Install Event Grid extension on Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster
This article guides you through the steps to install Event Grid on an Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster.
For brevity, this article refers to "Event Grid on Kubernetes extension" as "Event Grid on Kubernetes" or just "Event Grid".
Important
Event Grid on Kubernetes with Azure Arc is currently in public preview. This preview version is provided without a service level agreement, and it's not recommended for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or might have constrained capabilities. For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
Supported Kubernetes distributions
Following are the supported Kubernetes distributions to which Event Grid can be deployed and run.
- Azure AKS supported Kubernetes distributions.
- RedHat OpenShift Container Platform.
Event Grid Extension
The operation that installs an Event Grid service instance on a Kubernetes cluster is the creation of an Azure Arc cluster extension, which deploys both an Event Grid broker and an Event Grid operator. For more information on the function of the broker and operator, see Event Grid on Kubernetes components. Azure Arc cluster extension feature provides lifecycle management using Azure Resource Manager (ARM) control plane operations to Event Grid deployed to Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters.
Note
The preview version of the service only supports a single instance of the Event Grid extension on a Kubernetes cluster as the Event Grid extension is currently defined as a cluster-scoped extension. There is no support for namespace-scoped deployments for Event Grid yet that would allow for multiple instances to be deployed to a cluster. For more information, see Extension scope.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the installation of Event Grid, make sure the following prerequisites are met.
- A cluster running on one of the supported Kubernetes distributions.
- An Azure subscription.
- PKI Certificates to be used for establishing an HTTPS connection with the Event Grid broker.
- Connect your cluster to Azure Arc.
Getting support
If you run into an issue, see the Troubleshooting section for help with common conditions. If you still have problems, create an Azure support request.
PKI Certificate requirements
The Event Grid broker (server) serves two kinds of clients. Server authentication is done using Certificates. Client authentication is done using either certificates or SAS keys based on the client type.
- Event Grid operators that make control-plane requests to the Event Grid broker are authenticated using certificates.
- Event Grid publishers that publisher events to an Event Grid topic are authenticated with the topic's SAS keys.
To establish a secure HTTPS communication with the Event Grid broker and Event Grid operator, we use PKI Certificates during the installation of Event Grid extension. Here are the general requirements for these PKI certificates:
The certificates and keys must be X.509 certificates and Privacy-Enhanced Mail PEM encoded.
To configure the Event Grid broker (server) certificate during installation, you'll need to provide:
- A CA certificate
- A public certificate
- A private key
To configure the Event Grid operator (client) certificate, you'll need to provide:
- A CA certificate
- A public certificate
- A private key
Publishing clients can use the Event Grid broker CA certificate to validate the server when publishing events to a topic.
Important
While a domain associated to client might have more than one public certificate issued by different certificate authorities, Event Grid on Kubernetes only allows uploading a single CA certificate for clients when installing Event Grid. As a consequence, the certificates for the Event Grid operator should be issued (signed) by the same CA in order for the certificate chain validation to succeed and a TLS session to be successfully established.
When configuring the Common Name (CN) for server and client certificates, make sure they're different to the CN provided for the Certificate Authority certificate.
Important
For early proof-of-concept stages, self-signed certificates might be an option but in general, proper PKI certificates signed by a Certificate Authority (CA) should be procured and used.
Install using Azure portal
On the Azure portal, search (field on top) for Azure Arc
Select Kubernetes cluster on the left-hand-side menu in the Infrastructure section
Under the list of clusters, locate the one to which you want to install Event Grid, and select it. The Overview page for the cluster is displayed.

Select Extensions in the Settings group on the left menu.
Select + Add. A page showing the available Azure Arc Kubernetes extensions is displayed.

On the New resource page, select Event Grid on Kubernetes Extension.

On the Event Grid on Kubernetes Extension page, select Create.

