une exception avec la macro ENSURE si le CTaskDialog paramètre d’entrée est affiché ou null.
A CTaskDialog ne peut accepter qu’une HICON icône de pied de page ou LPCWSTR un pied de page. Cette option est configurée en définissant l’option TDF_USE_HICON_FOOTER dans le constructeur ou CTaskDialog ::SetOptions. Par défaut, il CTaskDialog est configuré pour être utilisé LPCWSTR comme type d’entrée pour l’icône de pied de page. Cette méthode génère une exception si vous essayez de définir l’icône à l’aide du type inapproprié.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetFooterText
Met à jour le texte sur le pied de page du CTaskDialog.
void SetFooterText(const CString& strFooterText);
Paramètres
strFooterText
[in] Nouveau texte du pied de page.
Notes
L’icône de pied de page apparaît en regard du texte du pied de page en bas du CTaskDialog. Vous pouvez modifier l’icône de pied de page avec CTaskDialog ::SetFooterIcon.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetMainIcon
Met à jour l’icône principale du CTaskDialog.
void SetMainIcon(HICON hMainIcon);
void SetMainIcon(LPCWSTR lpszMainIcon);
Paramètres
hMainIcon
[in] Nouvelle icône.
lpszMainIcon
[in] Nouvelle icône.
Notes
Cette méthode lève une exception avec la macro ENSURE si le CTaskDialog paramètre d’entrée est affiché ou null.
A CTaskDialog ne peut accepter qu’une HICON icône principale ou LPCWSTR une icône principale. Vous pouvez le configurer en définissant l’option TDF_USE_HICON_MAIN dans le constructeur ou dans la méthode CTaskDialog ::SetOptions . Par défaut, il CTaskDialog est configuré pour être utilisé LPCWSTR comme type d’entrée pour l’icône principale. Cette méthode génère une exception si vous essayez de définir l’icône à l’aide du type inapproprié.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetMainInstruction
Met à jour l’instruction principale du CTaskDialog.
void SetMainInstruction(const CString& strInstructions);
Paramètres
strInstructions
[in] Nouvelle instruction principale.
Notes
L’instruction principale de la CTaskDialog classe est le texte affiché à l’utilisateur dans une police en gras volumineux. Elle se trouve dans la boîte de dialogue située sous la barre de titre.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetOptions
Configure les options pour le CTaskDialog.
void SetOptions(int nOptionFlag);
Paramètres
nOptionFlag
[in] Ensemble d’indicateurs à utiliser pour le CTaskDialog.
Notes
Cette méthode efface toutes les options actuelles pour le CTaskDialog. Pour conserver les options actuelles, vous devez d’abord les récupérer avec CTaskDialog ::GetOptions et les combiner avec les options que vous souhaitez définir.
Le tableau suivant répertorie toutes les options valides.
| Nom | Description |
|---|---|
| TDF_ENABLE_HYPERLINKS | Active les liens hypertexte dans le CTaskDialog. |
| TDF_USE_HICON_MAIN | Configure l’option CTaskDialog à utiliser HICON pour l’icône principale. L’alternative consiste à utiliser un LPCWSTR. |
| TDF_USE_HICON_FOOTER | Configure l’option CTaskDialog à utiliser HICON pour l’icône de pied de page. L’alternative consiste à utiliser un LPCWSTR. |
| TDF_ALLOW_DIALOG_CANCELLATION | Permet à l’utilisateur de fermer CTaskDialog le clavier à l’aide du clavier ou en utilisant l’icône dans le coin supérieur droit de la boîte de dialogue, même si le bouton Annuler n’est pas activé. Si cet indicateur n’est pas défini et que le bouton Annuler n’est pas activé, l’utilisateur ne peut pas fermer la boîte de dialogue à l’aide de Alt+F4, de la touche d’échappement ou du bouton fermer de la barre de titre. |
| TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS | Configure l’utilisation CTaskDialog des contrôles de bouton de commande. |
| TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS_NO_ICON | Configure l’utilisation CTaskDialog des contrôles de bouton de commande sans afficher une icône en regard du contrôle. TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS remplace TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS_NO_ICON. |
| TDF_EXPAND_FOOTER_AREA | Indique que la zone d’expansion est actuellement développée. |
| TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT | Détermine si la zone d’expansion est développée par défaut. |
| TDF_VERIFICATION_FLAG_CHECKED | Indique que la case à cocher de vérification est actuellement cochée. |
| TDF_SHOW_PROGRESS_BAR | Configure la CTaskDialog barre de progression pour afficher une barre de progression. |
| TDF_SHOW_MARQUEE_PROGRESS_BAR | Configure la barre de progression pour qu’elle soit une barre de progression de marque. Si vous activez cette option, vous devez définir TDF_SHOW_PROGRESS_BAR pour avoir le comportement attendu. |
| TDF_CALLBACK_TIMER | Indique que l’intervalle de CTaskDialog rappel est défini sur environ 200 millisecondes. |
