Enable Stretch Database for a database
Applies to:
SQL Server 2016 (13.x) and later - Windows only
Important
Stretch Database is deprecated in SQL Server 2022 (16.x) and Azure SQL Database. This feature will be removed in a future version of the Database Engine. Avoid using this feature in new development work, and plan to modify applications that currently use this feature.
To configure an existing database for Stretch Database, select Tasks > Stretch > Enable for a database in SQL Server Management Studio to open the Enable Database for Stretch wizard. You can also use Transact-SQL to enable Stretch Database for a database.
If you select Tasks > Stretch > Enable for an individual table, and you haven't yet enabled the database for Stretch Database, the wizard configures the database for Stretch Database and lets you select tables as part of the process. Follow the steps in this article instead of the steps in Enable Stretch Database for a table.
Enabling Stretch Database on a database or a table requires db_owner permissions. Enabling Stretch Database on a database also requires CONTROL DATABASE permissions.
Note
Later, if you disable Stretch Database, remember that disabling Stretch Database for a table or for a database does not delete the remote object. If you want to delete the remote table or the remote database, you have to drop it by using the Azure management portal. The remote objects continue to incur Azure costs until you delete them manually.
Before you get started
Review Limitations for Stretch Database.
Stretch Database migrates data to Azure, so you need an Azure account and a subscription for billing. Sign up for an Azure account.
Have the connection and login info you need to create a new Azure server or to select an existing Azure server.
Prerequisite: Enable Stretch Database on the server
Before you can enable Stretch Database on a database or a table, you have to enable it on the local server. This operation requires sysadmin or serveradmin permissions.
If you have the required administrative permissions, the Enable Database for Stretch wizard configures the server for Stretch Database.
If you don't have the required permissions, an administrator has to enable the option manually by running
sp_configurebefore you run the wizard, or an administrator has to run the wizard.
To enable Stretch Database on the server manually, run sp_configure and turn on the remote data archive option. The following example enables the remote data archive option by setting its value to 1.
EXEC sp_configure 'remote data archive' , '1';
GO
RECONFIGURE;
GO
For more info, see Configure the remote data archive Server Configuration Option and sp_configure (Transact-SQL).
Use the wizard
For info about the Enable Database for Stretch Wizard, including the info that you have to enter and the choices that you have to make, see Get started by running the Enable Database for Stretch Wizard.
Use Transact-SQL
Before you can enable Stretch Database on individual tables, you have to enable it on the database.
Enabling Stretch Database on a database or a table requires db_owner permissions. Enabling Stretch Database on a database also requires CONTROL DATABASE permissions.
Before you begin, choose an existing Azure server for the data that Stretch Database migrates, or create a new Azure server.
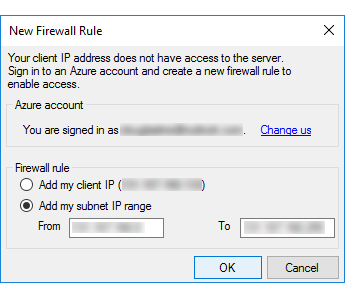
On the Azure server, create a firewall rule with the IP address range of the SQL Server that lets SQL Server communicate with the remote server.
You can easily find the values you need and create the firewall rule by attempting to connect to the Azure server from Object Explorer in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). SSMS helps you to create the rule by opening the following dialog box, which already includes the required IP address values.
Important
Stretch Database support is removed in SQL Server Management Studio v19. To manage Stretch Database, you can use SQL Server Management Studio v18.9.1 or lower.
To configure a SQL Server database for Stretch Database, the database has to have a database master key. The database master key secures the credentials that Stretch Database uses to connect to the remote database. The following example creates a new database master key.
USE <database>; GO CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD='<password>'; GOFor more info about the database master key, see CREATE MASTER KEY (Transact-SQL) and Create a Database Master Key.
When you configure a database for Stretch Database, you have to provide a credential for Stretch Database to use for communication between the on-premises SQL Server and the remote Azure server. You have two options.
You can provide an administrator credential.
If you enable Stretch Database by running the wizard, you can create the credential at that time.
If you plan to enable Stretch Database by running ALTER DATABASE, you have to create the credential manually before you run ALTER DATABASE to enable Stretch Database.
The following example creates a new credential.
CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL [<db_scoped_credential_name>] WITH IDENTITY = '<identity>' , SECRET = '<secret>'; GOFor more information about the credential, see CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL (Transact-SQL). Creating the credential requires ALTER ANY CREDENTIAL permissions.
You can use a federated service account for the SQL Server to communicate with the remote Azure server when the following conditions are all true.
The service account under which the instance of SQL Server is running is a domain account.
The domain account belongs to a domain whose Active Directory is federated with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory).
The remote Azure server is configured to support Microsoft Entra authentication.
The service account under which the instance of SQL Server is running must be configured as a
dbmanagerorsysadminaccount on the remote Azure server.
To configure a database for Stretch Database, run the ALTER DATABASE command.
For the SERVER argument, provide the name of an existing Azure server, including the
.database.windows.netportion of the name - for example,MyStretchDatabaseServer.database.windows.net.Provide an existing administrator credential with the CREDENTIAL argument, or specify FEDERATED_SERVICE_ACCOUNT = ON. The following example provides an existing credential.
ALTER DATABASE [<database name>] SET REMOTE_DATA_ARCHIVE = ON ( SERVER = '<server_name>' , CREDENTIAL = [<db_scoped_credential_name>] ); GO
Next steps
- Enable Stretch Database for a table
- Monitor and troubleshoot data migration (Stretch Database)
- Pause and resume data migration (Stretch Database)
- Manage and troubleshoot Stretch Database
- Back up Stretch-enabled databases
- Restore Stretch-enabled databases