Configure Outlook clients
When Outlook users connect to Microsoft 365, they must provide their Microsoft 365 email address and password when they start Outlook for the first time. The Autodiscover functionality in Microsoft 365 automatically configures Outlook for use with Microsoft 365. For Autodiscover to work properly, you must configure the appropriate DNS records during the Microsoft 365 tenant setup.
Connectivity protocols
The connectivity protocols that Outlook uses to communicate with Exchange changed over the past several years. The following graphic shows the progression from old to new protocols - from RPC/TCP to RPC/HTTP to MAPI/HTTP.
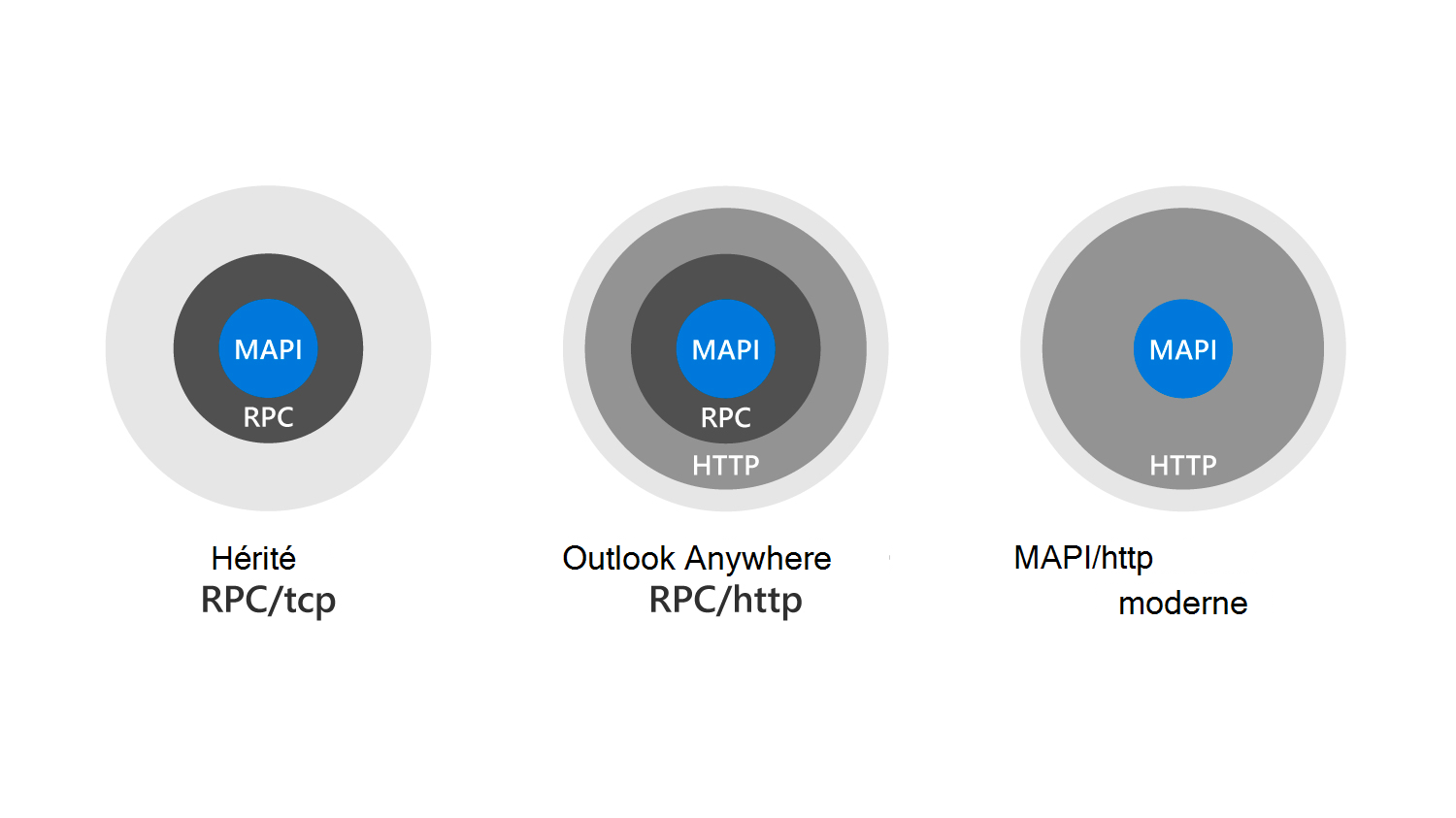
Messaging Application Programming Interface (MAPI) over HTTP is the latest transport protocol that provides connectivity to Outlook. It's also the only protocol that supports Outlook connectivity to Exchange Online in Microsoft 365 and to Exchange Server 2019. In addition, MAPI/HTTP is the only protocol supported by Hybrid modern authentication.