The Basics tab of the Install Event Grid page, follow these steps.
The Project Details section shows read-only subscription and resource group values because Azure Arc extensions are deployed under the same Azure subscription and resource group of the connected cluster on which they're installed.
Provide a name in the Event Grid extension name field. This name should be unique among other Azure Arc extensions deployed to the same Azure Arc connected cluster.
For Release namespace, you may want to provide the name of a Kubernetes namespace where Event Grid components will be deployed into. For example, you might want to have a single namespace for all Azure Arc-enabled services deployed to your cluster. The default is eventgrid-system. If the namespace provided doesn't exist, it's created for you.
On the Event Grid broker details section, the service type is shown. The Event Grid broker, which is the component that exposes the topic endpoints to which events are sent, is exposed as a Kubernetes service type ClusterIP. Hence, the IPs assigned to all topics use the private IP space configured for the cluster.
Provide the storage class name that you want to use for the broker and that's supported by your Kubernetes distribution. For example, if you're using AKS, you could use
azurefile, which uses Azure Standard storage. For more information on predefined storage classes supported by AKS, see Storage Classes in AKS. If you're using other Kubernetes distributions, see your Kubernetes distribution documentation for predefined storage classes supported or the way you can provide your own.Storage size. Default is 1 GiB. Consider the ingestion rate when determining the size of your storage. Ingestion rate in MiB/second measured as the size of your events times the publishing rate (events per second) across all topics on the Event Grid broker is a key factor when allocating storage. Events are transient in nature and once they're delivered, there's no storage consumption for those events. While ingestion rate is a main driver for storage use, it isn't the only one. Metadata holding topic and event subscription configuration also consumes storage space, but that normally requires a lower amount of storage space than the events ingested and being delivered by Event Grid.
Memory limit. Default is 1 GiB.
Memory request. Default is 200 MiB. This field isn't editable.

Select Next: Configuration at the bottom of the page.
In the Configuration tab of the Install Event Grid page, do the following steps:
Enable HTTP (not secure) communication. Check this box if you want to use a non-secured channel when clients communicate with the Event Grid broker.
Important
Enabling this option makes the communication with the Event Grid broker to use HTTP as transport. Hence, any publishing client and the Event Grid operator won't communicate with the Event Grid broker securely. You should use this option only during early stages of development.
If you didn't enable HTTP communication, select each of the PKI certificate files that you procured and meet the PKI certificate requirements.

Select the Next: Monitoring at the bottom of the page.
In the Monitoring tab of the Install Event Grid page, do the following steps:
Select Enable metrics (optional). If you select this option, Event Grid on Kubernetes exposes metrics for topics and event subscriptions using the Prometheus exposition format.

Select Next: Tags to navigate to the Tags page.
On the Tags page, do the following steps:
Define tags, if necessary.