| TDF_POSITION_RELATIVE_TO_WINDOW | Configure la CTaskDialog valeur à centrer par rapport à la fenêtre parente. Si cet indicateur n’est pas activé, celui-ci CTaskDialog est centré par rapport au moniteur. |
| TDF_RTL_LAYOUT | Configure la CTaskDialog disposition de lecture de droite à gauche. |
| TDF_NO_DEFAULT_RADIO_BUTTON | Indique qu’aucune case d’option n’est sélectionnée lorsque l’affichage CTaskDialog s’affiche. |
| TDF_CAN_BE_MINIMIZED | Permet à l’utilisateur de réduire le CTaskDialog. Pour prendre en charge cette option, elle CTaskDialog ne peut pas être modale. MFC ne prend pas en charge cette option, car MFC ne prend pas en charge un modeless CTaskDialog. |
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarMarquee
Configure une barre de marque pour la CTaskDialog boîte de dialogue et l’ajoute à la boîte de dialogue.
void SetProgressBarMarquee(
BOOL bEnabled = TRUE,
int nMarqueeSpeed = 0);
Paramètres
bEnabled
[in] TRUE pour activer la barre de marque ; FALSE pour désactiver la barre de marque et la supprimer de la barre CTaskDialog.
nMarqueeSpeed
[in] Entier qui indique la vitesse de la barre de marque.
Notes
La barre de marque apparaît sous le texte principal de la CTaskDialog classe.
Utilisez nMarqueeSpeed pour définir la vitesse de la barre de marque ; les valeurs supérieures indiquent une vitesse plus lente. La valeur 0 pour nMarqueeSpeed déplace la barre de marque à la vitesse par défaut pour Windows.
Cette méthode lève une exception avec la macro ENSURE si nMarqueeSpeed est inférieur à 0.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add a marquee progress bar.
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee();
taskDialog.DoModal();
// Remove the marquee bar and replace it with a standard progress bar
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee(0);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarRange(0, 100);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarPosition(75);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarState();
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarPosition
Ajuste la position de la barre de progression.
void SetProgressBarPosition(int nProgressPos);
Paramètres
nProgressPos
[in] Position de la barre de progression.
Notes
Cette méthode lève une exception avec la macro ENSURE si nProgressPos n’est pas dans la plage de barres de progression. Vous pouvez modifier la plage de barres de progression avec CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarRange.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add a marquee progress bar.
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee();
taskDialog.DoModal();
// Remove the marquee bar and replace it with a standard progress bar
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee(0);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarRange(0, 100);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarPosition(75);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarState();
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarRange
Ajuste la plage de la barre de progression.
void SetProgressBarRange(
int nRangeMin,
int nRangeMax);
Paramètres
nRangeMin
[in] Limite inférieure de la barre de progression.
nRangeMax
[in] Limite supérieure de la barre de progression.
Notes
La position de la barre de progression est relative à nRangeMin et nRangeMax. Par exemple, si nRangeMin est 50 et nRangeMax est 100, une position de 75 est à mi-chemin dans la barre de progression. Utilisez CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarPosition pour définir la position de la barre de progression.
Pour afficher la barre de progression, l’option TDF_SHOW_PROGRESS_BAR doit être activée et TDF_SHOW_MARQUEE_PROGRESS_BAR ne doit pas être activée. Cette méthode définit automatiquement TDF_SHOW_PROGRESS_BAR et efface TDF_SHOW_MARQUEE_PROGRESS_BAR. Utilisez CTaskDialog ::SetOptions pour modifier manuellement les options de cette instance de la classe CTaskDialog.
Cette méthode lève une exception avec la macro ENSURE si nRangeMin n’est pas inférieur à nRangeMax. Cette méthode lève également une exception si elle CTaskDialog est déjà affichée et a une barre de progression de marque.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add a marquee progress bar.
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee();
taskDialog.DoModal();
// Remove the marquee bar and replace it with a standard progress bar
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee(0);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarRange(0, 100);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarPosition(75);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarState();
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarState
Définit l’état de la barre de progression et l’affiche sur le CTaskDialog.
void SetProgressBarState(int nState = PBST_NORMAL);
Paramètres
nState
[in] État de la barre de progression. Consultez la section Remarques pour connaître les valeurs possibles.