By placing MAPI commands directly in HTTPS packets, MAPI/HTTP provides greater efficiency than its predecessors for several reasons:
- Reduced latency. MAPI/HTTP reduces latency by using HTTP as the transport protocol. HTTP is a more lightweight protocol compared to the Remote Procedure Call (RPC) used in the previous versions. This design results in quicker communication between the email client and the server.
- Improved connection handling. MAPI/HTTP handles unreliable or intermittent network connections more effectively. It provides better support for scenarios where the connection between the client and the server might be less stable or prone to interruptions.
- Enhanced security. MAPI/HTTP supports modern authentication protocols, such as OAuth, providing improved security compared to its predecessors. OAuth helps in secure authentication without exposing user credentials, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Better scalability. MAPI/HTTP is more scalable, particularly in environments with a large number of concurrent users. The protocol demonstrates superior capability in managing a high volume of connections and requests.
- Adaptability to modern network architectures. MAPI/HTTP provides superior design for modern network architectures, including networks with firewalls and proxies. Its use of HTTP makes it more firewall-friendly, allowing organizations to deploy it in diverse networking environments.
- Improved troubleshooting and diagnostics. The use of HTTP facilitates easier troubleshooting and diagnostics compared to the complex RPC traffic. Network administrators can more readily analyze HTTP traffic, leading to quicker identification and resolution of issues.
MAPI/HTTP also improves the reliability and stability of the Outlook and Exchange connections. It does so by moving the transport layer to the industry-standard HTTP model. This design allows a higher level of visibility of transport errors and enhanced recoverability. MAPI/HTTP also supports an explicit pause-and-resume function. This feature enables supported clients to change networks or resume from hibernation while maintaining the same server context.
MAPI over HTTP offers the following benefits:
- Enables future innovation in authentication by using an HTTP based protocol.
- Provides faster reconnection times after a communications break because only TCP connections (not RPC connections) must be rebuilt. Examples of a communication break include:
- Device hibernation
- Changing from a wired network to a wireless or cellular network
- Device hibernation
- Offers a session context that isn't dependent on the connection. The server maintains the session context for a configurable period of time, even if the user changes networks.
Given the benefits of MAPI/HTTP and the fact that it's the only protocol that support Exchange Online, Microsoft enabled it by default in Microsoft 365.
Additional reading. For more information, see MAPI over HTTP in Exchange Server.
Outlook connectivity for cloud-only and hybrid deployments
Outlook clients connect in different ways, depending on whether an organization has a cloud-only or hybrid Microsoft 365 deployment. In a cloud-only deployment, Outlook clients on an internal network connect to Microsoft 365 services by using Autodiscover DNS records on internal or Internet DNS servers. Internet-based Outlook clients connect to Microsoft 365 services by using Autodiscover DNS records on the Internet DNS servers.
However, in a hybrid deployment of Microsoft 365, Outlook clients must always connect to the Autodiscover service that's running on the organization’s Exchange server. When a client is on an internal network, Outlook locates the Exchange server by searching for the Autodiscover Service Connection Point located in Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS). After Outlook connects to the Exchange server, the Exchange server determines whether the user’s mailbox is in an on-premises environment or in Microsoft 365.
- If the user’s mailbox is in Microsoft 365, the Exchange server provides alternate SMTP domain information to Outlook. Outlook uses that alternate SMTP domain to search for the Microsoft 365 Autodiscover service’s record on the Internet. It then connects to Exchange Online in Microsoft 365.
- When a client is on the Internet, Outlook locates the Exchange server by searching for the Autodiscover record that points to the Exchange client access services on the internal network. After Outlook connects to the Exchange server, the Exchange server determines if the user’s mailbox is in an on-premises environment or in Microsoft 365.
Network configuration
Microsoft 365 services contain multiple endpoints. Clients use these endpoints to connect to services, such as Exchange Online, Skype for Business Online, and SharePoint Online. Microsoft 365 endpoints include fully qualified domain names (FQDNs), ports, uniform resource locators (URLs), and IPv4 and IPv6 address ranges. Some organizations restrict computers on their networks from accessing certain Internet resources. For this reason, it's important for an organization to know all of its endpoints that Microsoft 365 uses. This information enables organizations to properly configure their network devices, such as routers and firewalls. After an organization configures its network devices, its clients can connect successfully to Microsoft 365 services.
Knowledge check
Choose the best response for the following question. Then select “Check your answers.”