Select Review + create at the bottom of the page.
On the Review + create tab, select Create.
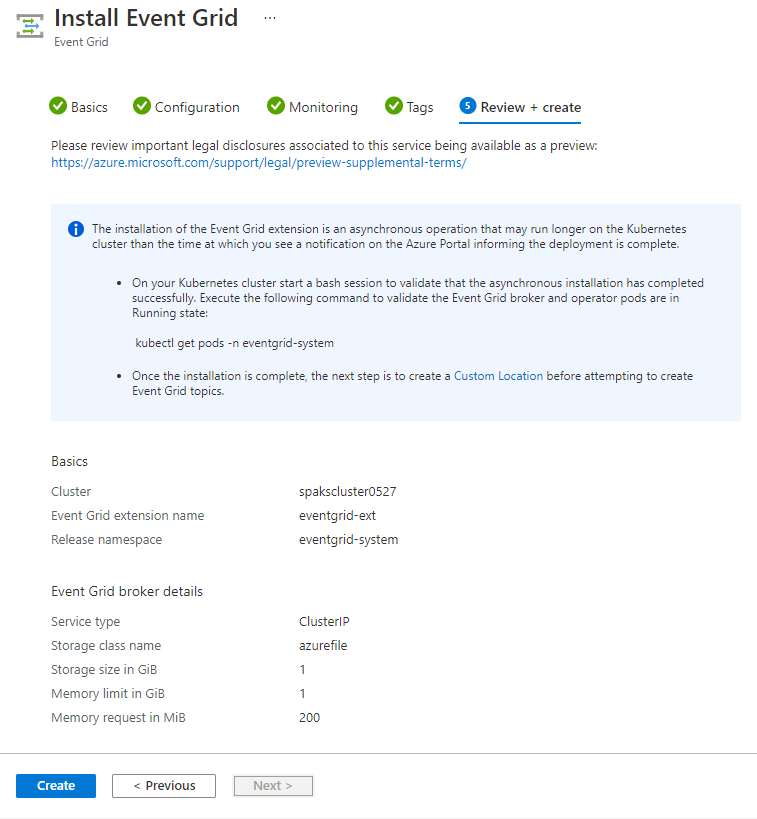
Important
The installation of Event Grid is an asynchronous operation that may run longer on the Kubernetes cluster than the time you see a notification on the Azure Portal informing the deployment is complete. Wait at least 5 minutes after you see a notification that "Your deployment is complete" before attempting to create a custom location (next step). If you have access to the Kubernetes cluster, on a bash session you can execute the following command to validate if the Event Grid broker and Event Grid operator pods are in Running state, which would indicate the installation has completed:
kubectl get pods -n \<release-namespace-name\>Here's the sample output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE eventgrid-broker-568f75976-wxkd2 1/1 Running 0 2m28s eventgrid-operator-6c4c6c675d-ttjv5 1/1 Running 0 2m28sImportant
A Custom Location needs to be created before attempting to deploy Event Grid topics. To create a custom location, you can select the Context page at the bottom 5 minutes after the "Your deployment is complete" notification is shown. Alternatively, you can create a custom location using the Azure portal. For more information, see the Custom Location documentation.
After the deployment succeeds, you'll be able to see an entry on the Extensions page with the name you provided to your Event Grid extension. If you see Pending for the Install status, wait for a few minutes, and then select Refresh on the toolbar.