Notes
Cette méthode lève une exception avec la macro ENSURE si elle CTaskDialog est déjà affichée et a une barre de progression de marque.
Le tableau suivant répertorie les valeurs possibles pour nState. Dans tous ces cas, la barre de progression remplira la couleur normale jusqu’à ce qu’elle atteigne la position d’arrêt désignée. À ce stade, il modifie la couleur en fonction de l’état.
| Nom | Description |
|---|---|
| PBST_NORMAL | Une fois la barre de progression remplie, la CTaskDialog barre de progression ne change pas la couleur de la barre. Par défaut, la couleur normale est verte. |
| PBST_ERROR | Une fois la barre de progression remplie, la CTaskDialog couleur de la barre devient la couleur d’erreur. Par défaut, il s’agit de rouge. |
| PBST_PAUSED | Une fois la barre de progression remplie, la CTaskDialog couleur de la barre devient la couleur suspendue. Par défaut, il s’agit d’un jaune. |
Vous pouvez définir l’emplacement où la barre de progression s’arrête avec CTaskDialog ::SetProgressBarPosition.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add a marquee progress bar.
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee();
taskDialog.DoModal();
// Remove the marquee bar and replace it with a standard progress bar
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee(0);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarRange(0, 100);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarPosition(75);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarState();
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::SetRadioButtonOptions
Active ou désactive une case d’option.
void SetRadioButtonOptions(
int nRadioButtonID,
BOOL bEnabled);
Paramètres
nRadioButtonID
[in] ID du contrôle de case d’option.
bEnabled
[in] TRUE pour activer la case d’option ; FALSE pour désactiver la case d’option.
Notes
Cette méthode lève une exception avec la macro ENSURE si nRadioButtonID n’est pas un ID valide pour une case d’option.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog ::SetVerificationCheckbox
Définit l’état activé de la case à cocher de vérification.
void SetVerificationCheckbox(BOOL bChecked);
Paramètres
bChecked
[in] TRUE pour que la case à cocher de vérification soit cochée lors de l’affichage CTaskDialog ; FALSE pour que la case à cocher de vérification ne soit pas cochée lorsque celle-ci CTaskDialog est affichée.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add the verification checkbox and set the default state.
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckboxText(L"Remember your selection.");
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckbox(false);
taskDialog.DoModal();
if (taskDialog.GetVerificationCheckboxState())
{
// TODO: Write settings of the task dialog to the registry
}
CTaskDialog ::SetVerificationCheckboxText
Définit le texte affiché à droite de la case à cocher de vérification.
void SetVerificationCheckboxText(CString& strVerificationText);
Paramètres
strVerificationText
[in] Texte affiché par cette méthode en regard de la case à cocher de vérification.
Notes
Cette méthode lève une exception avec la macro ENSURE si cette instance de la CTaskDialog classe est déjà affichée.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add the verification checkbox and set the default state.
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckboxText(L"Remember your selection.");
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckbox(false);
taskDialog.DoModal();
if (taskDialog.GetVerificationCheckboxState())
{
// TODO: Write settings of the task dialog to the registry
}
CTaskDialog ::SetWindowTitle
Définit le titre du CTaskDialog.
void SetWindowTitle(CString& strWindowTitle);
Paramètres
strWindowTitle
[in] Nouveau titre pour le CTaskDialog.
Notes
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog ::ShowDialog
Crée et affiche un CTaskDialog.
static INT_PTR ShowDialog(
const CString& strContent,
const CString& strMainInstruction,
const CString& strTitle,
int nIDCommandControlsFirst,
int nIDCommandControlsLast,
int nCommonButtons = TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON,
int nTaskDialogOptions = TDF_ENABLE_HYPERLINKS | TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS,
const CString& strFooter = _T(""));
Paramètres
strContent
[in] Chaîne à utiliser pour le contenu du CTaskDialog.
strMainInstruction
[in] L’instruction principale du CTaskDialog.
strTitle
[in] Le titre du CTaskDialog.
nIDCommandControlsFirst
[in] ID de chaîne de la première commande.
nIDCommandControlsLast
[in] ID de chaîne de la dernière commande.
nCommonButtons
[in] Masque des boutons à ajouter au CTaskDialog.
nTaskDialogOptions
[in] Ensemble d’options à utiliser pour le CTaskDialog.
strFooter
[in] Chaîne à utiliser comme pied de page.
Valeur de retour
Entier qui correspond à la sélection effectuée par l’utilisateur.
