Plan the build, test, and quality control processes
This unit reviews development processes that you can use to manage the build, test, and quality control processes. It also provides information about how to plan for managing these processes.
Create a project plan for builds
Depending on the methodology that you choose, you need to select times and locations for builds. You also need to decide in what order your builds occur. For example, you wouldn't want to build your code from the Development environment to the Production environment without going through the Testing environment first.
You also need to consider how to handle development that doesn't pass testing because you need to roll back that development. This approach prevents you from promoting errors. You can use Microsoft Dynamics 365 Lifecycle Services to help manage your build from environment to environment.
For example, a build might roll back any code with errors from your Testing environment to your Development environment, promote the successful code from Testing to Production, and then finally promote your finished code from the Development environment to Testing.
Decide what environments are needed
You should plan the selection of your environments at the beginning of the implementation. When planning your environments, you should:
- Decide the environment's purpose. Consider whether you plan to use the environments for development, system testing, user acceptance testing (UAT), or operations.
- Consider the environment topology, such as Develop or Build and Test.
- Consider the environment tier (Tier-1 or Tier-2).
A Tier-1 environment is a single-box environment with all the components installed on the same server. A Tier-1 environment uses Microsoft SQL Server and is structured to maximize development efficiency. This tier isn't a good option for UAT or performance testing.
A Tier-2 or higher environment is a multiple-box environment with components that are installed on multiple servers. Instead of Microsoft SQL Server, Tier-2 environments use Microsoft Azure SQL Database. The architecture in this environment is the same as the Production environment, but it doesn't use disaster recovery. You should use this environment for UAT and performance testing.
The standard cloud offer for environments includes a Tier-1 environment for development and testing, a Tier-2 environment for UAT, and a production environment. The system provides these environments at different times:
- Tier-2 environment - During the installation process.
- Tier-1 Develop and Test environment - When the Design phase starts and after you configure Microsoft Azure DevOps.
- Production environment - During production system readiness with Microsoft. You must request this environment through Lifecycle Services.
You can also add another add-on environment for Tier-1 and Tier-2 environments if needed. Additionally, you can deploy Tier-1 environments as a cloud-hosted environment or an environment image. Customers or partners manage the cloud-hosted environments. The environment image is an on-premises environment that uses a virtual hard disk.
You can select which environments you need and when you need them. You must summarize your required environment lists in a matrix for Microsoft.
You can use the environment plan to help choose the flow for building code in all your environments and to structure your ALM.
Plan for how much testing is required
While implementing finance and operations apps, you need to decide how to test your development for approval, who is testing, what criteria you use for approval, and how to track testing. You can use unit tests, regression tests, and performance testing to test the system.
Unit testing is useful for testing whether a specific piece of functionality is working. Unit testing doesn't check if the new code affects existing features in the system.
Regression testing runs a test against an entire process to make sure that existing features still function with the new development. For instance, if you make a modification to add functionality that's related to customers, you might want to perform regression tests to make sure that the new functionality doesn't interfere with existing functionality, such as sales orders.
You might also consider performance testing the system to make sure that the system is stable. To do so, have multiple users enter the system and perform high-volume taxing processes. This approach can help you find opportunities for increasing performance.
Finance and operations apps includes the Task recorder tool to help you document the steps of a process that a user takes. With Microsoft Azure DevOps, you can link tasks to a development project solution. Then, you can use the task to track updates, testing documents, and other notes.
Source control and quality control for developers
Occasionally, several developers might be working in finance and operations apps simultaneously. To prevent developers from interfering with each other's work, you can set up source control with an Azure DevOps project.
The Azure DevOps project hosts the source code of your model, which allows users to check objects in and out. When checking out an object, you're telling the system that you're making changes. When you check in the object, the system creates a new version of that object.
Version control allows you to view previous changes that someone made. You can undo pending changes to the most recent checked-in changes. Additionally, you can select Get latest on objects, which pulls in the most recent checked-in version of the object. Developers should use this feature regularly to make sure that they're using the most up-to-date code.
To ensure quality among development, follow the Microsoft Dynamics 365 X++ best practices. Also, you might want to develop your own best practice, such as naming conventions, to keep all development standardized throughout the organization.
Select a version control system
In finance and operations apps, a version control system is mandatory. Azure DevOps supports Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) and Git.
Azure DevOps Team Foundation Version Control
The Azure DevOps Team Foundation Version Control system is a one-version control system for finance and operations apps. It’s a centralized version control system, which means that developers work in one branch and have one version of each file on their development machines. Each branch belongs to a server workspace, and each developer works in a local workspace. When a developer checks in source code, they must ensure that they check in the latest version and resolve existing conflicts.
By default, TFVC repositories are deactivated in the Organization settings area of Azure DevOps. You need to activate the repositories before you can create a new Azure DevOps project with TFVC as the version control system.
To activate Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) in your organization, follow these steps:
- Open Azure DevOps by going to dev.azure.com/<your organization>.
- Select Organization settings in the lower-left corner of the dashboard.
- Open Repos > Repositories.
- Turn off the Disable creation of TFVC repositories toggle in the All Repository Settings section.
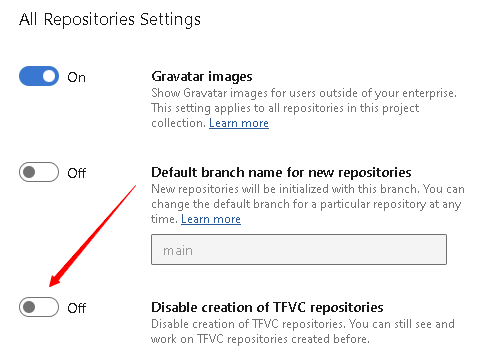
You can create new Azure DevOps projects with TFVC as the version control system.
Git
Git is the recommended Microsoft default version control system for development.
While TFVC is a centralized version control system, Git is a distributed system. Each developer has their own copy of a source repository (or lightweight branch) and can commit changes into it. Developers can create new private branches and switch from one branch to another. In TFVC, it's more difficult to switch from one branch to another, and it often requires multiple development environments.
It’s important to note that you can migrate from TFVC to Git, and vice versa.