Install using Azure CLI
Start a shell session. You can start a session on your computer or you can open a browser to https://shell.azure.com.
Create configuration file
protected-settings-extension.json. This file is passed as a parameter when creating the Event Grid extension.In the following command and in each of the configuration lines, replace
filenameby the name that contains the public certificate, CA certificate, or key for the operator (client) or broker (server), accordingly. All certificates provided should be base64 encoded with no line wrap. Hence, the use of thebase64 --wrap=0command.echo "{ \"eventgridoperator.identityCert.base64EncodedIdentityCert\":\"$(base64 <filename> --wrap=0)\", \"eventgridoperator.identityCert.base64EncodedIdentityKey\":\"$(base64 <filename> --wrap=0)\", \"eventgridoperator.identityCert.base64EncodedIdentityCaCert\":\"$(base64 <filename> --wrap=0)\", \"eventgridbroker.service.tls.base64EncodedServerCert\": \"$(base64 <filename> --wrap=0)\" , \"eventgridbroker.service.tls.base64EncodedServerKey\": \"$(base64 <filename> --wrap=0)\" , \"eventgridbroker.service.tls.base64EncodedServerCaCert\": \"$(base64 <filename> --wrap=0)\" }" > protected-settings-extension.jsonFor example, if the public certificate for the broker (first configuration item above) is called
client.cer, then the first configuration line should look like the following one:\"eventgridoperator.identityCert.base64EncodedIdentityCert\":\"$(base64 client.cer --wrap=0)\",Create configuration file
settings-extension.json. This file is passed as a parameter when creating the Event Grid extension.Important
You may not change the values for
ServiceAccountandserviceType. During the preview version, the only Kubernetes service type supported isClusterIP.For
storageClassNameprovide the storage class that you want to use for the broker and that is supported by your Kubernetes distribution. For example, if you're using AKS, you could useazurefile, which uses Azure Standard storage. For more information on predefined storage classes supported by AKS, see Storage Classes in AKS. If you're using other Kubernetes distributions, see your Kubernetes distribution documentation for predefined storage classes supported or the way you can provide your own.Set
reporterTypetoprometheusto enable metrics for topics and event subscriptions using the Prometheus exposition format.Important
During the preview version, using a Prometheus client is the only supported mechanism to get metrics.
echo "{ \"Microsoft.CustomLocation.ServiceAccount\":\"eventgrid-operator\", \"eventgridbroker.service.serviceType\": \"ClusterIP\", \"eventgridbroker.dataStorage.storageClassName\": \"<storage_class_name>\", \"eventgridbroker.diagnostics.metrics.reporterType\":\"prometheus\" }" > settings-extension.jsonCreate a Kubernetes extension that installs Event Grid components on your cluster.
For parameters
cluster-nameandresource-group, you must use the same names provided when you connected your cluster to Azure Arc.release-namespaceis the namespace where Event Grid components will be deployed into. The default is eventgrid-system. You might want to provide a value to override the default. For example, you might want to have a single namespace for all Azure Arc-enabled services deployed to your cluster. If the namespace provided doesn't exist, it's created for you.Important
During the preview version,
clusteris the only scope supported when creating or updating an Event Grid extension. That means the service only supports a single instance of the Event Grid extension on a Kubernetes cluster.There is no support for namespace-scoped deployments yet. For more information, see Extension scope.az k8s-extension create \ --cluster-type connectedClusters \ --cluster-name <connected_cluster_name> \ --resource-group <resource_group_of_connected_cluster> \ --name <event_grid_extension_name> \ --extension-type Microsoft.EventGrid \ --scope cluster \ --auto-upgrade-minor-version true \ --release-train Stable \ --release-namespace <namespace_name> \ --configuration-protected-settings-file protected-settings-extension.json \ --configuration-settings-file settings-extension.jsonFor more information on the CLI command, see az k8s-extension create. Notice that you can use the
--config-fileparameter to pass the name of a json file that contains configuration information related to Event Grid. In order to support HTTP, include the following setting."eventgridbroker.service.supportedProtocols[0]": "http"Here's a sample settings-extension.json with the above setting.
{ "Microsoft.CustomLocation.ServiceAccount": "eventgrid-operator", "eventgridbroker.service.serviceType": "ClusterIP", "eventgridbroker.service.supportedProtocols[0]": "http", "eventgridbroker.dataStorage.storageClassName": "default", "eventgridbroker.diagnostics.metrics.reporterType": "prometheus" }Validate that the Event Grid extension has successfully installed.
az k8s-extension show --cluster-type connectedClusters --cluster-name <connected_cluster_name> --resource-group <resource_group_of_connected_cluster> --name <event_grid_extension_name>The
installedStateproperty should beInstalledif the Event Grid extension components deployed successfully.
Custom location
Important
A Custom Location needs to be created before attempting to deploy Event Grid topics. You can create a custom location using the Azure portal.
Troubleshooting
Azure Arc connect cluster issues
Problem: When you navigate to Azure Arc and select Kubernetes cluster on the left-hand side menu, the page displayed doesn't show the Kubernetes cluster where I intent to install Event Grid.
Resolution: Your Kubernetes cluster isn't registered with Azure. Follow the steps in article Connect an existing Kubernetes cluster to Azure Arc. If you have a problem during this step, file a support request with the Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes team.
Event Grid extension issues
Problem: When trying to install an "Event Grid extension", you get the following message: "Invalid operation - An instance of Event Grid has already been installed on this connected Kubernetes cluster. The Event Grid extension is scoped at the cluster level, which means that only one instance can be installed on a cluster."
Explanation: You already have Event Grid installed. The preview version of Event Grid only supports one Event Grid extension instance deployed to a cluster.
Next steps
Create a custom location and then follow instructions in the quick start Route cloud events to Webhooks with Azure Event Grid on Kubernetes.