Notes
Cette méthode statique vous permet de créer une instance de la CTaskDialog classe sans créer explicitement d’objet CTaskDialog dans votre code. Étant donné qu’il n’existe aucun CTaskDialog objet, vous ne pouvez pas appeler d’autres méthodes de la CTaskDialog méthode si vous utilisez cette méthode pour afficher un CTaskDialog objet à l’utilisateur.
Cette méthode crée des contrôles de bouton de commande à l’aide de données à partir du fichier de ressources de votre application. La table de chaînes du fichier de ressources comporte plusieurs chaînes avec des ID de chaîne associés. Cette méthode ajoute un contrôle de bouton de commande pour chaque entrée valide dans la table de chaînes entre nIDCommandControlsFirst et nCommandControlsLast, inclus. Pour ces contrôles de bouton de commande, la chaîne de la table de chaînes est la légende du contrôle et l’ID de chaîne est l’ID du contrôle.
Consultez CTaskDialog ::SetOptions pour obtenir la liste des options valides .
La CTaskDialog fermeture se ferme lorsque l’utilisateur sélectionne un bouton commun, un contrôle de lien de commande ou ferme le CTaskDialog. La valeur de retour est l’identificateur qui indique comment l’utilisateur a fermé la boîte de dialogue.
Exemple
// TODO: Replace the string below with the actual message to the user
CString message("Important information to the user");
// TODO: Replace the string below with the title of this project
CString title("Project Title");
CString emptyString;
if (CTaskDialog::IsSupported())
{
CTaskDialog::ShowDialog(message, emptyString, title, 0, 0,
TDCBF_OK_BUTTON);
}
else
{
AfxMessageBox(message);
}
CTaskDialog ::TaskDialogCallback
L’infrastructure appelle cette méthode en réponse à différents messages Windows.
friend:
HRESULT TaskDialogCallback(
HWND hWnd,
UINT uNotification,
WPARAM wParam,
LPARAM lParam,
LONG_PTR dwRefData);
Paramètres
hwnd
[in] Handle de la m_hWnd structure pour le CTaskDialog.
uNotification
[in] Code de notification qui spécifie le message généré.
wParam
[in] Plus d’informations sur le message.
lParam
[in] Plus d’informations sur le message.
dwRefData
[in] Pointeur vers l’objet CTaskDialog auquel le message de rappel s’applique.
Valeur de retour
Dépend du code de notification spécifique. Pour plus d'informations, consultez la section Notes.
Notes
L’implémentation par défaut de TaskDialogCallback handles le message spécifique, puis appelle la méthode On appropriée de la classe CTaskDialog. Par exemple, en réponse au message TDN_BUTTON_CLICKED, TaskDialogCallback appelle CTaskDialog ::OnCommandControlClick.
Les valeurs de wParam et lParam dépendent du message généré spécifique. Il est possible que ces deux valeurs soient vides ou vides. Le tableau suivant répertorie les notifications par défaut prises en charge et les valeurs de wParam et lParam représentées. Si vous remplacez cette méthode dans une classe dérivée, vous devez implémenter le code de rappel pour chaque message du tableau suivant.
| Notification Message | valeur wParam | lParam , valeur |
|---|---|---|
| TDN_CREATED | Non utilisé. | Non utilisé. |
| TDN_NAVIGATED | Non utilisé. | Non utilisé. |
| TDN_BUTTON_CLICKED | ID de contrôle du bouton de commande. | Aucun affichage. |
| TDN_HYPERLINK_CLICKED | Aucun affichage. | Structure LPCWSTR qui contient le lien. |
| TDN_TIMER | Durée en millisecondes depuis la CTaskDialog création ou la réinitialisation du minuteur. |
Aucun affichage. |
| TDN_DESTROYED | Non utilisé. | Non utilisé. |
| TDN_RADIO_BUTTON_CLICKED | ID de case d’option. | Aucun affichage. |
| TDN_DIALOG_CONSTRUCTED | Non utilisé. | Non utilisé. |
| TDN_VERIFICATION_CLICKED | 1 si la case à cocher est cochée, 0 si ce n’est pas le cas. | Aucun affichage. |
| TDN_HELP | Non utilisé. | Non utilisé. |
| TDN_EXPANDO_BUTTON_CLICKED | 0 si la zone d’expansion est réduite ; différent de zéro si le texte d’extension est affiché. | Aucun affichage. |
Voir aussi
Classes
CObject, classe
Graphique hiérarchique
Procédure pas à pas : ajout d’une classe CTaskDialog à une application